| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2039134 | 1073029 | 2016 | 10 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
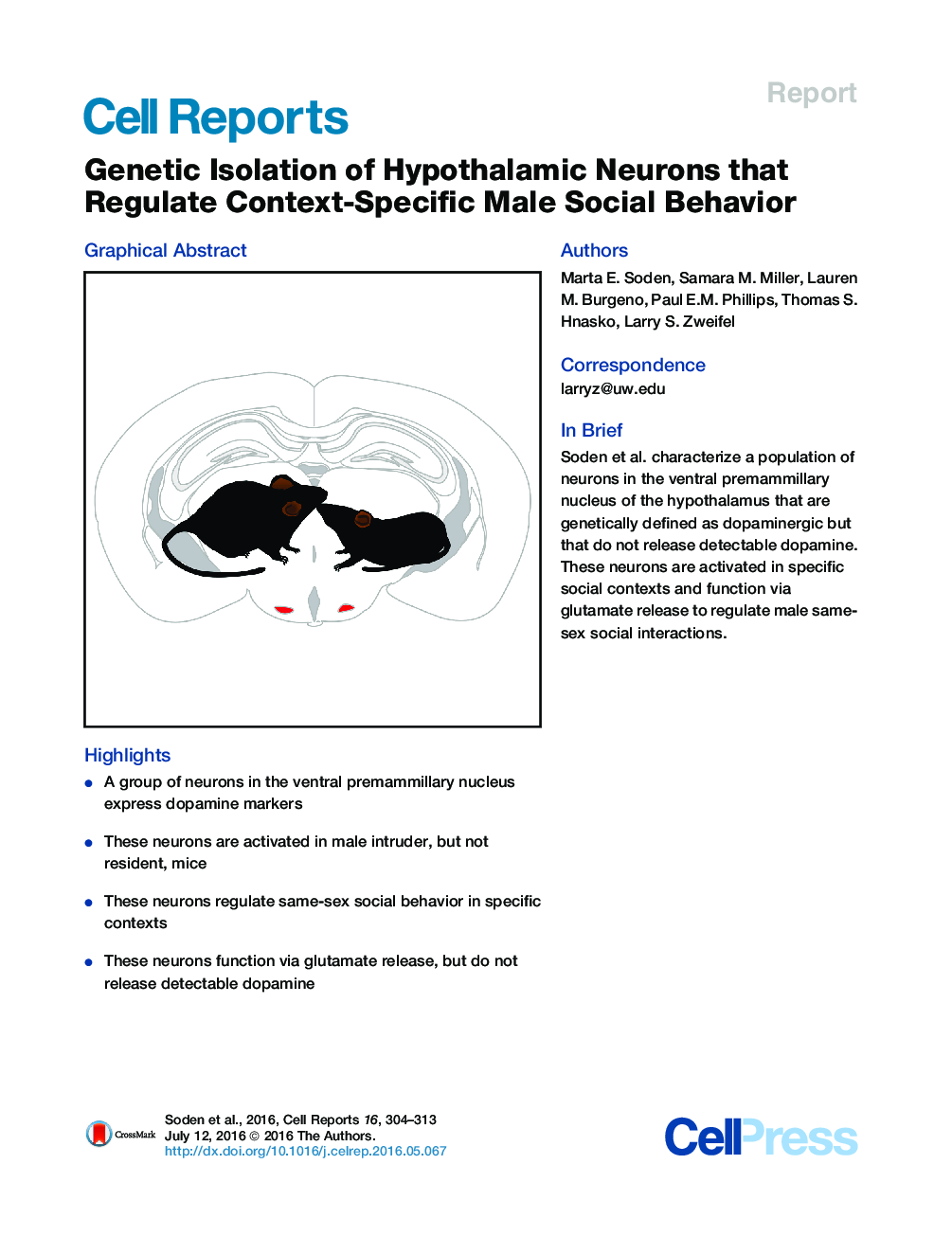
• A group of neurons in the ventral premammillary nucleus express dopamine markers
• These neurons are activated in male intruder, but not resident, mice
• These neurons regulate same-sex social behavior in specific contexts
• These neurons function via glutamate release, but do not release detectable dopamine
SummaryNearly all animals engage in a complex assortment of social behaviors that are essential for the survival of the species. In mammals, these behaviors are regulated by sub-nuclei within the hypothalamus, but the specific cell types within these nuclei responsible for coordinating behavior in distinct contexts are only beginning to be resolved. Here, we identify a population of neurons in the ventral premammillary nucleus of the hypothalamus (PMV) that are strongly activated in male intruder mice in response to a larger resident male but that are not responsive to females. Using a combination of molecular and genetic approaches, we demonstrate that these PMV neurons regulate intruder-specific male social behavior and social novelty recognition in a manner dependent on synaptic release of the excitatory neurotransmitter glutamate. These data provide direct evidence for a unique population of neurons that regulate social behaviors in specific contexts.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: - Volume 16, Issue 2, 12 July 2016, Pages 304–313