| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2039153 | 1073029 | 2016 | 14 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
• The GluK2 cytoplasmic domain mediates synaptic stabilization
• Surface kainate receptor activity depends on GluK2 but not its cytoplasmic domain
• The extracellular domain of high-affinity GluK subunits mediates synaptic specificity
• Input-specific synaptic localization of kainate receptors is mediated by two mechanisms
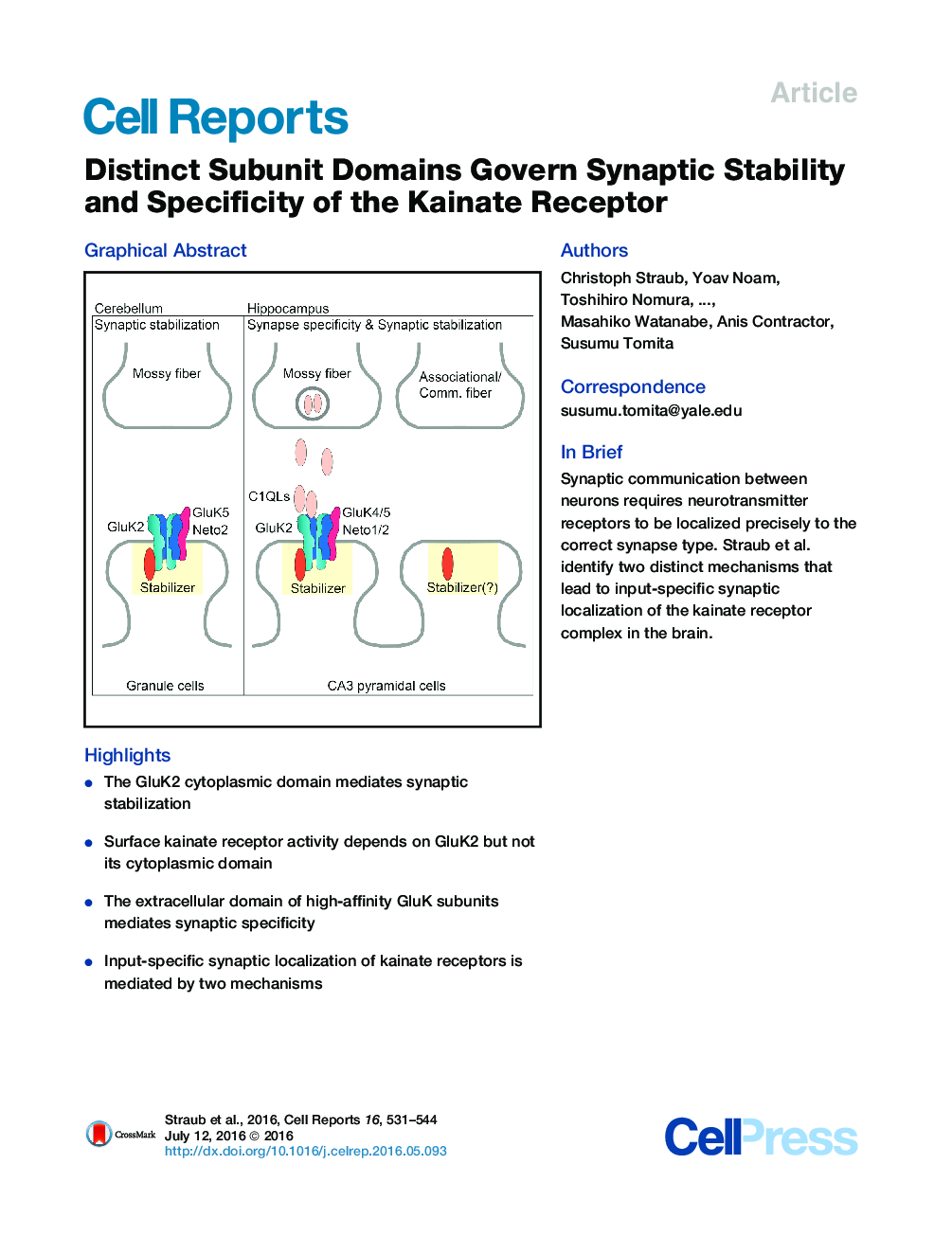
SummarySynaptic communication between neurons requires the precise localization of neurotransmitter receptors to the correct synapse type. Kainate-type glutamate receptors restrict synaptic localization that is determined by the afferent presynaptic connection. The mechanisms that govern this input-specific synaptic localization remain unclear. Here, we examine how subunit composition and specific subunit domains contribute to synaptic localization of kainate receptors. The cytoplasmic domain of the GluK2 low-affinity subunit stabilizes kainate receptors at synapses. In contrast, the extracellular domain of the GluK4/5 high-affinity subunit synergistically controls the synaptic specificity of kainate receptors through interaction with C1q-like proteins. Thus, the input-specific synaptic localization of the native kainate receptor complex involves two mechanisms that underlie specificity and stabilization of the receptor at synapses.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: - Volume 16, Issue 2, 12 July 2016, Pages 531–544