| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2039538 | 1073066 | 2016 | 11 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
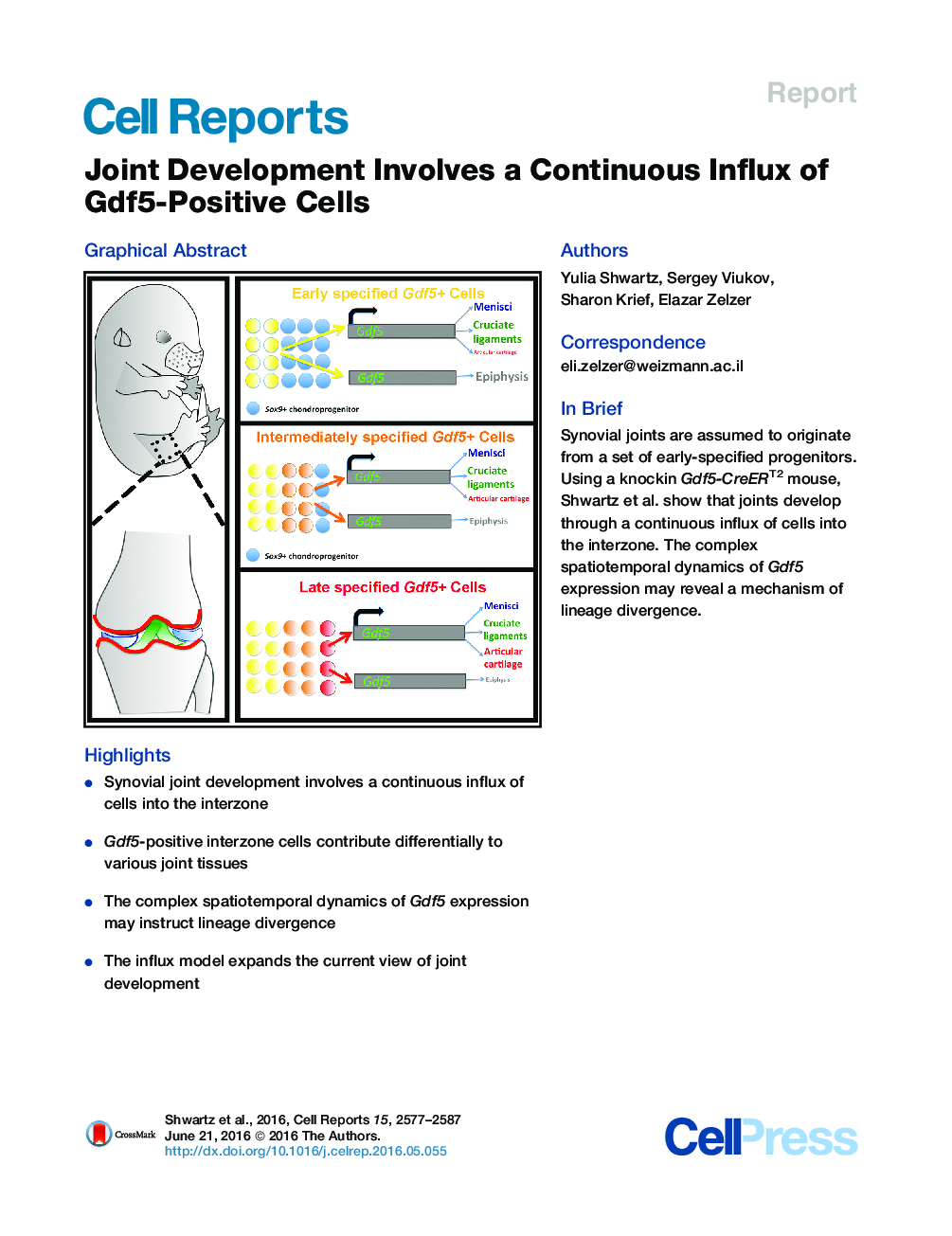
• Synovial joint development involves a continuous influx of cells into the interzone
• Gdf5-positive interzone cells contribute differentially to various joint tissues
• The complex spatiotemporal dynamics of Gdf5 expression may instruct lineage divergence
• The influx model expands the current view of joint development
SummarySynovial joints comprise several tissue types, including articular cartilage, the capsule, and ligaments. All of these compartments are commonly assumed to originate from an early set of Gdf5-expressing progenitors populating the interzone domain. Here, we provide evidence that joints develop through a continuous influx of cells into the interzone, where they contribute differentially to forming joint tissues. Using a knockin Gdf5-CreERT2 mouse, we show that early labeling of Gdf5-positive interzone cells failed to mark the entire organ. Conversely, multiple Cre activation steps indicated a contribution of these cells to various joint compartments later in development. Spatiotemporal differences between Gdf5 and tdTomato reporter expression support the notion of a continuous recruitment process. Finally, differential contribution of Gdf5-positive cells to various tissues suggests that the spatiotemporal dynamics of Gdf5 expression may instruct lineage divergence. This work supports the influx model of joint development, which may apply to other organogenic processes.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: - Volume 15, Issue 12, 21 June 2016, Pages 2577–2587