| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2039584 | 1073068 | 2015 | 11 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
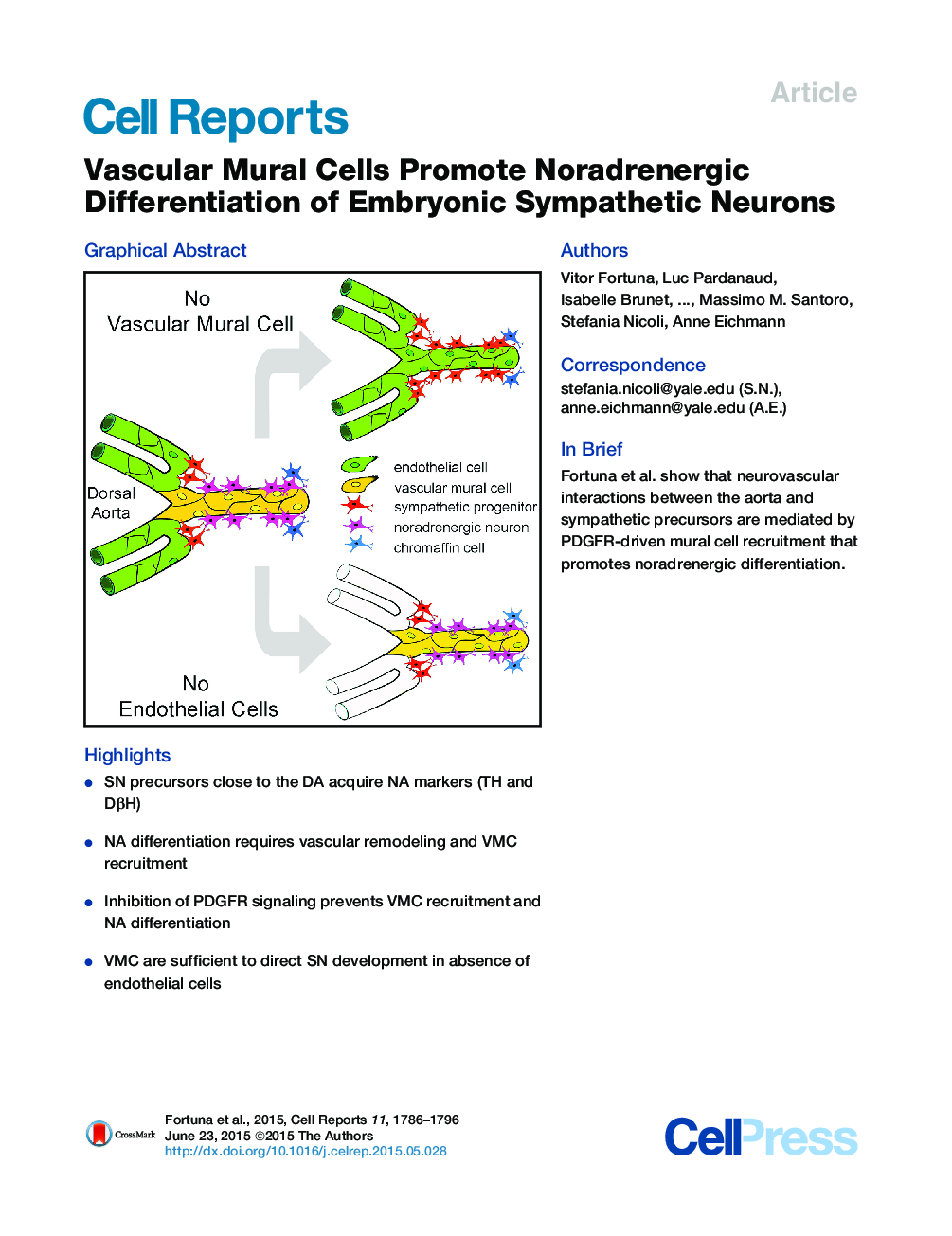
• SN precursors close to the DA acquire NA markers (TH and DβH)
• NA differentiation requires vascular remodeling and VMC recruitment
• Inhibition of PDGFR signaling prevents VMC recruitment and NA differentiation
• VMC are sufficient to direct SN development in absence of endothelial cells
SummaryThe sympathetic nervous system controls smooth muscle tone and heart rate in the cardiovascular system. Postganglionic sympathetic neurons (SNs) develop in close proximity to the dorsal aorta (DA) and innervate visceral smooth muscle targets. Here, we use the zebrafish embryo to ask whether the DA is required for SN development. We show that noradrenergic (NA) differentiation of SN precursors temporally coincides with vascular mural cell (VMC) recruitment to the DA and vascular maturation. Blocking vascular maturation inhibits VMC recruitment and blocks NA differentiation of SN precursors. Inhibition of platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR) signaling prevents VMC differentiation and also blocks NA differentiation of SN precursors. NA differentiation is normal in cloche mutants that are devoid of endothelial cells but have VMCs. Thus, PDGFR-mediated mural cell recruitment mediates neurovascular interactions between the aorta and sympathetic precursors and promotes their noradrenergic differentiation.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: - Volume 11, Issue 11, 23 June 2015, Pages 1786–1796