| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2039656 | 1073073 | 2014 | 16 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
• HSV-1 induces telomere dysfunction
• ICP0 ubiquitin ligase is required for TERRA induction and telomere remodeling
• ICP0 promotes ICP8 binding and colocalization with telomeric DNA
• Telomeric factors restrict HSV-1 replication
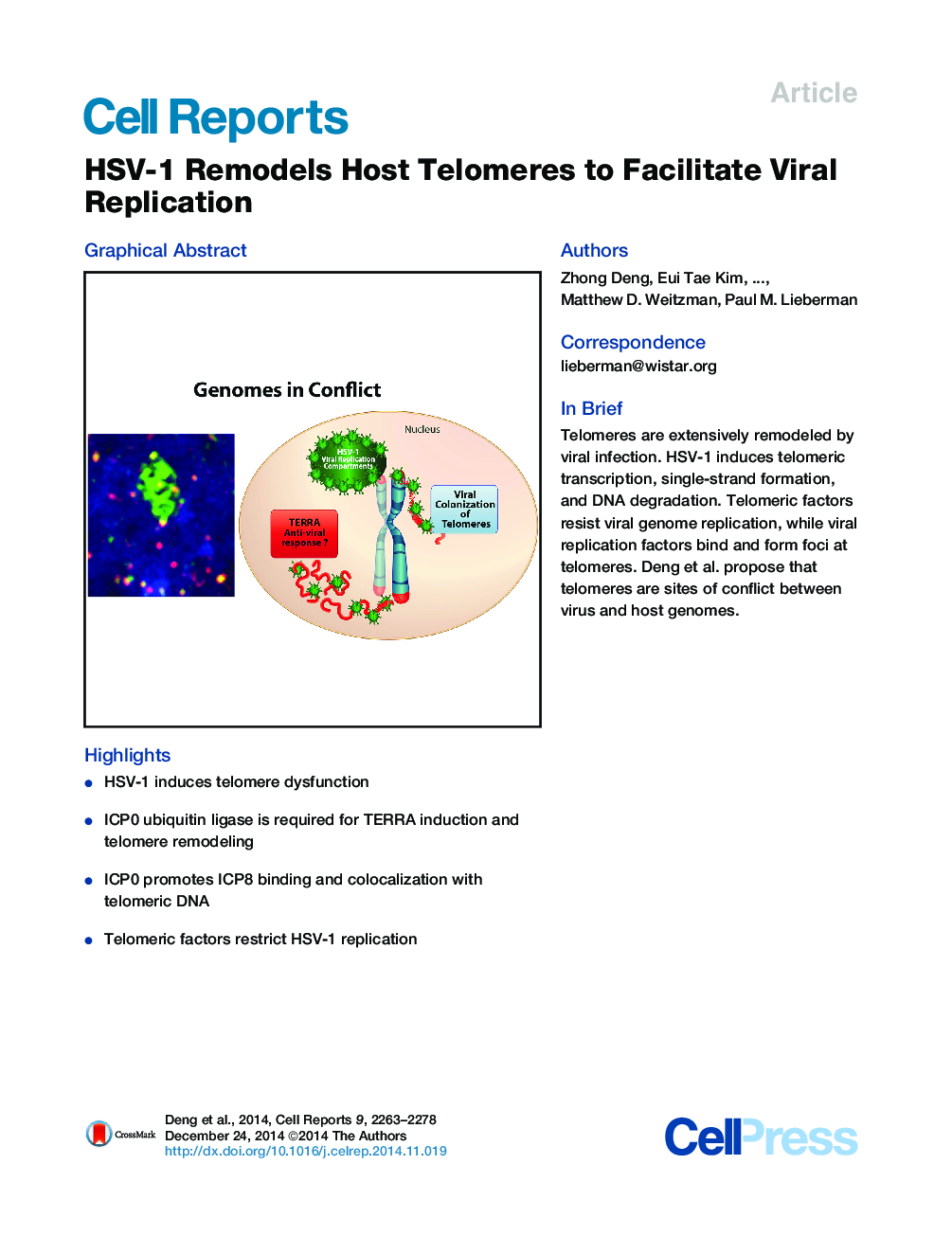
SummaryTelomeres protect the ends of cellular chromosomes. We show here that infection with herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1) results in chromosomal structural aberrations at telomeres and the accumulation of telomere dysfunction-induced DNA damage foci (TIFs). At the molecular level, HSV-1 induces transcription of telomere repeat-containing RNA (TERRA), followed by the proteolytic degradation of the telomere protein TPP1 and loss of the telomere repeat DNA signal. The HSV-1-encoded E3 ubiquitin ligase ICP0 is required for TERRA transcription and facilitates TPP1 degradation. Small hairpin RNA (shRNA) depletion of TPP1 increases viral replication, indicating that TPP1 inhibits viral replication. Viral replication protein ICP8 forms foci that coincide with telomeric proteins, and ICP8-null virus failed to degrade telomere DNA signal. These findings suggest that HSV-1 reorganizes telomeres to form ICP8-associated prereplication foci and to promote viral genomic replication.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: - Volume 9, Issue 6, 24 December 2014, Pages 2263–2278