| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2039711 | 1073076 | 2016 | 15 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
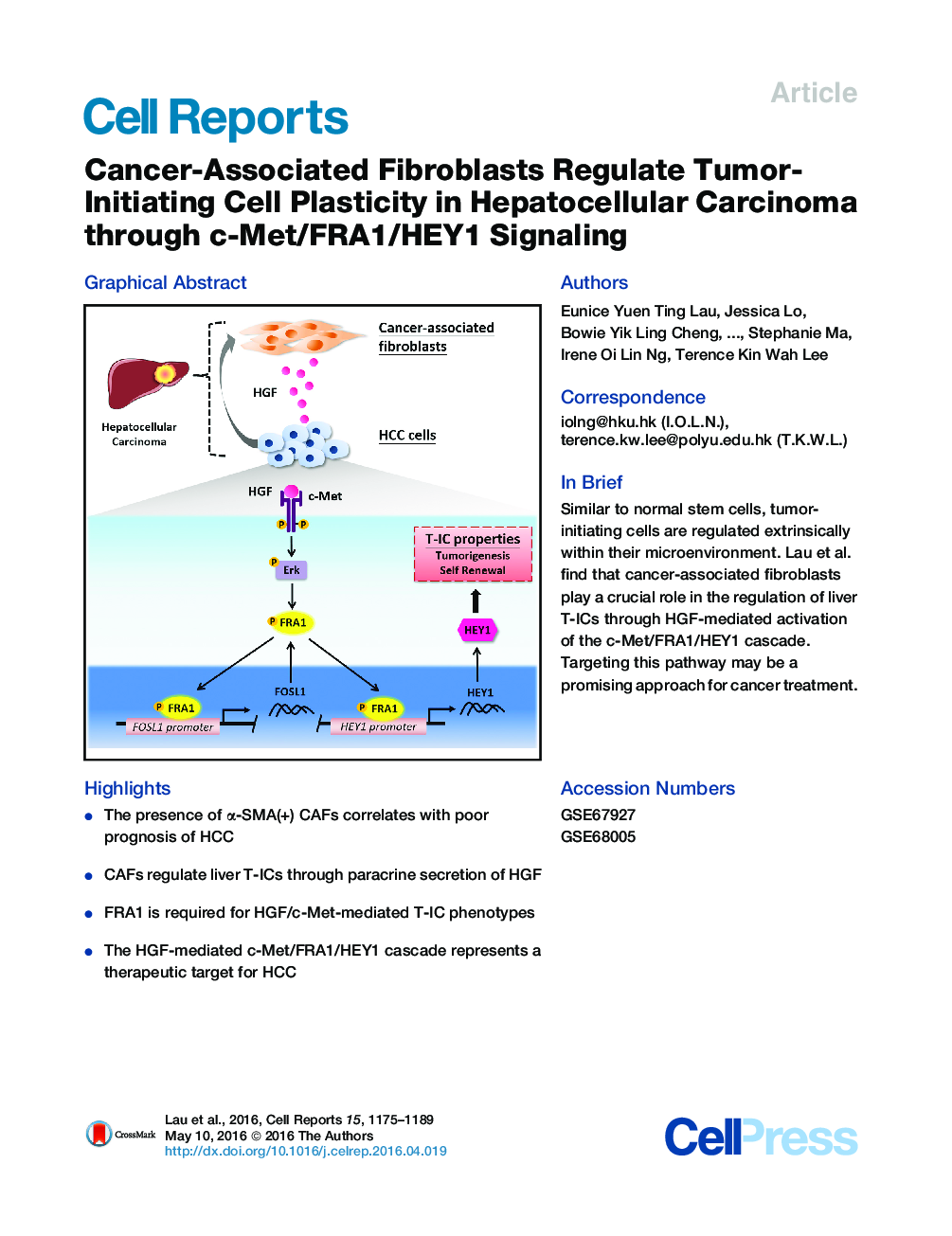
• The presence of α-SMA(+) CAFs correlates with poor prognosis of HCC
• CAFs regulate liver T-ICs through paracrine secretion of HGF
• FRA1 is required for HGF/c-Met-mediated T-IC phenotypes
• The HGF-mediated c-Met/FRA1/HEY1 cascade represents a therapeutic target for HCC
SummaryLike normal stem cells, tumor-initiating cells (T-ICs) are regulated extrinsically within the tumor microenvironment. Because HCC develops primarily in the context of cirrhosis, in which there is an enrichment of activated fibroblasts, we hypothesized that cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) would regulate liver T-ICs. We found that the presence of α-SMA(+) CAFs correlates with poor clinical outcome. CAF-derived HGF regulates liver T-ICs via activation of FRA1 in an Erk1,2-dependent manner. Further functional analysis identifies HEY1 as a direct downstream effector of FRA1. Using the STAM NASH-HCC mouse model, we find that HGF-induced FRA1 activation is associated with the fibrosis-dependent development of HCC. Thus, targeting the CAF-derived, HGF-mediated c-Met/FRA1/HEY1 cascade may be a therapeutic strategy for the treatment of HCC.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: - Volume 15, Issue 6, 10 May 2016, Pages 1175–1189