| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2039998 | 1073093 | 2016 | 15 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
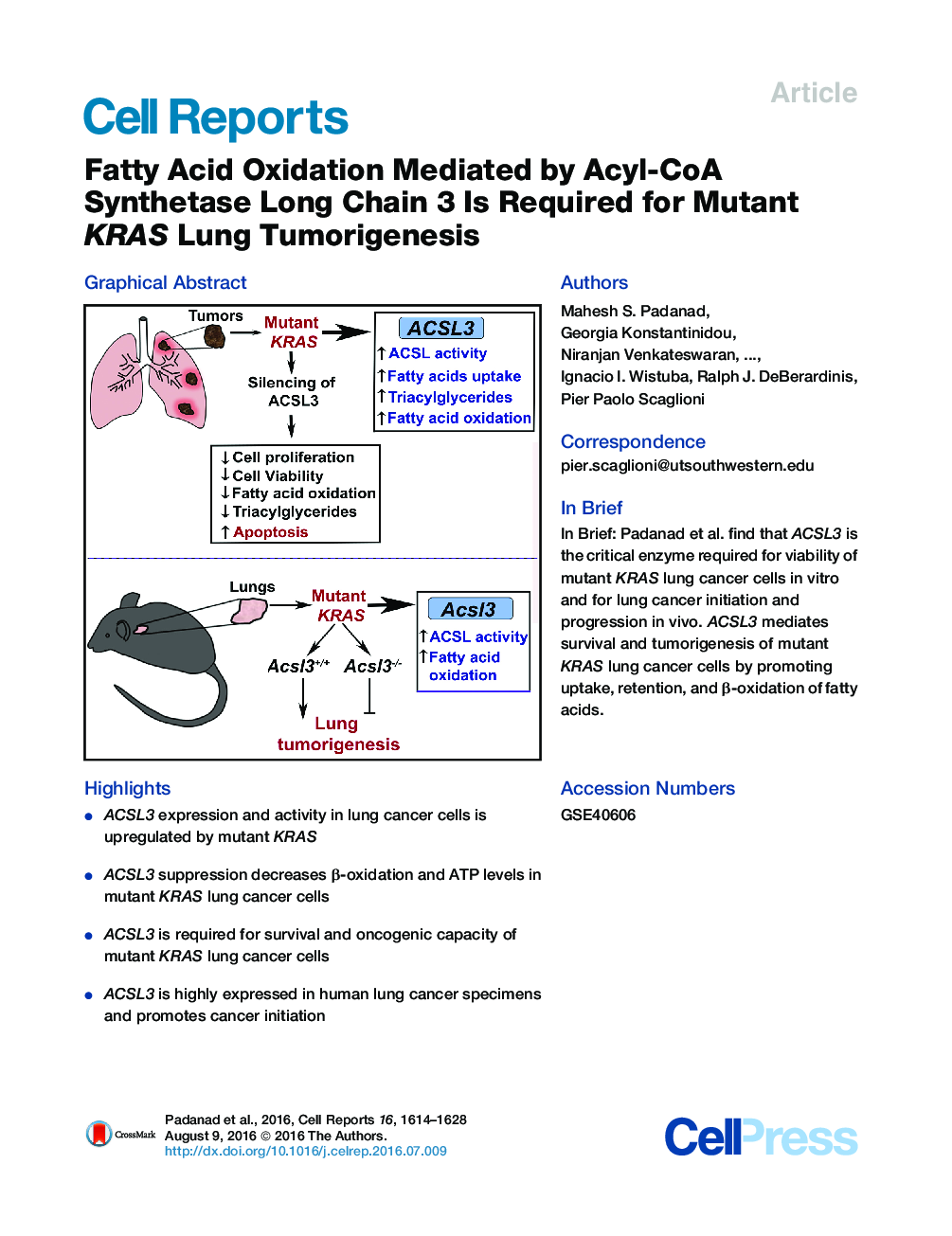
• ACSL3 expression and activity in lung cancer cells is upregulated by mutant KRAS
• ACSL3 suppression decreases β-oxidation and ATP levels in mutant KRAS lung cancer cells
• ACSL3 is required for survival and oncogenic capacity of mutant KRAS lung cancer cells
• ACSL3 is highly expressed in human lung cancer specimens and promotes cancer initiation
SummaryKRAS is one of the most commonly mutated oncogenes in human cancer. Mutant KRAS aberrantly regulates metabolic networks. However, the contribution of cellular metabolism to mutant KRAS tumorigenesis is not completely understood. We report that mutant KRAS regulates intracellular fatty acid metabolism through Acyl-coenzyme A (CoA) synthetase long-chain family member 3 (ACSL3), which converts fatty acids into fatty Acyl-CoA esters, the substrates for lipid synthesis and β-oxidation. ACSL3 suppression is associated with depletion of cellular ATP and causes the death of lung cancer cells. Furthermore, mutant KRAS promotes the cellular uptake, retention, accumulation, and β-oxidation of fatty acids in lung cancer cells in an ACSL3-dependent manner. Finally, ACSL3 is essential for mutant KRAS lung cancer tumorigenesis in vivo and is highly expressed in human lung cancer. Our data demonstrate that mutant KRAS reprograms lipid homeostasis, establishing a metabolic requirement that could be exploited for therapeutic gain.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: - Volume 16, Issue 6, 9 August 2016, Pages 1614–1628