| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2040049 | 1073095 | 2014 | 12 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
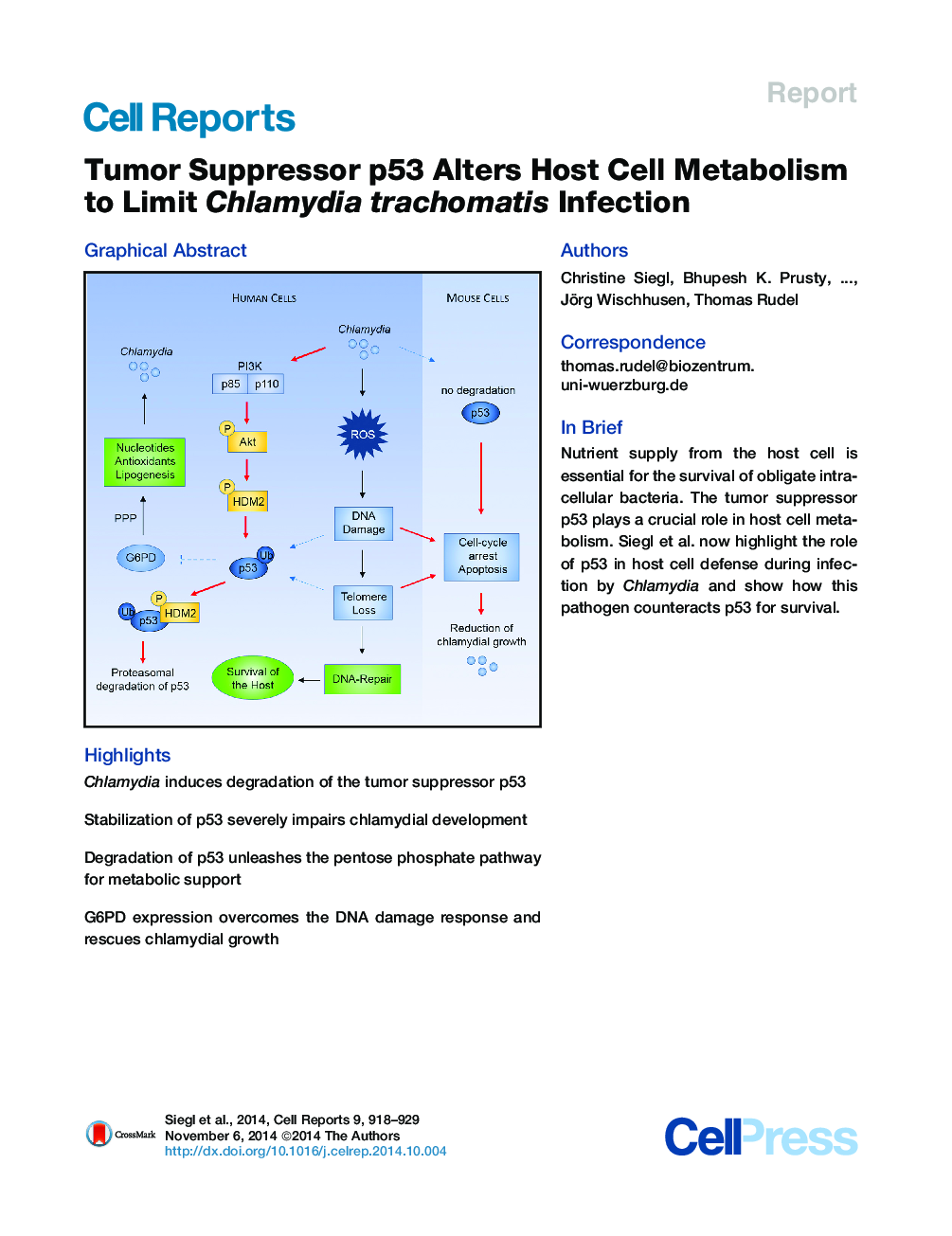
• Chlamydia induces degradation of the tumor suppressor p53
• Stabilization of p53 severely impairs chlamydial development
• Degradation of p53 unleashes the pentose phosphate pathway for metabolic support
• G6PD expression overcomes the DNA damage response and rescues chlamydial growth
SummaryObligate intracellular bacteria depend entirely on nutrients from the host cell for their reproduction. Here, we show that obligate intracellular Chlamydia downregulate the central tumor suppressor p53 in human cells. This reduction of p53 levels is mediated by the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, activation of HDM2, and subsequent proteasomal degradation of p53. The stabilization of p53 in human cells severely impaired chlamydial development and caused the loss of infectious particle formation. DNA-damage-induced p53 interfered with chlamydial development through downregulation of the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP). Increased expression of the PPP key enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase rescued the inhibition of chlamydial growth induced by DNA damage or stabilized p53. Thus, downregulation of p53 is a key event in the chlamydial life cycle that reprograms the host cell to create a metabolic environment supportive of chlamydial growth.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: - Volume 9, Issue 3, 6 November 2014, Pages 918–929