| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2040053 | 1073095 | 2014 | 16 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
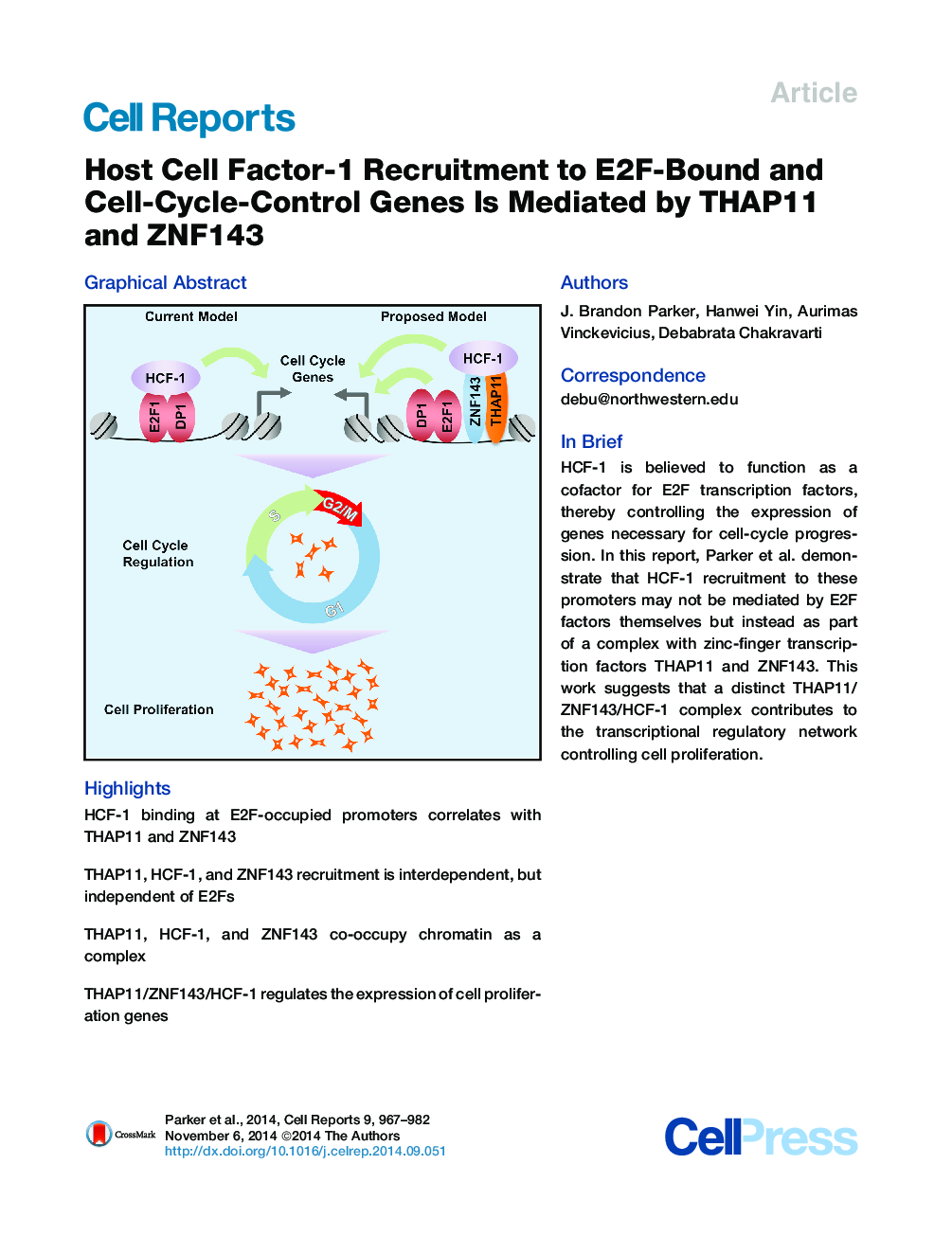
• HCF-1 binding at E2F-occupied promoters correlates with THAP11 and ZNF143
• THAP11, HCF-1, and ZNF143 recruitment is interdependent, but independent of E2Fs
• THAP11, HCF-1, and ZNF143 co-occupy chromatin as a complex
• THAP11/ZNF143/HCF-1 regulates the expression of cell proliferation genes
SummaryHost cell factor-1 (HCF-1) is a metazoan transcriptional coregulator essential for cell-cycle progression and cell proliferation. Current models suggest a mechanism whereby HCF-1 functions as a direct coregulator of E2F proteins, facilitating the expression of genes necessary for cell proliferation. In this report, we show that HCF-1 recruitment to numerous E2F-bound promoters is mediated by the concerted action of zinc finger transcription factors THAP11 and ZNF143, rather than E2F proteins directly. THAP11, ZNF143, and HCF-1 form a mutually dependent complex on chromatin, which is independent of E2F occupancy. Disruption of the THAP11/ZNF143/HCF-1 complex results in altered expression of cell-cycle control genes and leads to reduced cell proliferation, cell-cycle progression, and cell viability. These data establish a model in which a THAP11/ZNF143/HCF-1 complex is a critical component of the transcriptional regulatory network governing cell proliferation.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: - Volume 9, Issue 3, 6 November 2014, Pages 967–982