| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2040425 | 1073110 | 2016 | 7 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
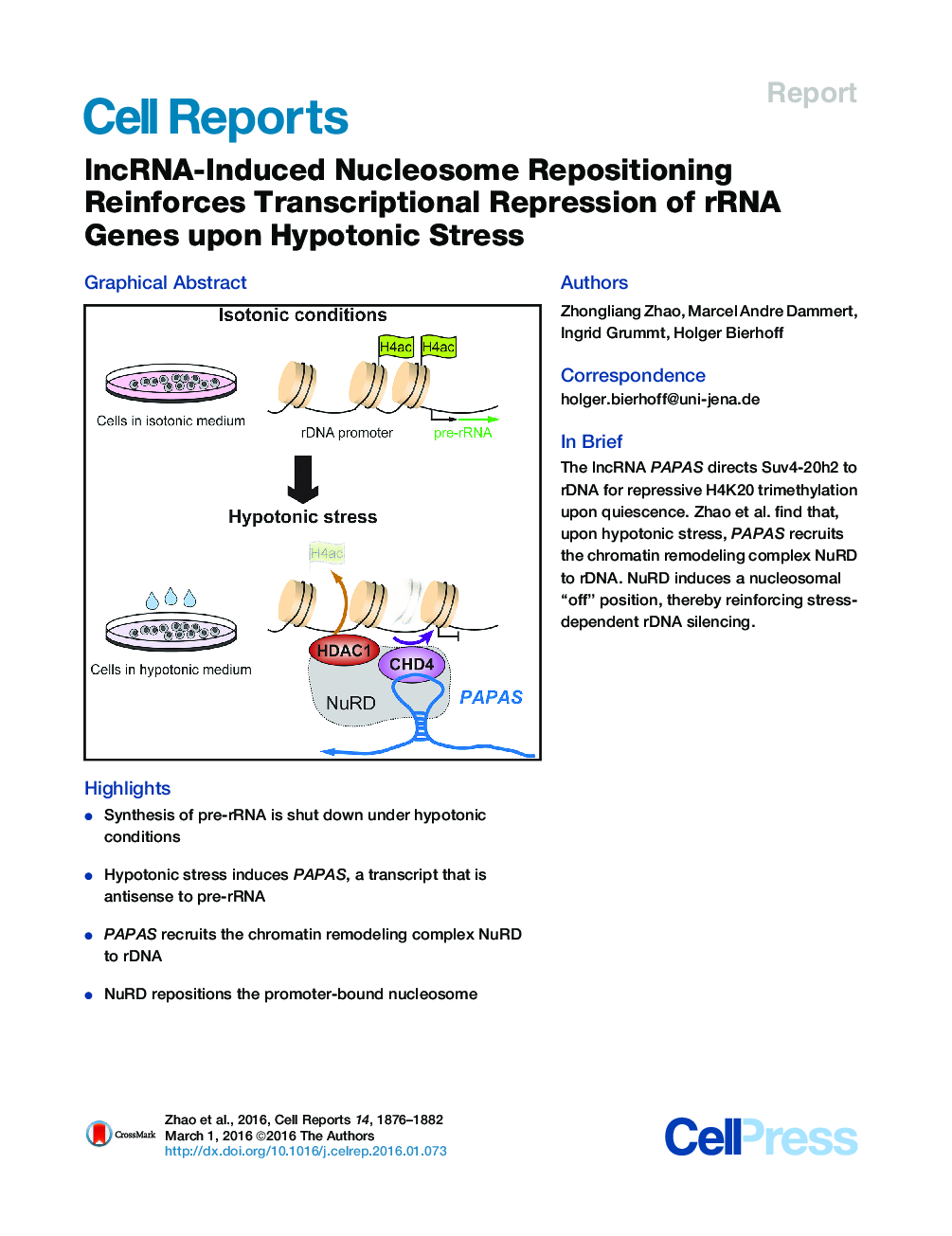
• Synthesis of pre-rRNA is shut down under hypotonic conditions
• Hypotonic stress induces PAPAS, a transcript that is antisense to pre-rRNA
• PAPAS recruits the chromatin remodeling complex NuRD to rDNA
• NuRD repositions the promoter-bound nucleosome
SummaryThe activity of rRNA genes (rDNA) is regulated by pathways that target the transcription machinery or alter the epigenetic state of rDNA. Previous work has established that downregulation of rRNA synthesis in quiescent cells is accompanied by upregulation of PAPAS, a long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) that recruits the histone methyltransferase Suv4-20h2 to rDNA, thus triggering trimethylation of H4K20 (H4K20me3) and chromatin compaction. Here, we show that upregulation of PAPAS in response to hypoosmotic stress does not increase H4K20me3 because of Nedd4-dependent ubiquitinylation and proteasomal degradation of Suv4-20h2. Loss of Suv4-20h2 enables PAPAS to interact with CHD4, a subunit of the chromatin remodeling complex NuRD, which shifts the promoter-bound nucleosome into the transcriptional “off” position. Thus, PAPAS exerts a “stress-tailored” dual function in rDNA silencing, facilitating either Suv4-20h2-dependent chromatin compaction or NuRD-dependent changes in nucleosome positioning.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: - Volume 14, Issue 8, 1 March 2016, Pages 1876–1882