| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2040655 | 1073122 | 2015 | 12 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
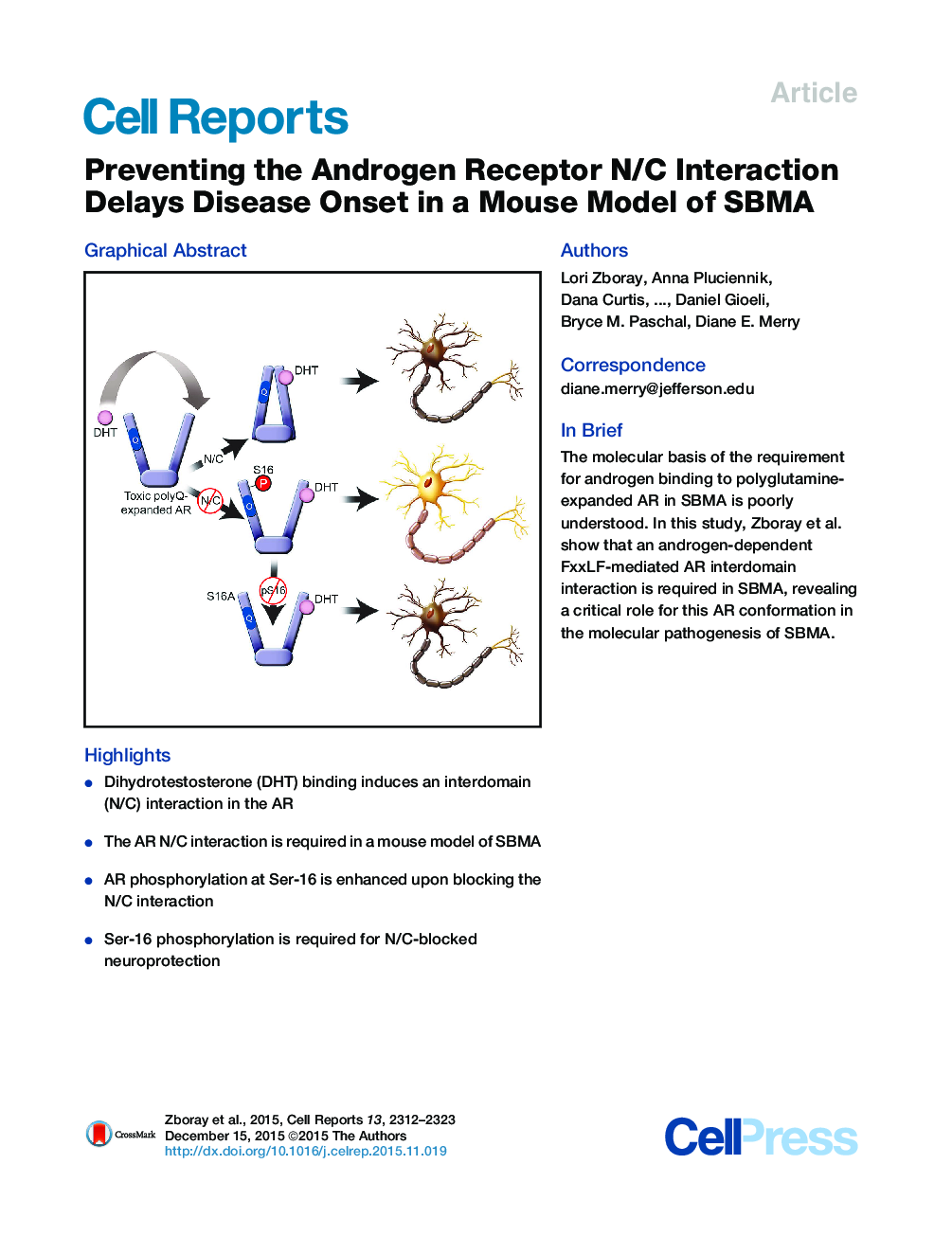
• Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) binding induces an interdomain (N/C) interaction in the AR
• The AR N/C interaction is required in a mouse model of SBMA
• AR phosphorylation at Ser-16 is enhanced upon blocking the N/C interaction
• Ser-16 phosphorylation is required for N/C-blocked neuroprotection
SummarySpinal and bulbar muscular atrophy (SBMA) is a neurodegenerative disease caused by a polyglutamine expansion in the androgen receptor (AR) and is associated with misfolding and aggregation of the mutant AR. We investigated the role of an interdomain interaction between the amino (N)-terminal FxxLF motif and carboxyl (C)-terminal AF-2 domain in a mouse model of SBMA. Male transgenic mice expressing polyQ-expanded AR with a mutation in the FxxLF motif (F23A) to prevent the N/C interaction displayed substantially improved motor function compared with N/C-intact AR-expressing mice and showed reduced pathological features of SBMA. Serine 16 phosphorylation was substantially enhanced by the F23A mutation; moreover, the protective effect of AR F23A was dependent on this phosphorylation. These results reveal an important role for the N/C interaction on disease onset in mice and suggest that targeting AR conformation could be a therapeutic strategy for patients with SBMA.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: - Volume 13, Issue 10, 15 December 2015, Pages 2312–2323