| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2041254 | 1073153 | 2016 | 9 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
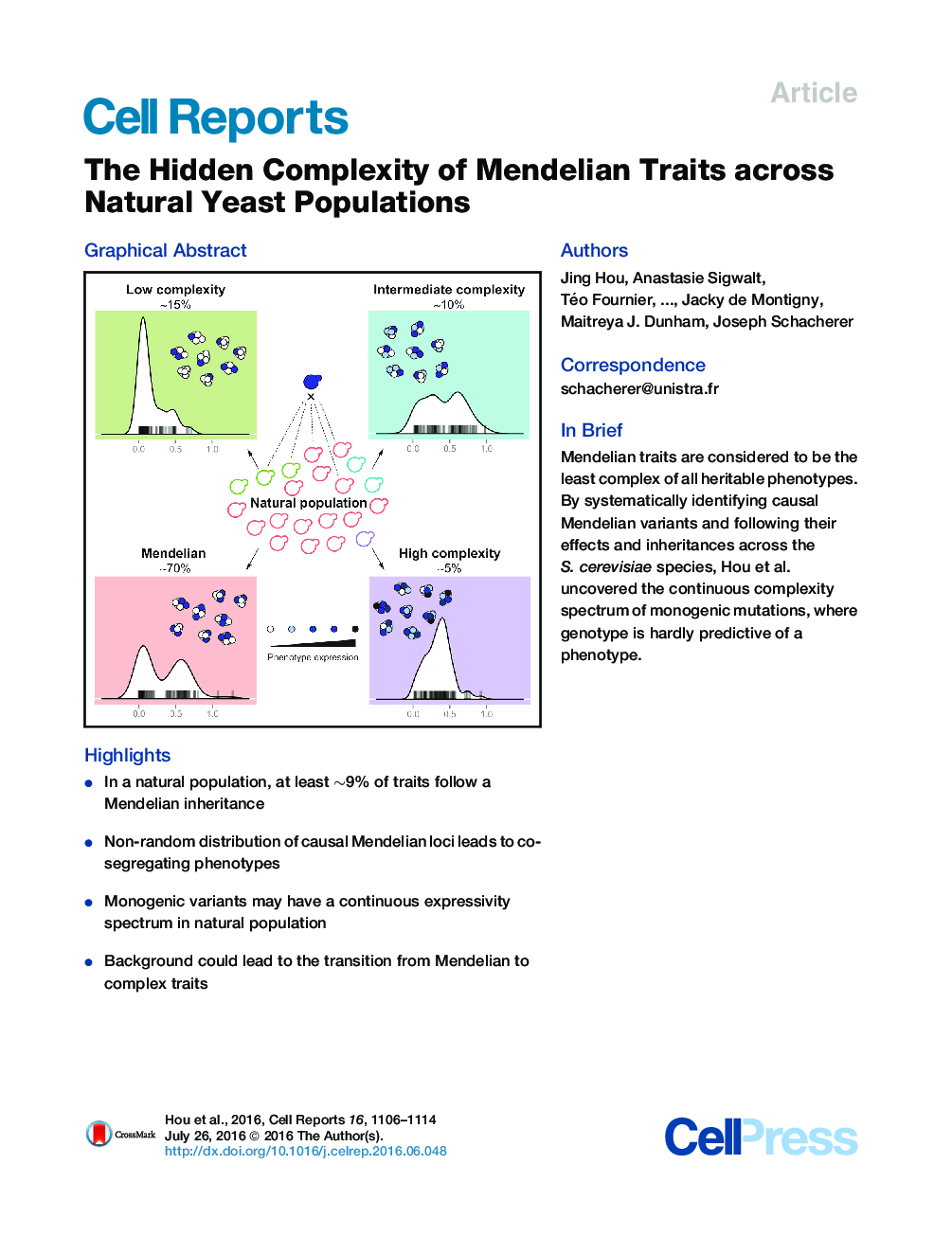
• In a natural population, at least ∼9% of traits follow a Mendelian inheritance
• Non-random distribution of causal Mendelian loci leads to co-segregating phenotypes
• Monogenic variants may have a continuous expressivity spectrum in natural population
• Background could lead to the transition from Mendelian to complex traits
SummaryMendelian traits are considered to be at the lower end of the complexity spectrum of heritable phenotypes. However, more than a century after the rediscovery of Mendel’s law, the global landscape of monogenic variants, as well as their effects and inheritance patterns within natural populations, is still not well understood. Using the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, we performed a species-wide survey of Mendelian traits across a large population of isolates. We generated offspring from 41 unique parental pairs and analyzed 1,105 cross/trait combinations. We found that 8.9% of the cases were Mendelian. Further tracing of causal variants revealed background-specific expressivity and modified inheritances, gradually transitioning from Mendelian to complex traits in 30% of the cases. In fact, when taking into account the natural population diversity, the hidden complexity of traits could be substantial, confounding phenotypic predictability even for simple Mendelian traits.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: - Volume 16, Issue 4, 26 July 2016, Pages 1106–1114