| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2041442 | 1073161 | 2015 | 14 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
• Neurons of the cerebellum are generated from FGF2-treated cultures of human ESCs
• The induced human Purkinje cells exhibit conserved and human-specific characteristics
• FGF19 and SDF1 promote the self-formation of polarized neural-tube-like structures
• The cerebellum is self-formed by ESC-derived cerebellar plate and rhombic lip neurons
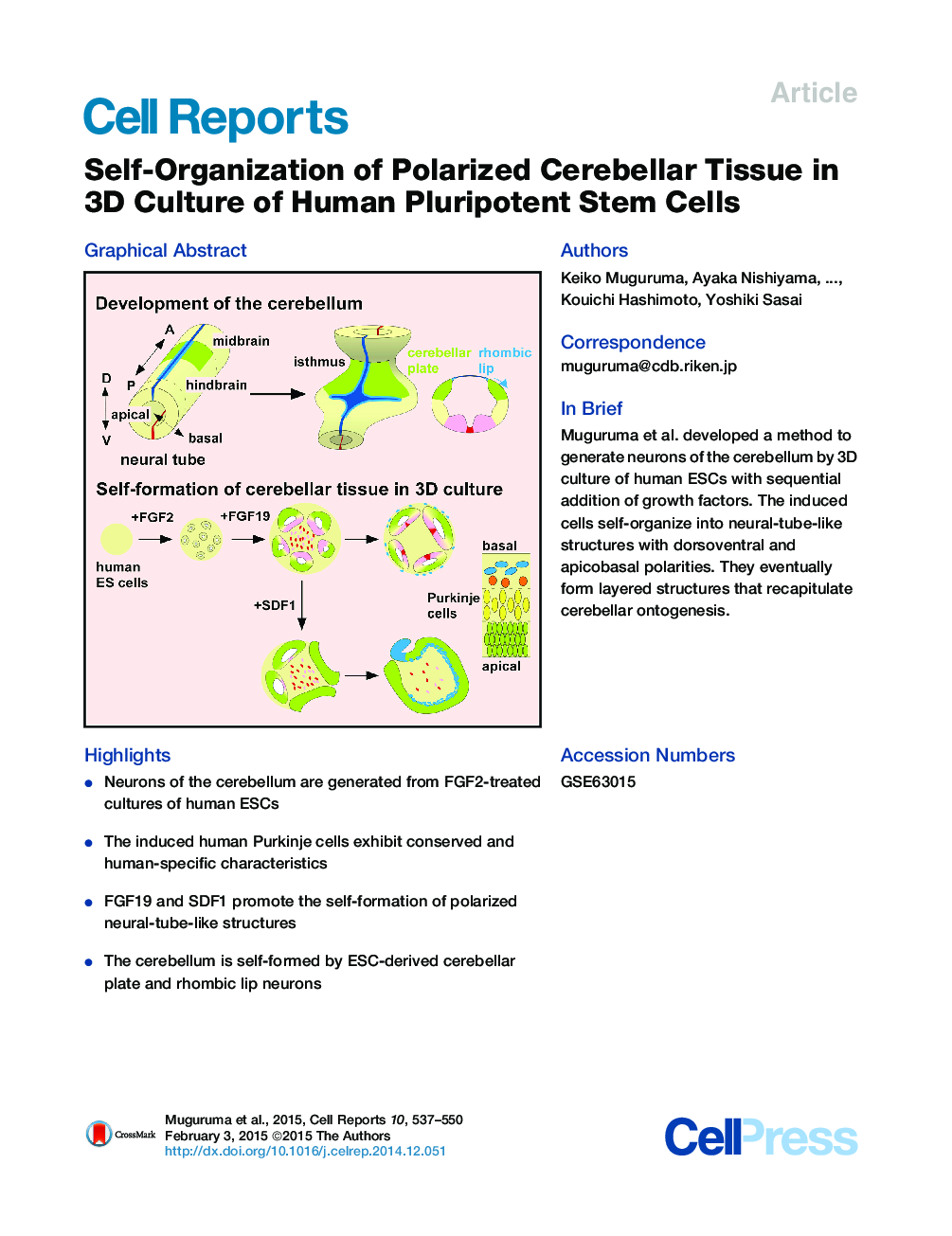
SummaryDuring cerebellar development, the main portion of the cerebellar plate neuroepithelium gives birth to Purkinje cells and interneurons, whereas the rhombic lip, the germinal zone at its dorsal edge, generates granule cells and cerebellar nuclei neurons. However, it remains elusive how these components cooperate to form the intricate cerebellar structure. Here, we found that a polarized cerebellar structure self-organizes in 3D human embryonic stem cell (ESC) culture. The self-organized neuroepithelium differentiates into electrophysiologically functional Purkinje cells. The addition of fibroblast growth factor 19 (FGF19) promotes spontaneous generation of dorsoventrally polarized neural-tube-like structures at the level of the cerebellum. Furthermore, addition of SDF1 and FGF19 promotes the generation of a continuous cerebellar plate neuroepithelium with rhombic-lip-like structure at one end and a three-layer cytoarchitecture similar to the embryonic cerebellum. Thus, human-ESC-derived cerebellar progenitors exhibit substantial self-organizing potential for generating a polarized structure reminiscent of the early human cerebellum at the first trimester.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: - Volume 10, Issue 4, 3 February 2015, Pages 537–550