| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2041763 | 1073172 | 2015 | 9 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
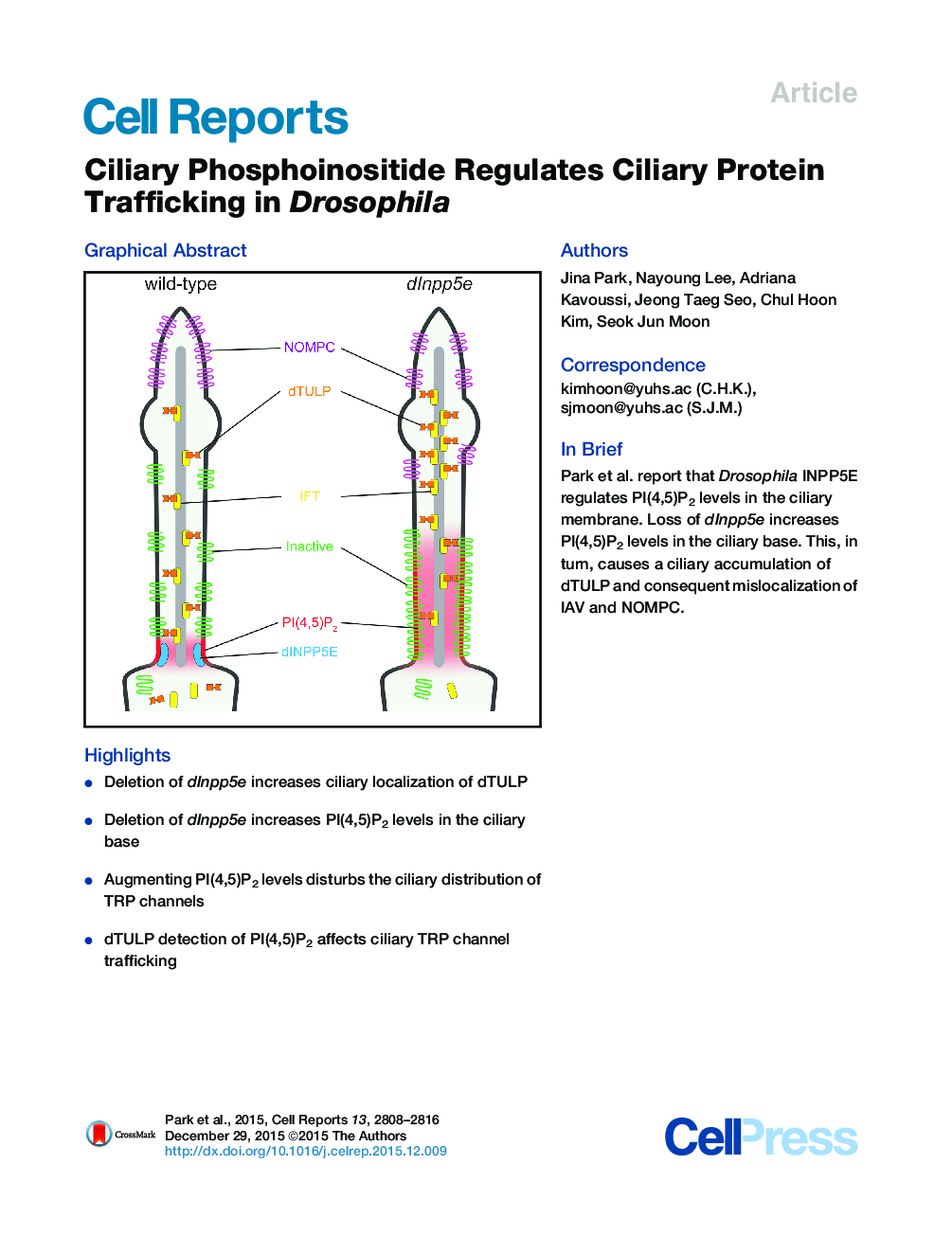
• Deletion of dInpp5e increases ciliary localization of dTULP
• Deletion of dInpp5e increases PI(4,5)P2 levels in the ciliary base
• Augmenting PI(4,5)P2 levels disturbs the ciliary distribution of TRP channels
• dTULP detection of PI(4,5)P2 affects ciliary TRP channel trafficking
SummaryCilia are highly specialized antennae-like cellular organelles. Inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase E (INPP5E) converts PI(4,5)P2 into PI4P and is required for proper ciliary function. Although Inpp5e mutations are associated with ciliopathies in humans and mice, the precise molecular role INPP5E plays in cilia remains unclear. Here, we report that Drosophila INPP5E (dINPP5E) regulates ciliary protein trafficking by controlling the phosphoinositide composition of ciliary membranes. Mutations in dInpp5e lead to hearing deficits due to the mislocalization of dTULP and mechanotransduction channels, Inactive and NOMPC, in chordotonal cilia. Both loss of dINPP5E and ectopic expression of the phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinase Skittles increase PI(4,5)P2 levels in the ciliary base. The fact that Skittles expression phenocopies the dInpp5e mutants confirms a central role for PI(4,5)P2 in the regulation of dTULP, Inactive, and NOMPC localization. These data suggest that the spatial localization and levels of PI(4,5)P2 in ciliary membranes are important regulators of ciliary trafficking and function.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: - Volume 13, Issue 12, 29 December 2015, Pages 2808–2816