| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4503748 | 1624245 | 2015 | 7 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
• Inundative release of T. pretiosum increased parasitism of H. zea eggs.
• Habitat management treatment enhanced predator:prey ratios.
• Inundative release of T. pretiosum increased quantity and quantity of corn ear yield.
• Inundative release is potentially a viable H. zea management tool in corn.
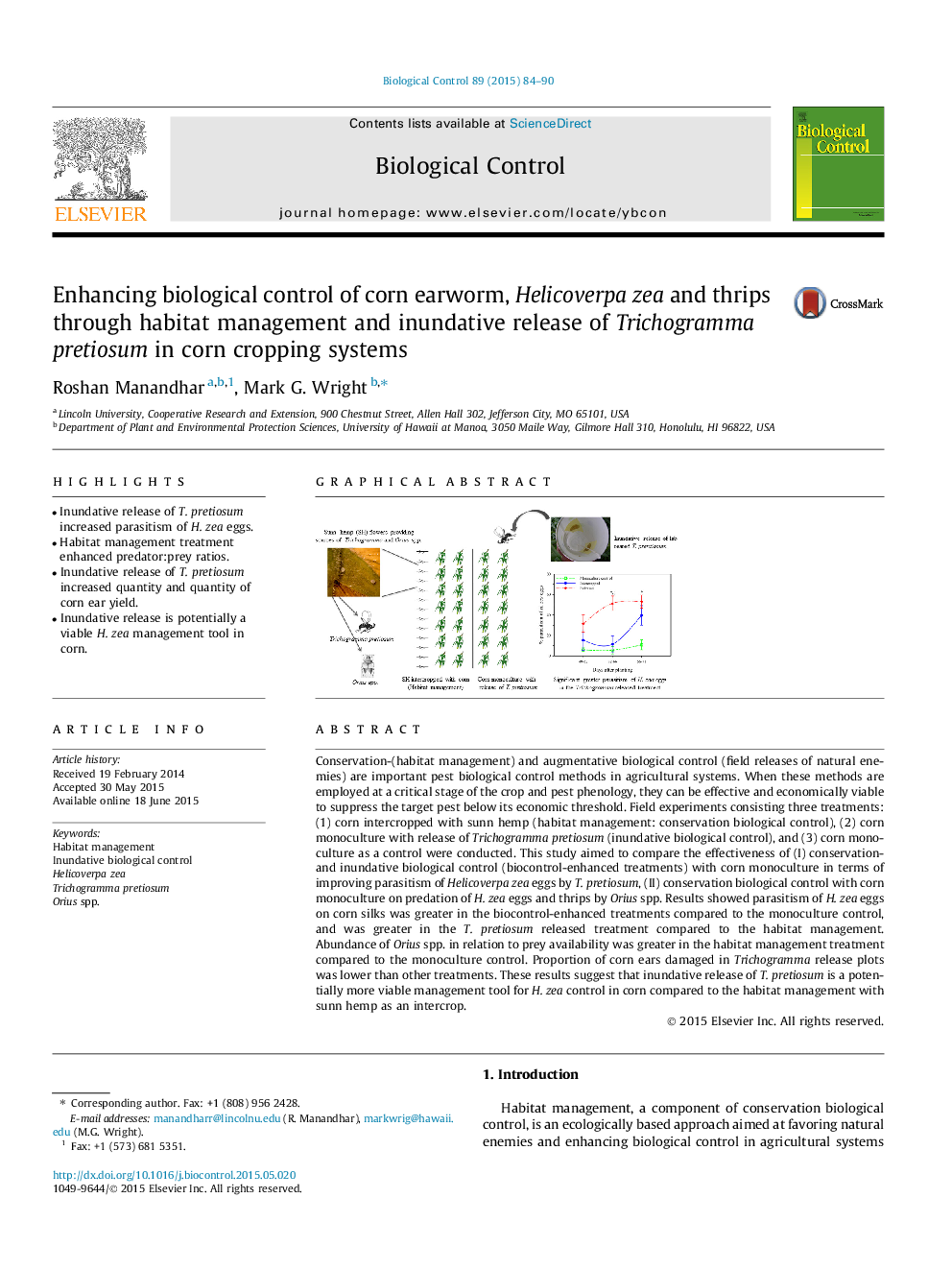
Conservation-(habitat management) and augmentative biological control (field releases of natural enemies) are important pest biological control methods in agricultural systems. When these methods are employed at a critical stage of the crop and pest phenology, they can be effective and economically viable to suppress the target pest below its economic threshold. Field experiments consisting three treatments: (1) corn intercropped with sunn hemp (habitat management: conservation biological control), (2) corn monoculture with release of Trichogramma pretiosum (inundative biological control), and (3) corn monoculture as a control were conducted. This study aimed to compare the effectiveness of (I) conservation- and inundative biological control (biocontrol-enhanced treatments) with corn monoculture in terms of improving parasitism of Helicoverpa zea eggs by T. pretiosum, (II) conservation biological control with corn monoculture on predation of H. zea eggs and thrips by Orius spp. Results showed parasitism of H. zea eggs on corn silks was greater in the biocontrol-enhanced treatments compared to the monoculture control, and was greater in the T. pretiosum released treatment compared to the habitat management. Abundance of Orius spp. in relation to prey availability was greater in the habitat management treatment compared to the monoculture control. Proportion of corn ears damaged in Trichogramma release plots was lower than other treatments. These results suggest that inundative release of T. pretiosum is a potentially more viable management tool for H. zea control in corn compared to the habitat management with sunn hemp as an intercrop.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Biological Control - Volume 89, October 2015, Pages 84–90