| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 606446 | 1454531 | 2016 | 7 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
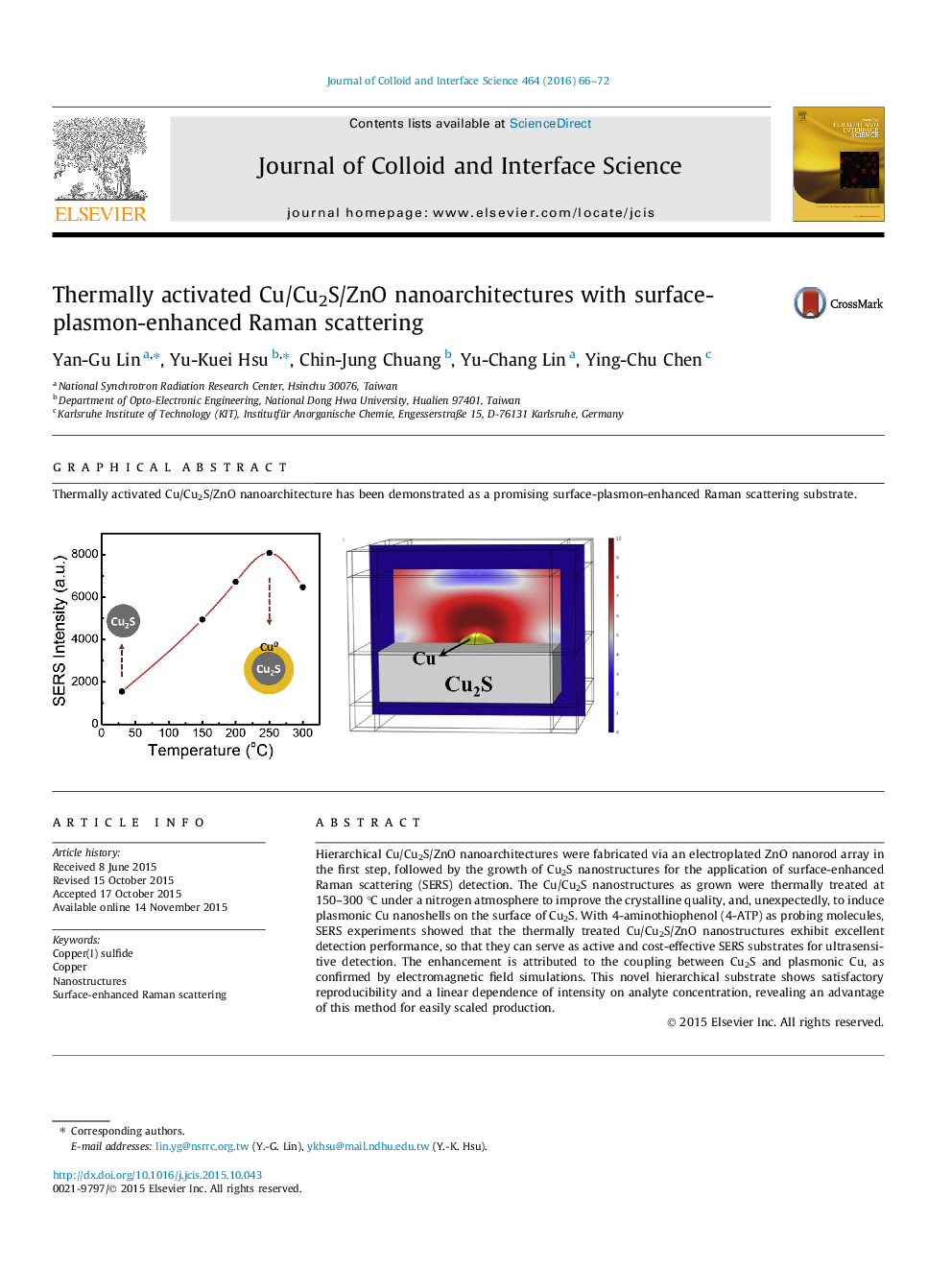
Hierarchical Cu/Cu2S/ZnO nanoarchitectures were fabricated via an electroplated ZnO nanorod array in the first step, followed by the growth of Cu2S nanostructures for the application of surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) detection. The Cu/Cu2S nanostructures as grown were thermally treated at 150–300 °C under a nitrogen atmosphere to improve the crystalline quality, and, unexpectedly, to induce plasmonic Cu nanoshells on the surface of Cu2S. With 4-aminothiophenol (4-ATP) as probing molecules, SERS experiments showed that the thermally treated Cu/Cu2S/ZnO nanostructures exhibit excellent detection performance, so that they can serve as active and cost-effective SERS substrates for ultrasensitive detection. The enhancement is attributed to the coupling between Cu2S and plasmonic Cu, as confirmed by electromagnetic field simulations. This novel hierarchical substrate shows satisfactory reproducibility and a linear dependence of intensity on analyte concentration, revealing an advantage of this method for easily scaled production.
Thermally activated Cu/Cu2S/ZnO nanoarchitecture has been demonstrated as a promising surface-plasmon-enhanced Raman scattering substrate.Figure optionsDownload high-quality image (74 K)Download as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Journal of Colloid and Interface Science - Volume 464, 15 February 2016, Pages 66–72