| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 606763 | 1454539 | 2015 | 9 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
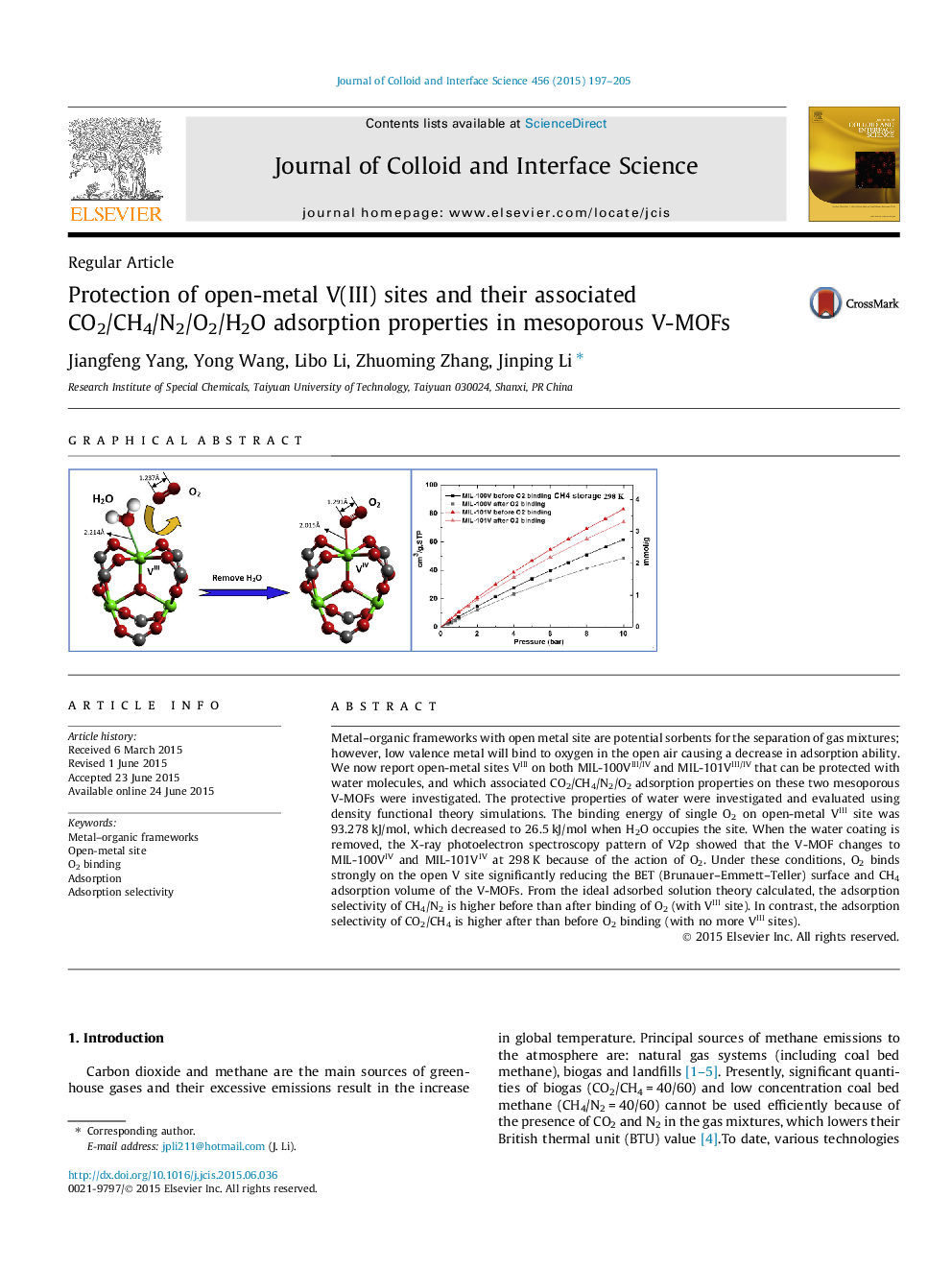
Metal–organic frameworks with open metal site are potential sorbents for the separation of gas mixtures; however, low valence metal will bind to oxygen in the open air causing a decrease in adsorption ability. We now report open-metal sites VIII on both MIL-100VIII/IV and MIL-101VIII/IV that can be protected with water molecules, and which associated CO2/CH4/N2/O2 adsorption properties on these two mesoporous V-MOFs were investigated. The protective properties of water were investigated and evaluated using density functional theory simulations. The binding energy of single O2 on open-metal VIII site was 93.278 kJ/mol, which decreased to 26.5 kJ/mol when H2O occupies the site. When the water coating is removed, the X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy pattern of V2p showed that the V-MOF changes to MIL-100VIV and MIL-101VIV at 298 K because of the action of O2. Under these conditions, O2 binds strongly on the open V site significantly reducing the BET (Brunauer–Emmett–Teller) surface and CH4 adsorption volume of the V-MOFs. From the ideal adsorbed solution theory calculated, the adsorption selectivity of CH4/N2 is higher before than after binding of O2 (with VIII site). In contrast, the adsorption selectivity of CO2/CH4 is higher after than before O2 binding (with no more VIII sites).
Figure optionsDownload high-quality image (169 K)Download as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Journal of Colloid and Interface Science - Volume 456, 15 October 2015, Pages 197–205