| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 719486 | 892278 | 2009 | 6 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
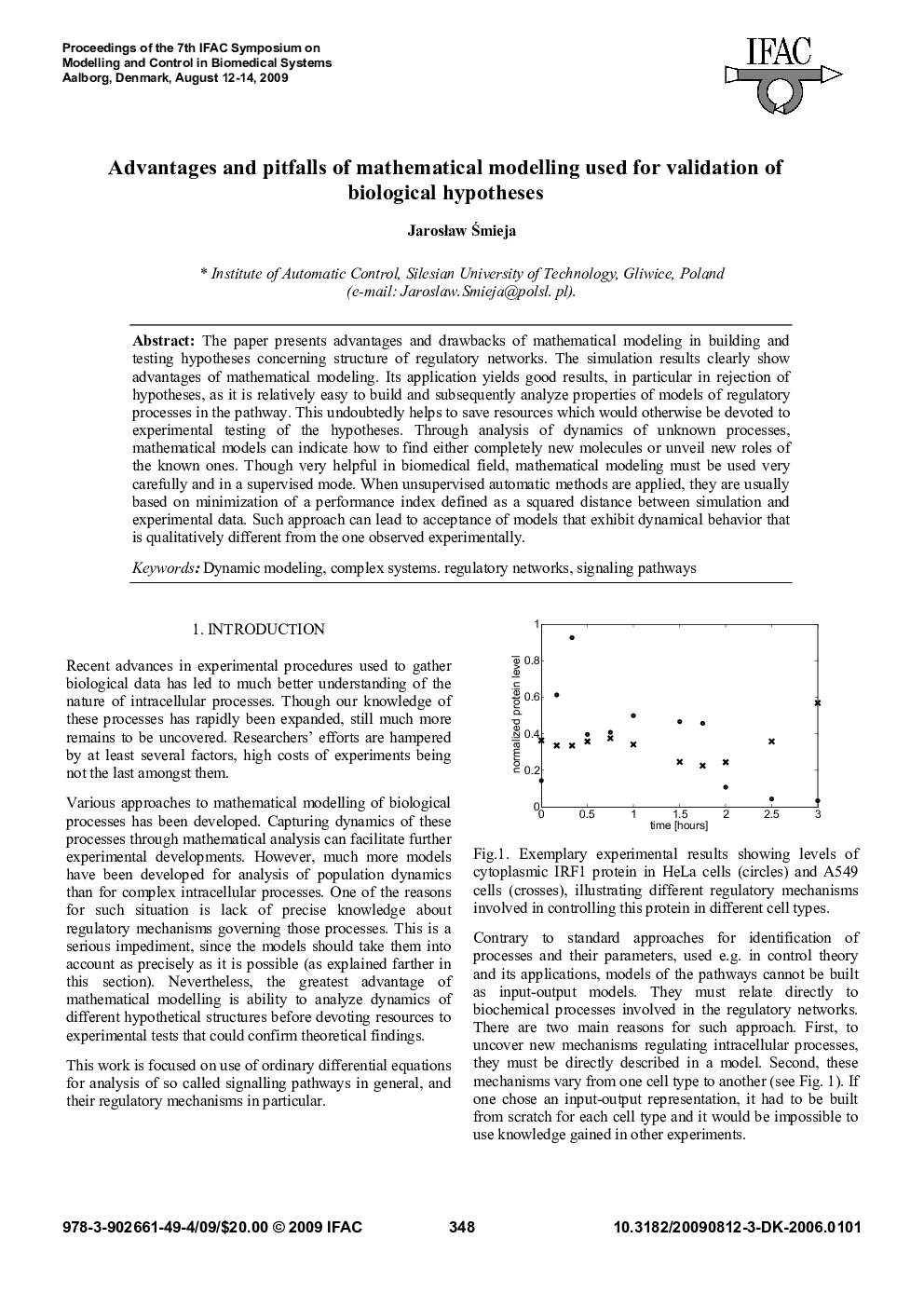
The paper presents advantages and drawbacks of mathematical modeling in building and testing hypotheses concerning structure of regulatory networks. The simulation results clearly show advantages of mathematical modeling. Its application yields good results, in particular in rejection of hypotheses, as it is relatively easy to build and subsequently analyze properties of models of regulatory processes in the pathway. This undoubtedly helps to save resources which would otherwise be devoted to experimental testing of the hypotheses. Through analysis of dynamics of unknown processes, mathematical models can indicate how to find either completely new molecules or unveil new roles of the known ones. Though very helpful in biomedical field, mathematical modeling must be used very carefully and in a supervised mode. When unsupervised automatic methods are applied, they are usually based on minimization of a performance index defined as a squared distance between simulation and experimental data. Such approach can lead to acceptance of models that exhibit dynamical behavior that is qualitatively different from the one observed experimentally.
Journal: IFAC Proceedings Volumes - Volume 42, Issue 12, 2009, Pages 348-353