| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1334210 | 1500151 | 2015 | 8 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
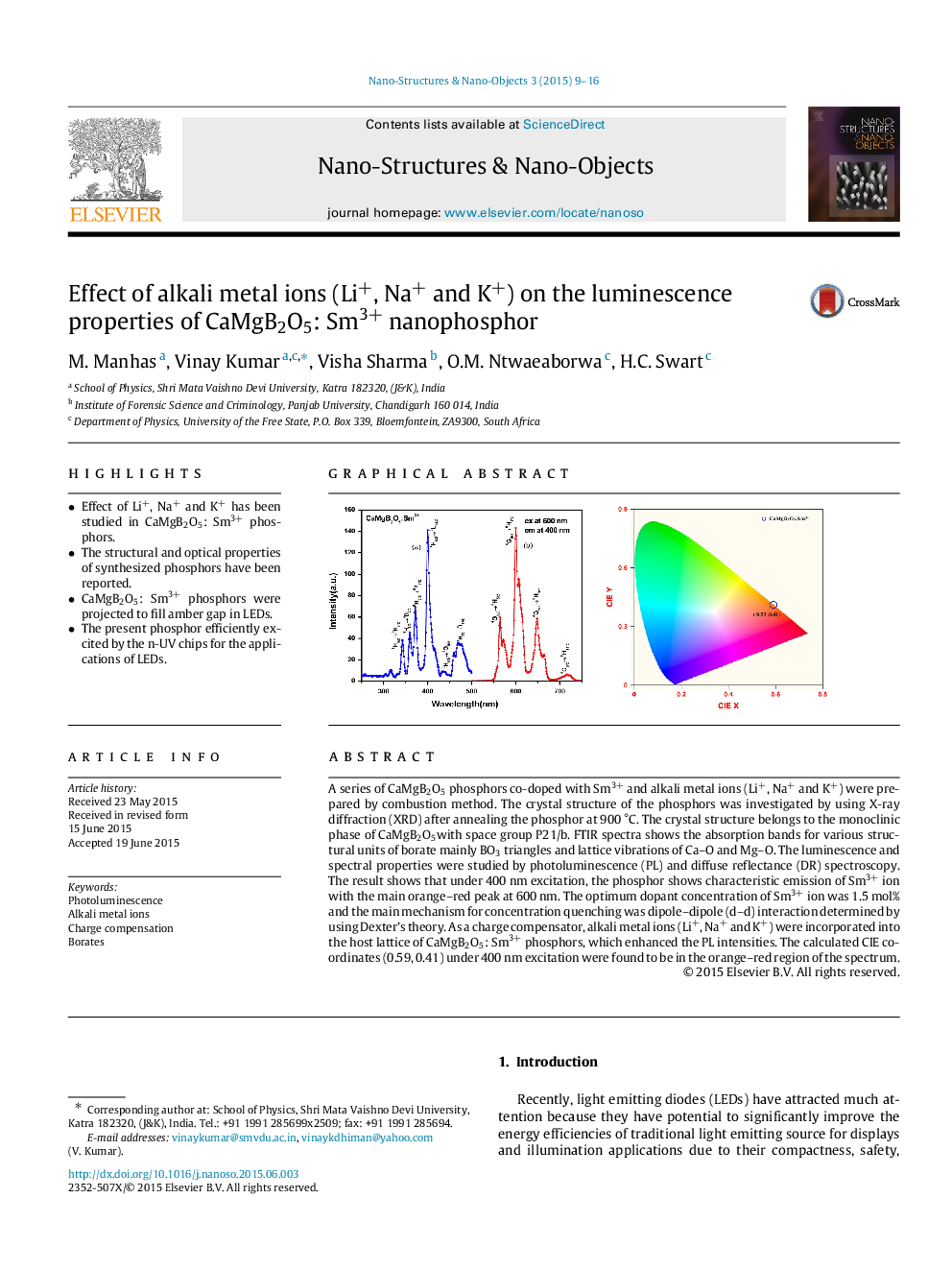
• Effect of Li+, Na+ and K+ has been studied in CaMgB2O5: Sm3+ phosphors.
• The structural and optical properties of synthesized phosphors have been reported.
• CaMgB2O5: Sm3+ phosphors were projected to fill amber gap in LEDs.
• The present phosphor efficiently excited by the n-UV chips for the applications of LEDs.
A series of CaMgB2O5 phosphors co-doped with Sm3+ and alkali metal ions (Li+, Na+ and K+) were prepared by combustion method. The crystal structure of the phosphors was investigated by using X-ray diffraction (XRD) after annealing the phosphor at 900 °C. The crystal structure belongs to the monoclinic phase of CaMgB2O5with space group P21/b. FTIR spectra shows the absorption bands for various structural units of borate mainly BO3 triangles and lattice vibrations of Ca–O and Mg–O. The luminescence and spectral properties were studied by photoluminescence (PL) and diffuse reflectance (DR) spectroscopy. The result shows that under 400 nm excitation, the phosphor shows characteristic emission of Sm3+ ion with the main orange–red peak at 600 nm. The optimum dopant concentration of Sm3+ ion was 1.5 mol% and the main mechanism for concentration quenching was dipole–dipole (d–d) interaction determined by using Dexter’s theory. As a charge compensator, alkali metal ions (Li+, Na+ and K+) were incorporated into the host lattice of CaMgB2O5: Sm3+ phosphors, which enhanced the PL intensities. The calculated CIE coordinates (0.59, 0.41) under 400 nm excitation were found to be in the orange–red region of the spectrum.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Nano-Structures & Nano-Objects - Volume 3, October 2015, Pages 9–16