| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1495391 | 992934 | 2011 | 5 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
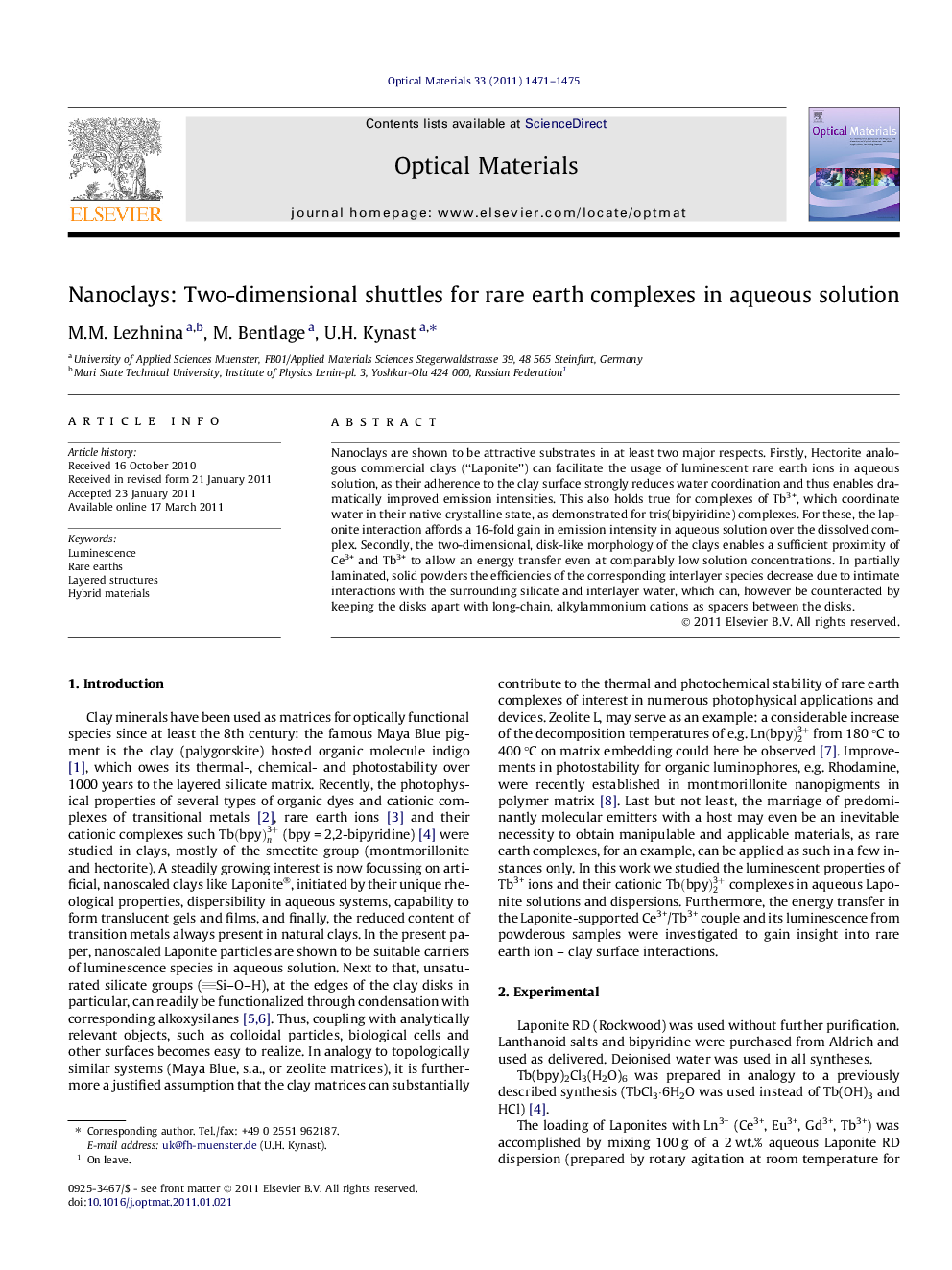
Nanoclays are shown to be attractive substrates in at least two major respects. Firstly, Hectorite analogous commercial clays (“Laponite”) can facilitate the usage of luminescent rare earth ions in aqueous solution, as their adherence to the clay surface strongly reduces water coordination and thus enables dramatically improved emission intensities. This also holds true for complexes of Tb3+, which coordinate water in their native crystalline state, as demonstrated for tris(bipyiridine) complexes. For these, the laponite interaction affords a 16-fold gain in emission intensity in aqueous solution over the dissolved complex. Secondly, the two-dimensional, disk-like morphology of the clays enables a sufficient proximity of Ce3+ and Tb3+ to allow an energy transfer even at comparably low solution concentrations. In partially laminated, solid powders the efficiencies of the corresponding interlayer species decrease due to intimate interactions with the surrounding silicate and interlayer water, which can, however be counteracted by keeping the disks apart with long-chain, alkylammonium cations as spacers between the disks.
The graphic sketches nanoclay-intercalated bipyridine complexes of rare earth ions, for which water-solubility is maintained and multifold luminescence enhancements in comparison to corresponding free complexes have been obtained (not to scale).Figure optionsDownload high-quality image (210 K)Download as PowerPoint slideResearch highlights
► Interaction of rare earth ions and complexes with nanoclays in aqueous solution.
► Efficiency improvement of rare earth luminescence.
► Energy transfer between Ce3+ and Tb3+ even at low rare earth contents.
► Disadvantageous effects emanating from clay lamination to sandwich-like aggregates counteracted by spacer molecules between clay platelets.
Journal: Optical Materials - Volume 33, Issue 10, August 2011, Pages 1471–1475