| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 154478 | 456841 | 2016 | 8 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
• This is the first compromise-based mesoscale model for heterogeneous catalysis.
• This model avoids the shortcomings of both the macroscopic and microscopic models.
• This model accounts for structural heterogeneity with low computational cost.
• Two competing tendencies are identified, corresponding to two competing mechanisms.
• Compromise between the tendencies is established to act as a stability condition.
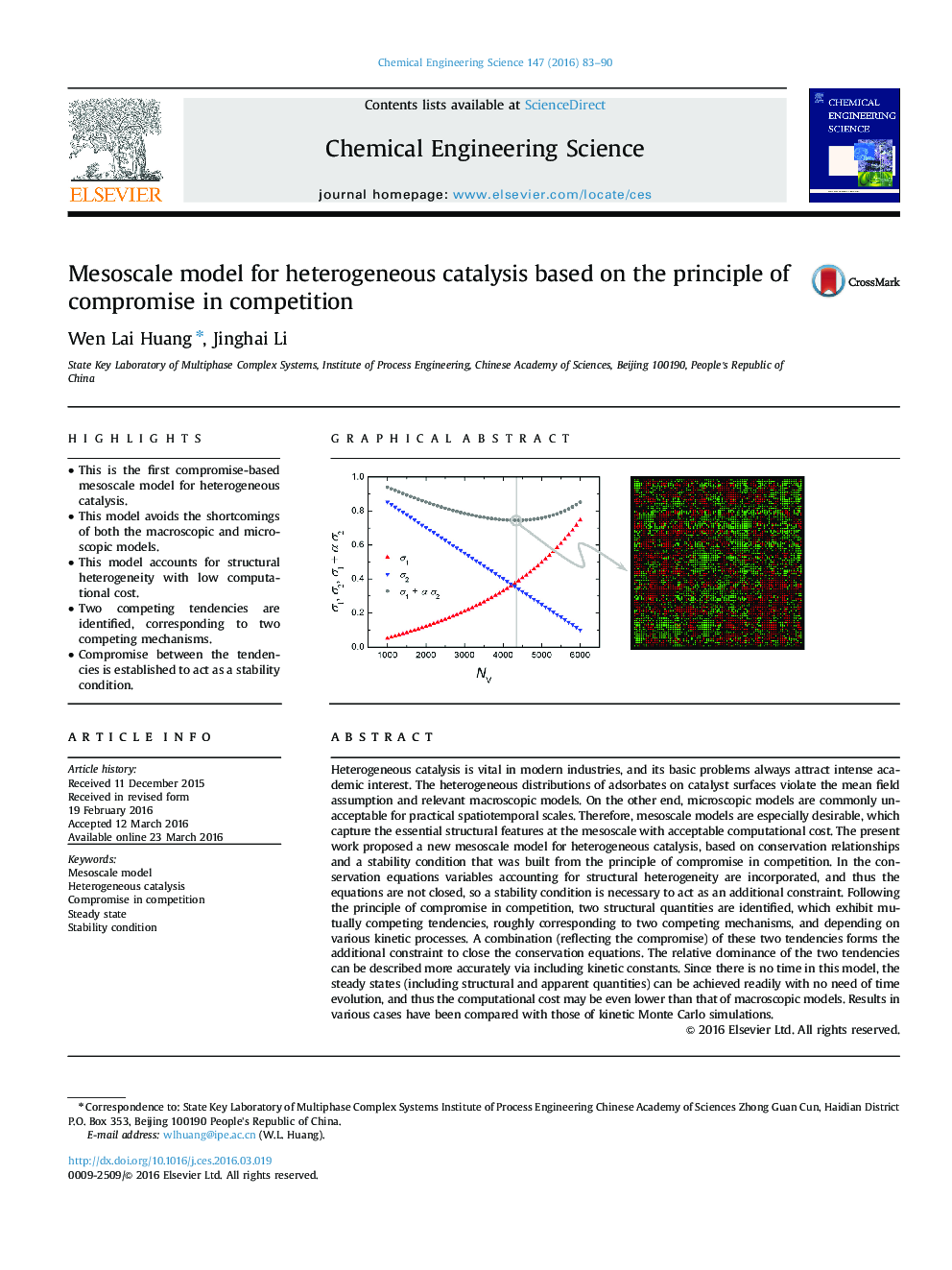
Heterogeneous catalysis is vital in modern industries, and its basic problems always attract intense academic interest. The heterogeneous distributions of adsorbates on catalyst surfaces violate the mean field assumption and relevant macroscopic models. On the other end, microscopic models are commonly unacceptable for practical spatiotemporal scales. Therefore, mesoscale models are especially desirable, which capture the essential structural features at the mesoscale with acceptable computational cost. The present work proposed a new mesoscale model for heterogeneous catalysis, based on conservation relationships and a stability condition that was built from the principle of compromise in competition. In the conservation equations variables accounting for structural heterogeneity are incorporated, and thus the equations are not closed, so a stability condition is necessary to act as an additional constraint. Following the principle of compromise in competition, two structural quantities are identified, which exhibit mutually competing tendencies, roughly corresponding to two competing mechanisms, and depending on various kinetic processes. A combination (reflecting the compromise) of these two tendencies forms the additional constraint to close the conservation equations. The relative dominance of the two tendencies can be described more accurately via including kinetic constants. Since there is no time in this model, the steady states (including structural and apparent quantities) can be achieved readily with no need of time evolution, and thus the computational cost may be even lower than that of macroscopic models. Results in various cases have been compared with those of kinetic Monte Carlo simulations.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload high-quality image (538 K)Download as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Chemical Engineering Science - Volume 147, 22 June 2016, Pages 83–90