| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2035063 | 1072129 | 2016 | 13 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
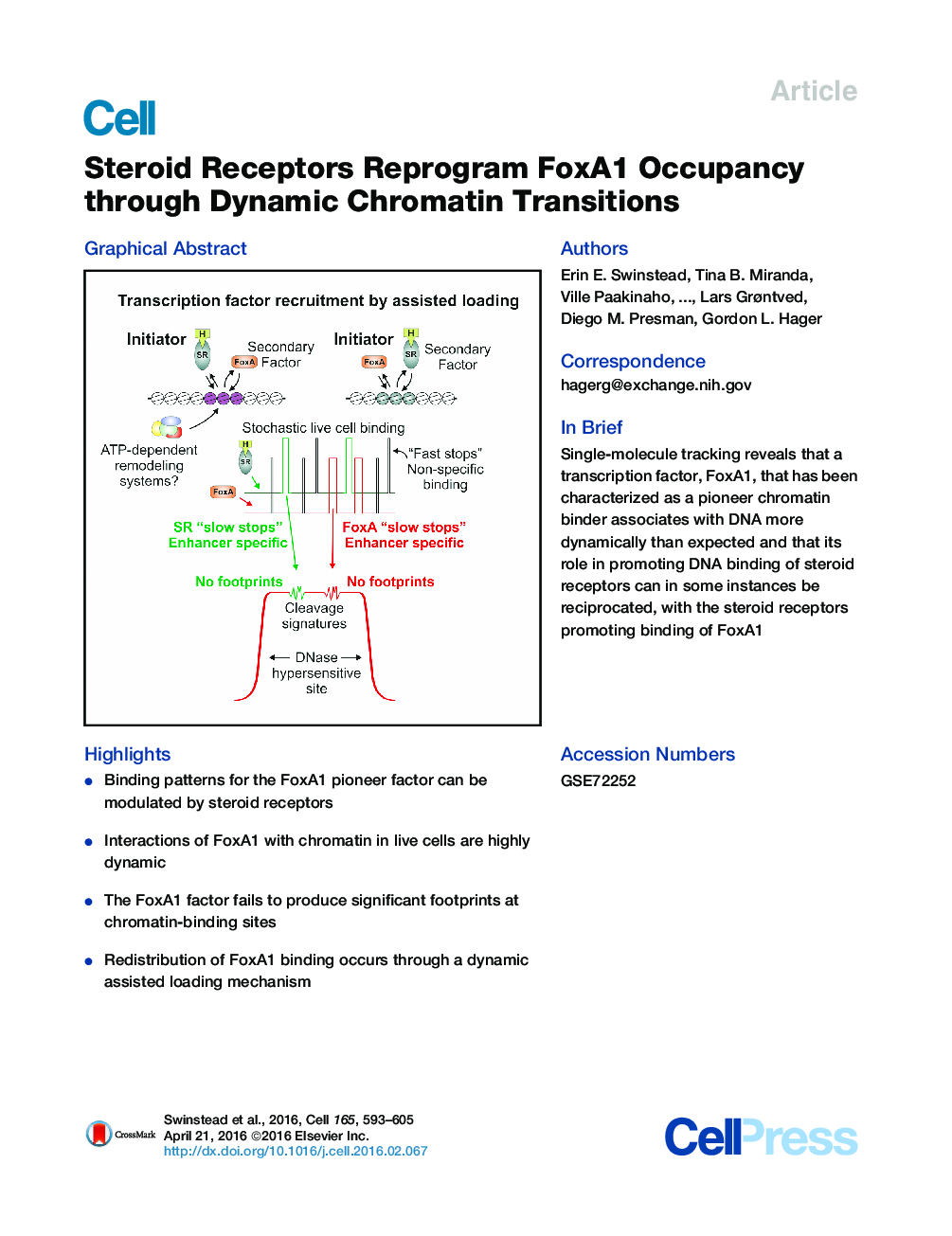
• Binding patterns for the FoxA1 pioneer factor can be modulated by steroid receptors
• Interactions of FoxA1 with chromatin in live cells are highly dynamic
• The FoxA1 factor fails to produce significant footprints at chromatin-binding sites
• Redistribution of FoxA1 binding occurs through a dynamic assisted loading mechanism
SummaryThe estrogen receptor (ER), glucocorticoid receptor (GR), and forkhead box protein 1 (FoxA1) are significant factors in breast cancer progression. FoxA1 has been implicated in establishing ER-binding patterns though its unique ability to serve as a pioneer factor. However, the molecular interplay between ER, GR, and FoxA1 requires further investigation. Here we show that ER and GR both have the ability to alter the genomic distribution of the FoxA1 pioneer factor. Single-molecule tracking experiments in live cells reveal a highly dynamic interaction of FoxA1 with chromatin in vivo. Furthermore, the FoxA1 factor is not associated with detectable footprints at its binding sites throughout the genome. These findings support a model wherein interactions between transcription factors and pioneer factors are highly dynamic. Moreover, at a subset of genomic sites, the role of pioneer can be reversed, with the steroid receptors serving to enhance binding of FoxA1.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload high-quality image (204 K)Download as PowerPoint slide
Journal: - Volume 165, Issue 3, 21 April 2016, Pages 593–605