| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2035064 | 1072129 | 2016 | 14 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
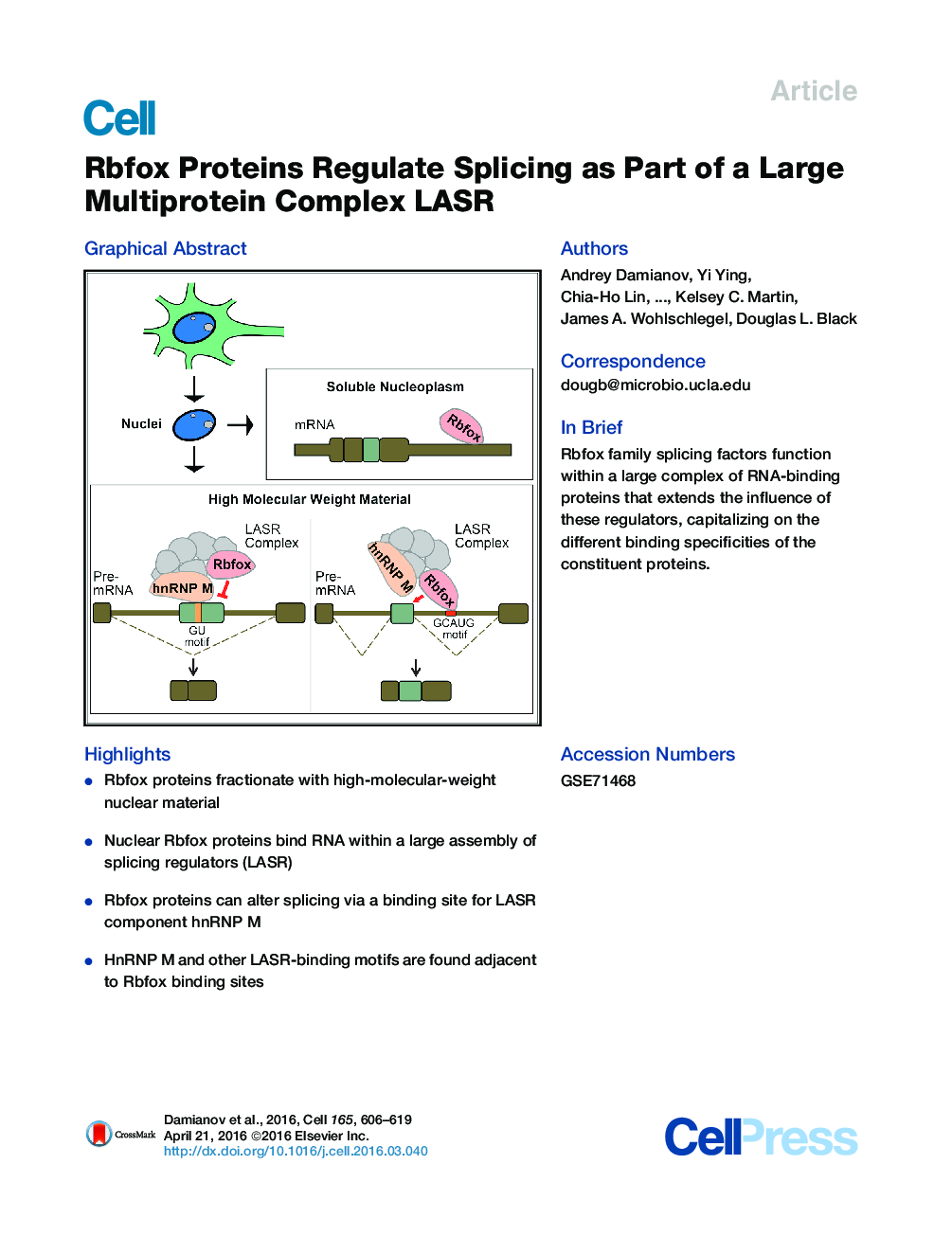
• Rbfox proteins fractionate with high-molecular-weight nuclear material
• Nuclear Rbfox proteins bind RNA within a large assembly of splicing regulators (LASR)
• Rbfox proteins can alter splicing via a binding site for LASR component hnRNP M
• HnRNP M and other LASR-binding motifs are found adjacent to Rbfox binding sites
SummaryRbfox proteins control alternative splicing and posttranscriptional regulation in mammalian brain and are implicated in neurological disease. These proteins recognize the RNA sequence (U)GCAUG, but their structures and diverse roles imply a variety of protein-protein interactions. We find that nuclear Rbfox proteins are bound within a large assembly of splicing regulators (LASR), a multimeric complex containing the proteins hnRNP M, hnRNP H, hnRNP C, Matrin3, NF110/NFAR-2, NF45, and DDX5, all approximately equimolar to Rbfox. We show that splicing repression mediated by hnRNP M is stimulated by Rbfox. Virtually all the intron-bound Rbfox is associated with LASR, and hnRNP M motifs are enriched adjacent to Rbfox crosslinking sites in vivo. These findings demonstrate that Rbfox proteins bind RNA with a defined set of cofactors and affect a broader set of exons than previously recognized. The function of this multimeric LASR complex has implications for deciphering the regulatory codes controlling splicing networks.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload high-quality image (156 K)Download as PowerPoint slide
Journal: - Volume 165, Issue 3, 21 April 2016, Pages 606–619