| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2035144 | 1072142 | 2015 | 11 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
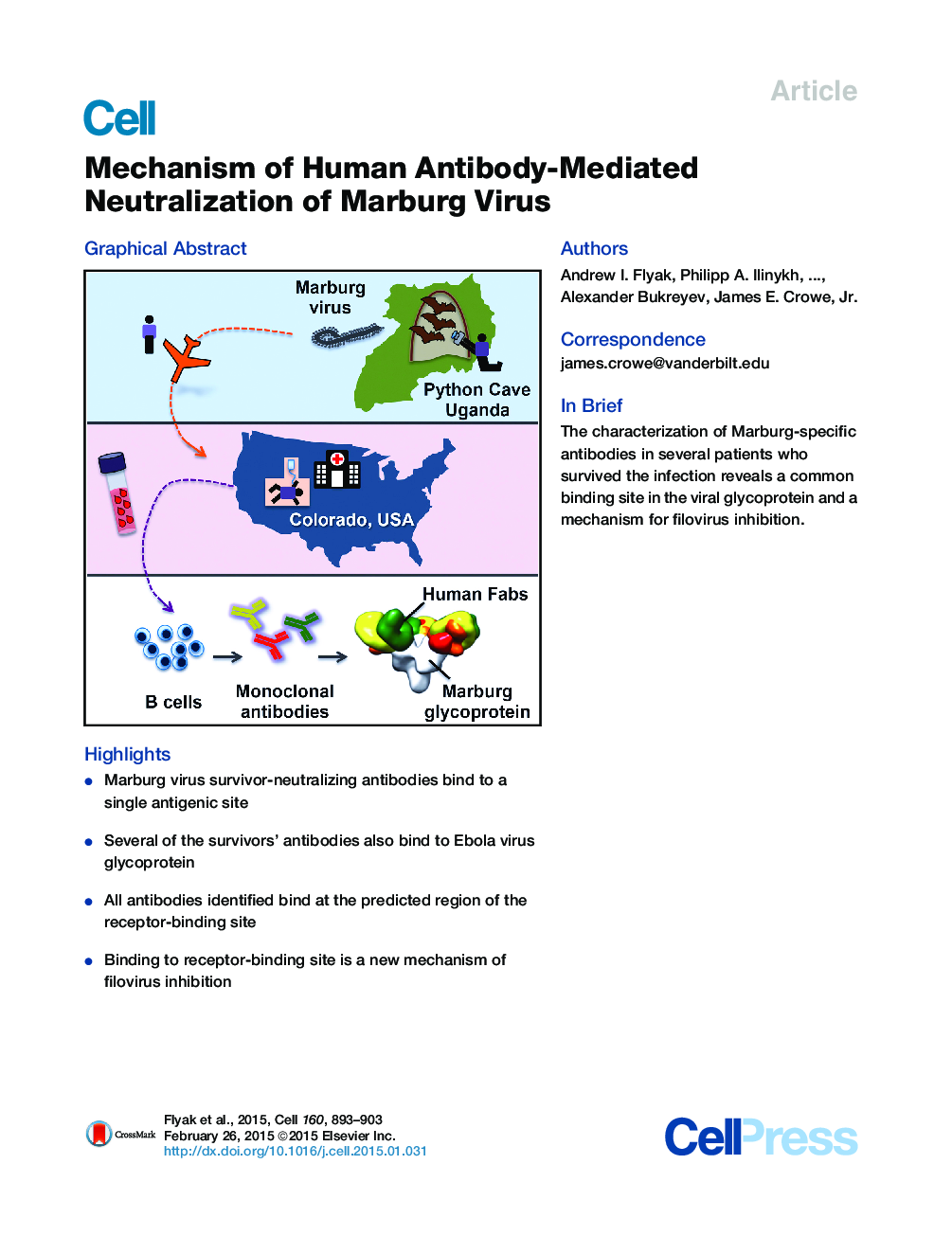
• Marburg virus survivor-neutralizing antibodies bind to a single antigenic site
• Several of the survivors’ antibodies also bind to Ebola virus glycoprotein
• All antibodies identified bind at the predicted region of the receptor-binding site
• Binding to receptor-binding site is a new mechanism of filovirus inhibition
SummaryThe mechanisms by which neutralizing antibodies inhibit Marburg virus (MARV) are not known. We isolated a panel of neutralizing antibodies from a human MARV survivor that bind to MARV glycoprotein (GP) and compete for binding to a single major antigenic site. Remarkably, several of the antibodies also bind to Ebola virus (EBOV) GP. Single-particle EM structures of antibody-GP complexes reveal that all of the neutralizing antibodies bind to MARV GP at or near the predicted region of the receptor-binding site. The presence of the glycan cap or mucin-like domain blocks binding of neutralizing antibodies to EBOV GP, but not to MARV GP. The data suggest that MARV-neutralizing antibodies inhibit virus by binding to infectious virions at the exposed MARV receptor-binding site, revealing a mechanism of filovirus inhibition.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload high-quality image (214 K)Download as PowerPoint slide
Journal: - Volume 160, Issue 5, 26 February 2015, Pages 893–903