| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2036458 | 1072266 | 2011 | 12 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
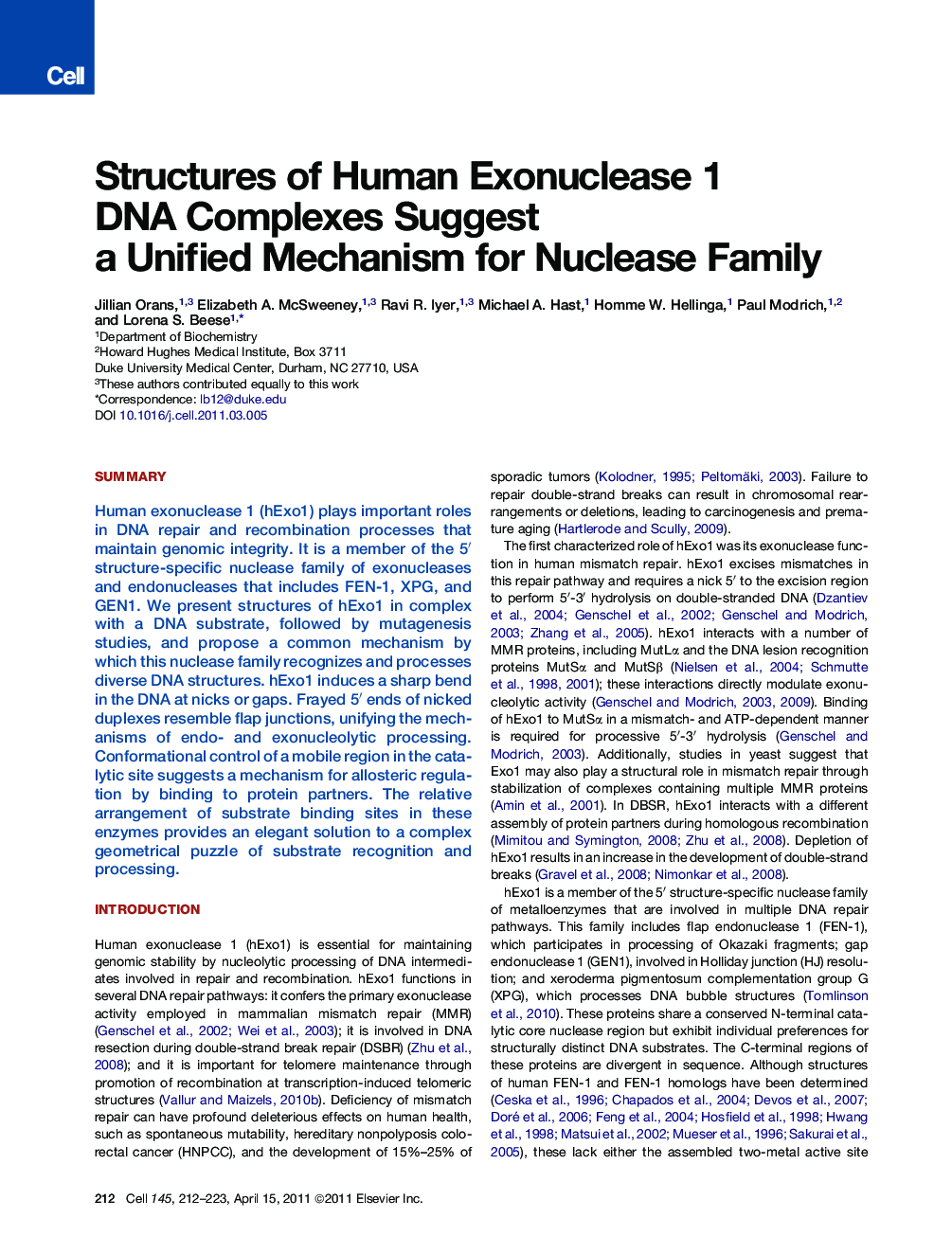
SummaryHuman exonuclease 1 (hExo1) plays important roles in DNA repair and recombination processes that maintain genomic integrity. It is a member of the 5′ structure-specific nuclease family of exonucleases and endonucleases that includes FEN-1, XPG, and GEN1. We present structures of hExo1 in complex with a DNA substrate, followed by mutagenesis studies, and propose a common mechanism by which this nuclease family recognizes and processes diverse DNA structures. hExo1 induces a sharp bend in the DNA at nicks or gaps. Frayed 5′ ends of nicked duplexes resemble flap junctions, unifying the mechanisms of endo- and exonucleolytic processing. Conformational control of a mobile region in the catalytic site suggests a mechanism for allosteric regulation by binding to protein partners. The relative arrangement of substrate binding sites in these enzymes provides an elegant solution to a complex geometrical puzzle of substrate recognition and processing.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload high-quality image (494 K)Download as PowerPoint slideHighlights
► Structures of human exonuclease 1 in complex with DNA
► hExo1 bends DNA at gaps or nicks, positioning cleavage site
► 5′ DNA end fraying unifies exo- and endonucleolytic activities
► Relative arrangement of DNA substructure binding sites determines specificity
Journal: - Volume 145, Issue 2, 15 April 2011, Pages 212–223