| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2039173 | 1073032 | 2015 | 12 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
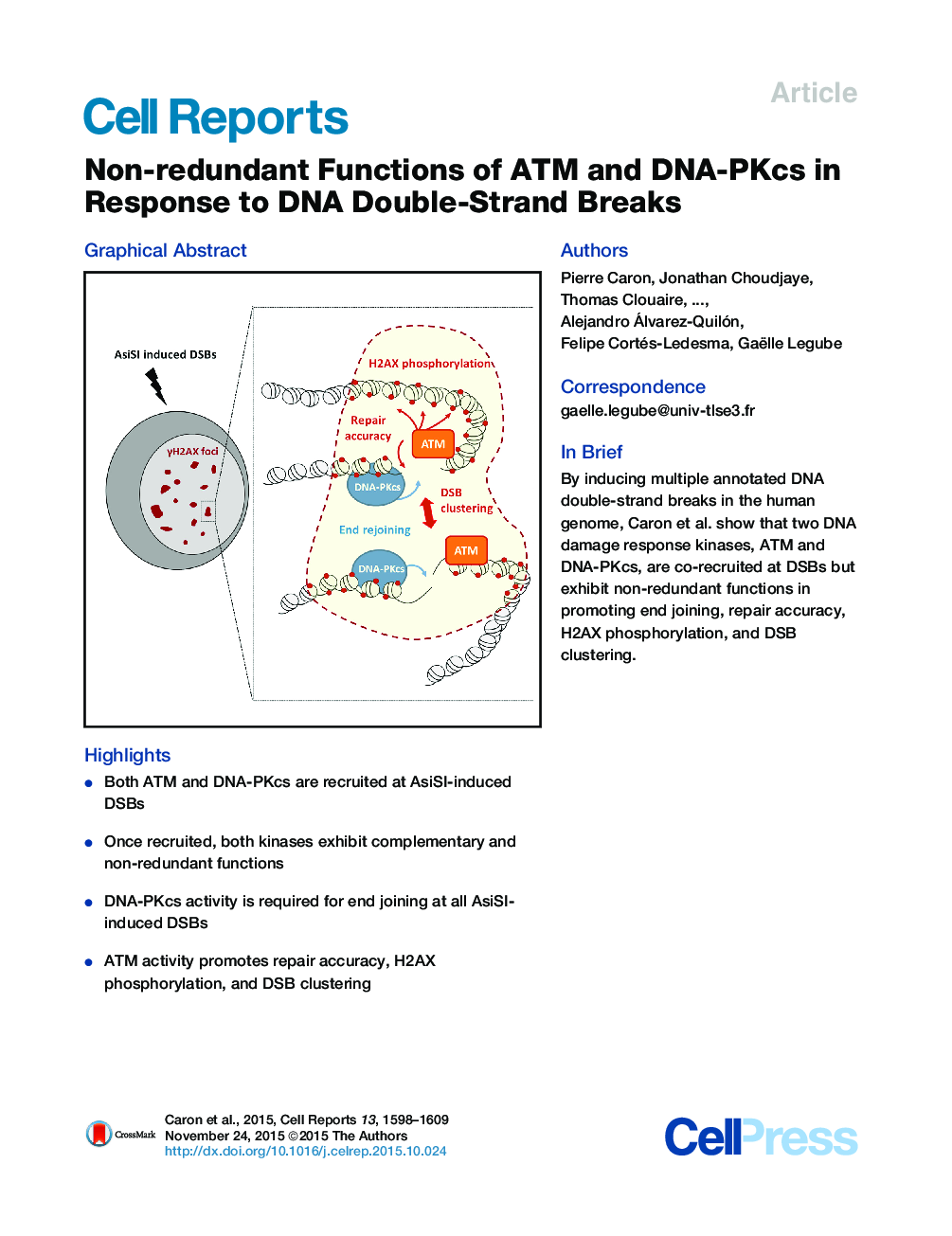
• Both ATM and DNA-PKcs are recruited at AsiSI-induced DSBs
• Once recruited, both kinases exhibit complementary and non-redundant functions
• DNA-PKcs activity is required for end joining at all AsiSI-induced DSBs
• ATM activity promotes repair accuracy, H2AX phosphorylation, and DSB clustering
SummaryDNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) elicit the so-called DNA damage response (DDR), largely relying on ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM) and DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PKcs), two members of the PI3K-like kinase family, whose respective functions during the sequential steps of the DDR remains controversial. Using the DIvA system (DSB inducible via AsiSI) combined with high-resolution mapping and advanced microscopy, we uncovered that both ATM and DNA-PKcs spread in cis on a confined region surrounding DSBs, independently of the pathway used for repair. However, once recruited, these kinases exhibit non-overlapping functions on end joining and γH2AX domain establishment. More specifically, we found that ATM is required to ensure the association of multiple DSBs within “repair foci.” Our results suggest that ATM acts not only on chromatin marks but also on higher-order chromatin organization to ensure repair accuracy and survival.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: - Volume 13, Issue 8, 24 November 2015, Pages 1598–1609