| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2040430 | 1073110 | 2016 | 10 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
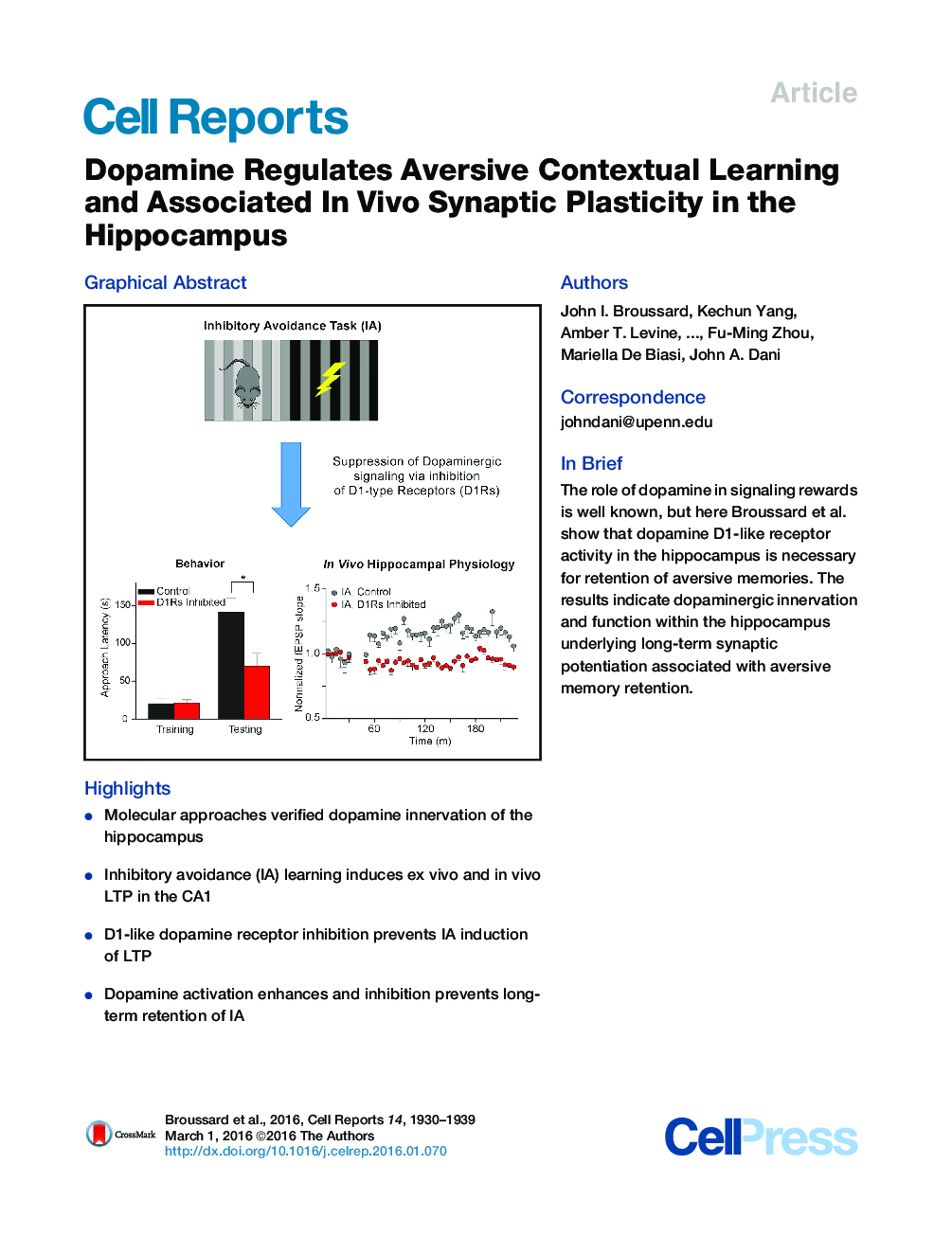
• Molecular approaches verified dopamine innervation of the hippocampus
• Inhibitory avoidance (IA) learning induces ex vivo and in vivo LTP in the CA1
• D1-like dopamine receptor inhibition prevents IA induction of LTP
• Dopamine activation enhances and inhibition prevents long-term retention of IA
SummaryDopamine release during reward-driven behaviors influences synaptic plasticity. However, dopamine innervation and release in the hippocampus and its role during aversive behaviors are controversial. Here, we show that in vivo hippocampal synaptic plasticity in the CA3-CA1 circuit underlies contextual learning during inhibitory avoidance (IA) training. Immunohistochemistry and molecular techniques verified sparse dopaminergic innervation of the hippocampus from the midbrain. The long-term synaptic potentiation (LTP) underlying the learning of IA was assessed with a D1-like dopamine receptor agonist or antagonist in ex vivo hippocampal slices and in vivo in freely moving mice. Inhibition of D1-like dopamine receptors impaired memory of the IA task and prevented the training-induced enhancement of both ex vivo and in vivo LTP induction. The results indicate that dopamine-receptor signaling during an aversive contextual task regulates aversive memory retention and regulates associated synaptic mechanisms in the hippocampus that likely underlie learning.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: - Volume 14, Issue 8, 1 March 2016, Pages 1930–1939