| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2106800 | 1083629 | 2015 | 15 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
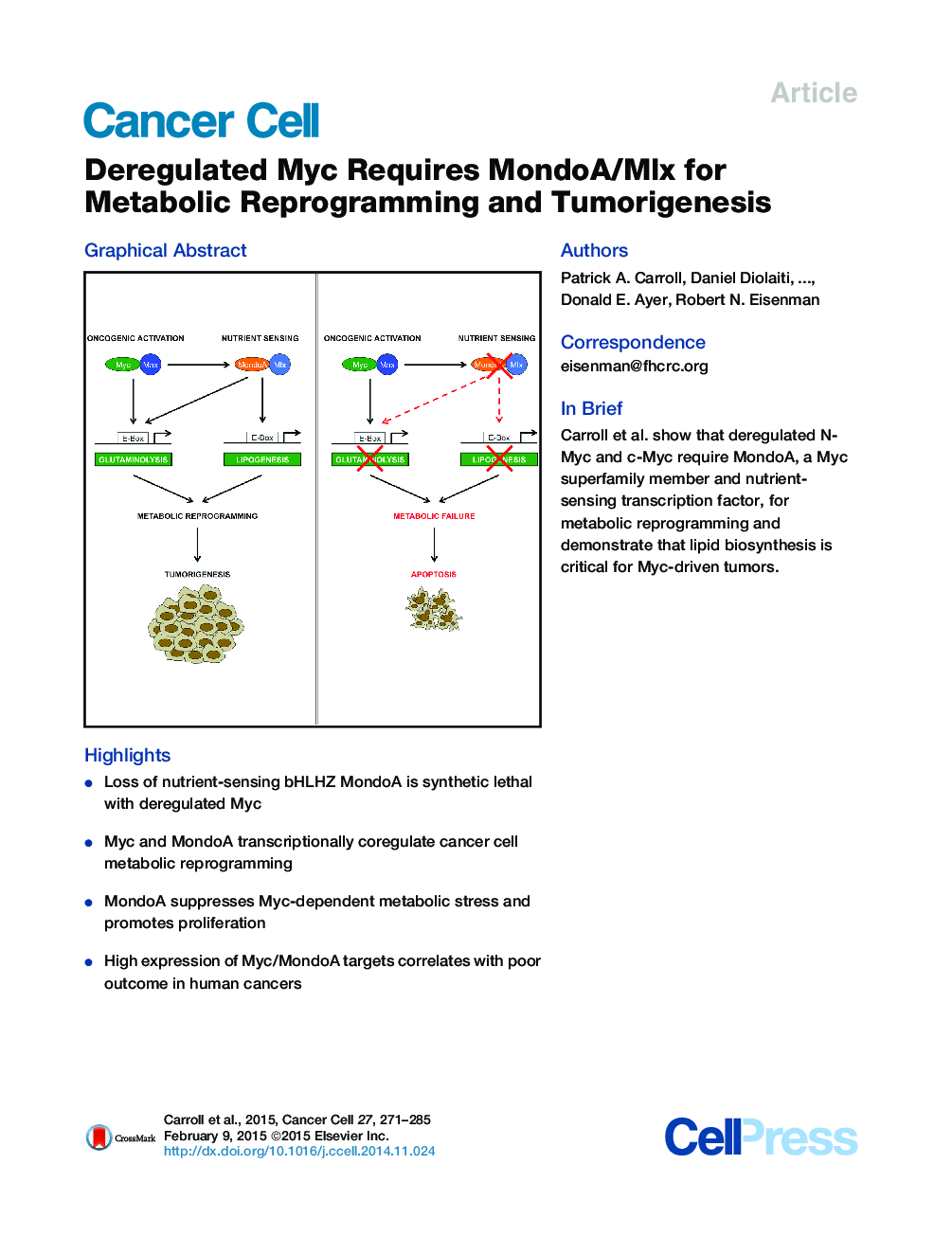
• Loss of nutrient-sensing bHLHZ MondoA is synthetic lethal with deregulated Myc
• Myc and MondoA transcriptionally coregulate cancer cell metabolic reprogramming
• MondoA suppresses Myc-dependent metabolic stress and promotes proliferation
• High expression of Myc/MondoA targets correlates with poor outcome in human cancers
SummaryDeregulated Myc transcriptionally reprograms cell metabolism to promote neoplasia. Here we show that oncogenic Myc requires the Myc superfamily member MondoA, a nutrient-sensing transcription factor, for tumorigenesis. Knockdown of MondoA, or its dimerization partner Mlx, blocks Myc-induced reprogramming of multiple metabolic pathways, resulting in apoptosis. Identification and knockdown of genes coregulated by Myc and MondoA have allowed us to define metabolic functions required by deregulated Myc and demonstrate a critical role for lipid biosynthesis in survival of Myc-driven cancer. Furthermore, overexpression of a subset of Myc and MondoA coregulated genes correlates with poor outcome of patients with diverse cancers. Coregulation of cancer metabolism by Myc and MondoA provides the potential for therapeutics aimed at inhibiting MondoA and its target genes.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload high-quality image (301 K)Download as PowerPoint slide
Journal: - Volume 27, Issue 2, 9 February 2015, Pages 271–285