| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3838864 | 1247749 | 2009 | 4 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
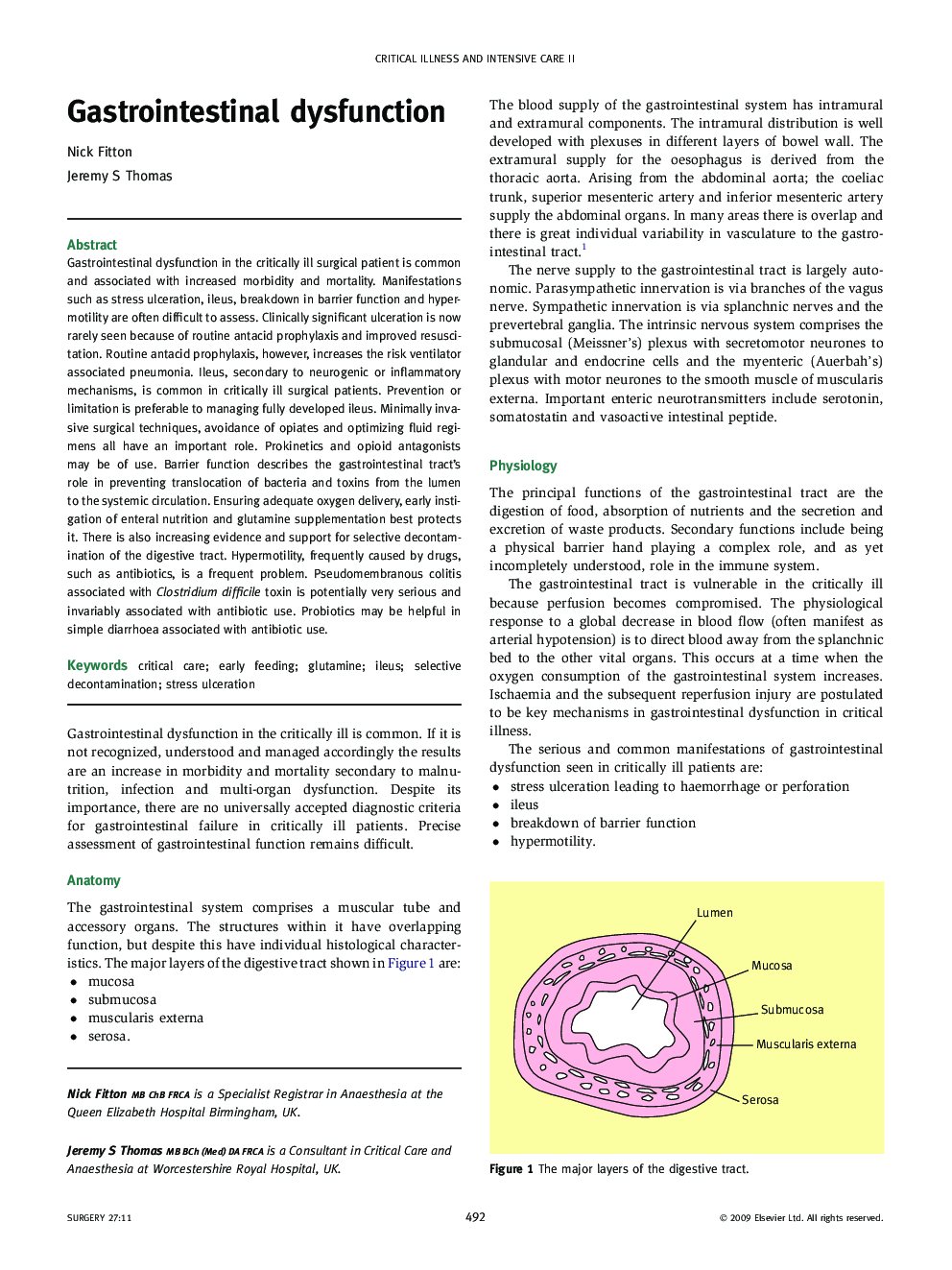
Gastrointestinal dysfunction in the critically ill surgical patient is common and associated with increased morbidity and mortality. Manifestations such as stress ulceration, ileus, breakdown in barrier function and hypermotility are often difficult to assess. Clinically significant ulceration is now rarely seen because of routine antacid prophylaxis and improved resuscitation. Routine antacid prophylaxis, however, increases the risk ventilator associated pneumonia. Ileus, secondary to neurogenic or inflammatory mechanisms, is common in critically ill surgical patients. Prevention or limitation is preferable to managing fully developed ileus. Minimally invasive surgical techniques, avoidance of opiates and optimizing fluid regimens all have an important role. Prokinetics and opioid antagonists may be of use. Barrier function describes the gastrointestinal tract's role in preventing translocation of bacteria and toxins from the lumen to the systemic circulation. Ensuring adequate oxygen delivery, early instigation of enteral nutrition and glutamine supplementation best protects it. There is also increasing evidence and support for selective decontamination of the digestive tract. Hypermotility, frequently caused by drugs, such as antibiotics, is a frequent problem. Pseudomembranous colitis associated with Clostridium difficile toxin is potentially very serious and invariably associated with antibiotic use. Probiotics may be helpful in simple diarrhoea associated with antibiotic use.
Journal: Surgery (Oxford) - Volume 27, Issue 11, November 2009, Pages 492–495