| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3884925 | 1249495 | 2007 | 4 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
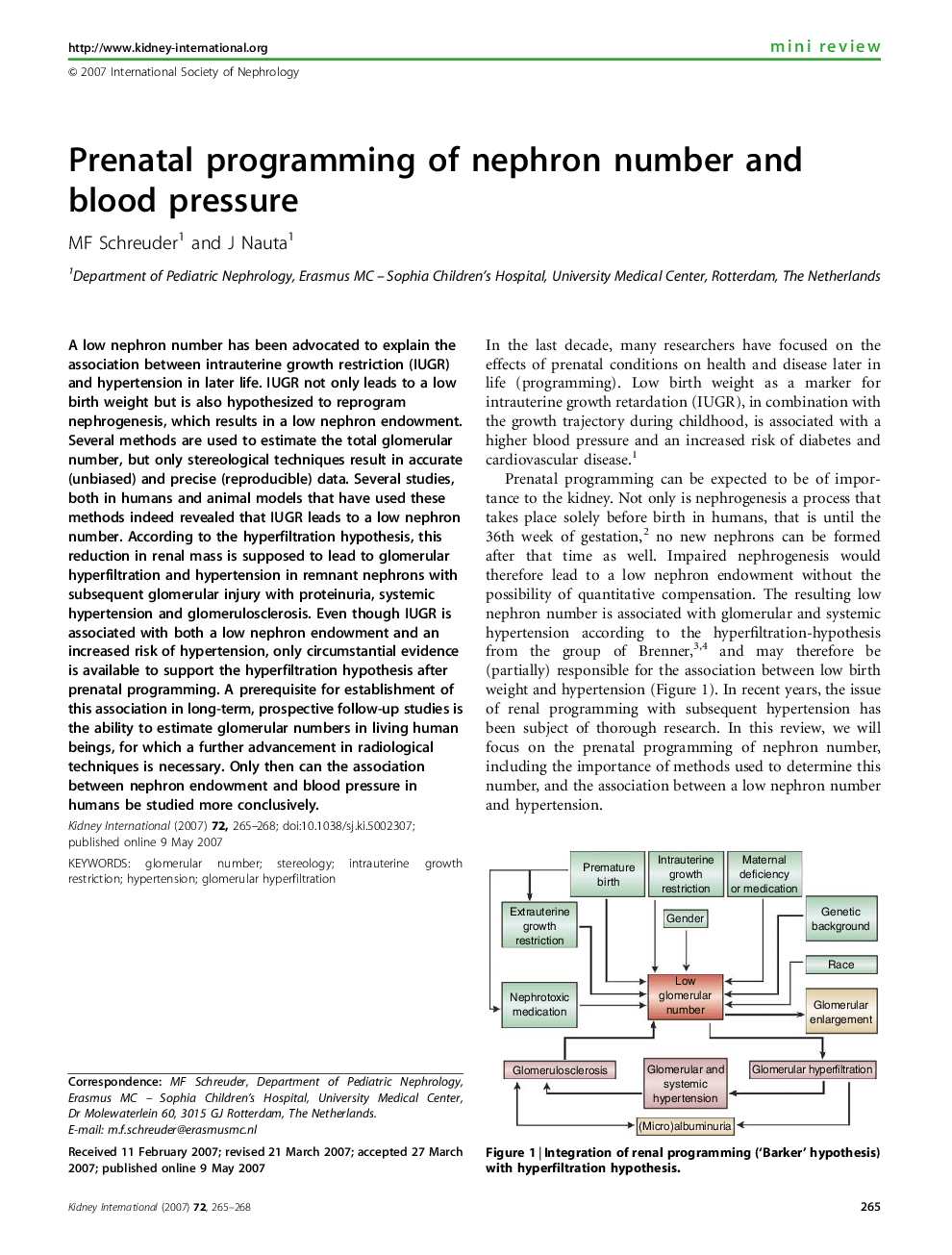
A low nephron number has been advocated to explain the association between intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) and hypertension in later life. IUGR not only leads to a low birth weight but is also hypothesized to reprogram nephrogenesis, which results in a low nephron endowment. Several methods are used to estimate the total glomerular number, but only stereological techniques result in accurate (unbiased) and precise (reproducible) data. Several studies, both in humans and animal models that have used these methods indeed revealed that IUGR leads to a low nephron number. According to the hyperfiltration hypothesis, this reduction in renal mass is supposed to lead to glomerular hyperfiltration and hypertension in remnant nephrons with subsequent glomerular injury with proteinuria, systemic hypertension and glomerulosclerosis. Even though IUGR is associated with both a low nephron endowment and an increased risk of hypertension, only circumstantial evidence is available to support the hyperfiltration hypothesis after prenatal programming. A prerequisite for establishment of this association in long-term, prospective follow-up studies is the ability to estimate glomerular numbers in living human beings, for which a further advancement in radiological techniques is necessary. Only then can the association between nephron endowment and blood pressure in humans be studied more conclusively.
Journal: Kidney International - Volume 72, Issue 3, 1 August 2007, Pages 265–268