| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4312084 | 1612921 | 2016 | 12 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
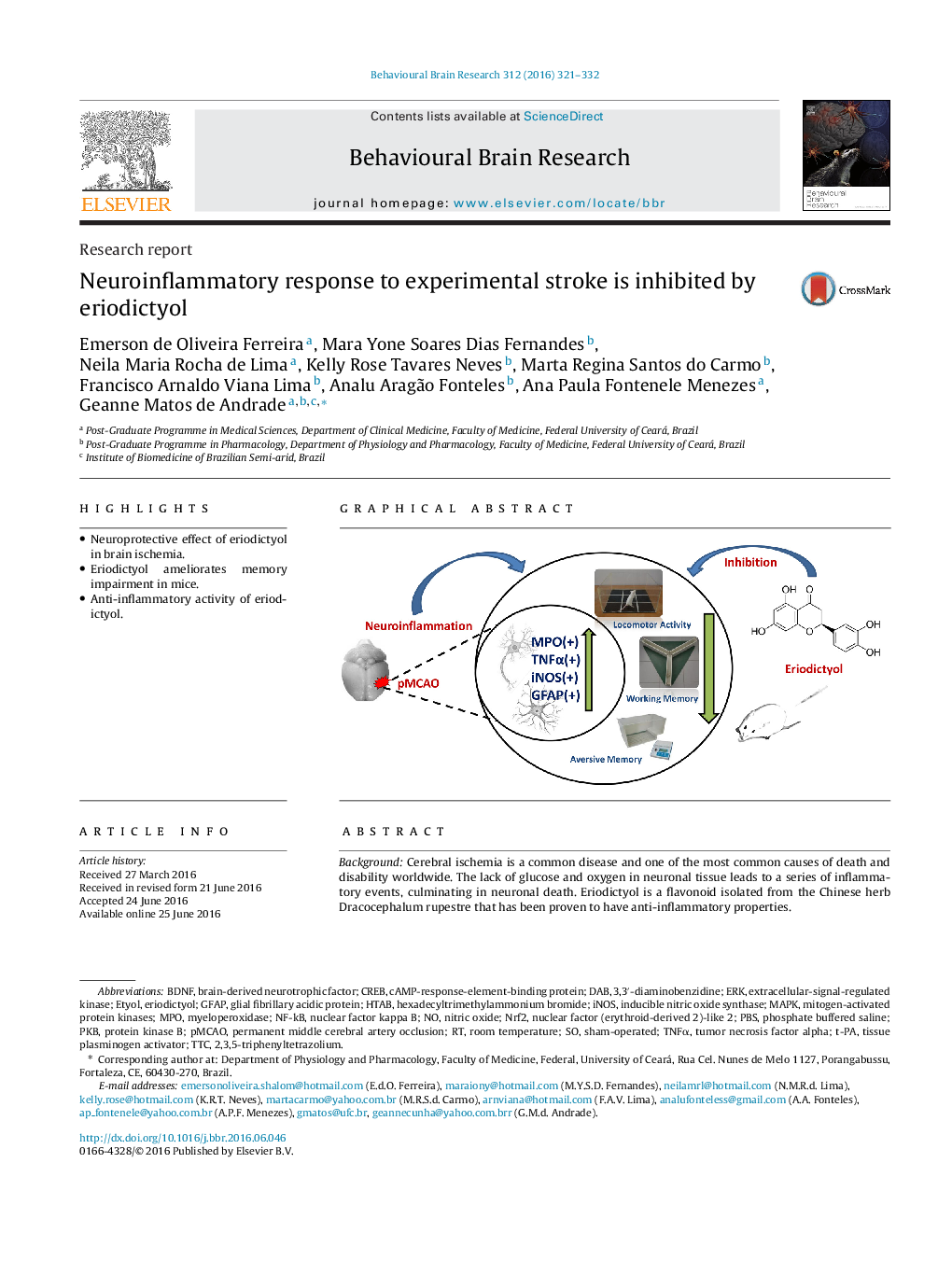
• Neuroprotective effect of eriodictyol in brain ischemia.
• Eriodictyol ameliorates memory impairment in mice.
• Anti-inflammatory activity of eriodictyol.
BackgroundCerebral ischemia is a common disease and one of the most common causes of death and disability worldwide. The lack of glucose and oxygen in neuronal tissue leads to a series of inflammatory events, culminating in neuronal death. Eriodictyol is a flavonoid isolated from the Chinese herb Dracocephalum rupestre that has been proven to have anti-inflammatory properties.Hypothesis/PurposeThus, the present study was designed to explore whether eriodictyol has neuroprotective effects against the neuronal damage, motor and memory deficits induced by permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion (pMCAO) in mice.Study DesignAnimals were orally treated with eriodictyol (1, 2 and 4 mg/kg) or vehicle (saline) 30 min before pMCAO, 2 h after, and then once daily for the following five days.MethodsThe parameters studied were neuronal viability, brain infarcted area; sensorimotor deficits; exploratory activity; working and aversive memory; myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity; TNFα, iNOS and GFAP immunoreactivity.ResultsThe treatment with eriodictyol prevented neuronal death, reduced infarct area and improved neurological and memory deficits induced by brain ischemia. The increase of MPO activity and TNF-α, iNOS and GFAP expression were also reduced by eriodictyol treatment.ConclusionThese findings demonstrate that eriodictyol exhibit promising neuroprotection effects against the permanent focal ischemia cerebral injury in the mice experimental model and the underlying mechanisms might be mediated through inhibition of neuroinflammation.
Figure optionsDownload high-quality image (194 K)Download as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Behavioural Brain Research - Volume 312, 1 October 2016, Pages 321–332