| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5660304 | 1590324 | 2017 | 13 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
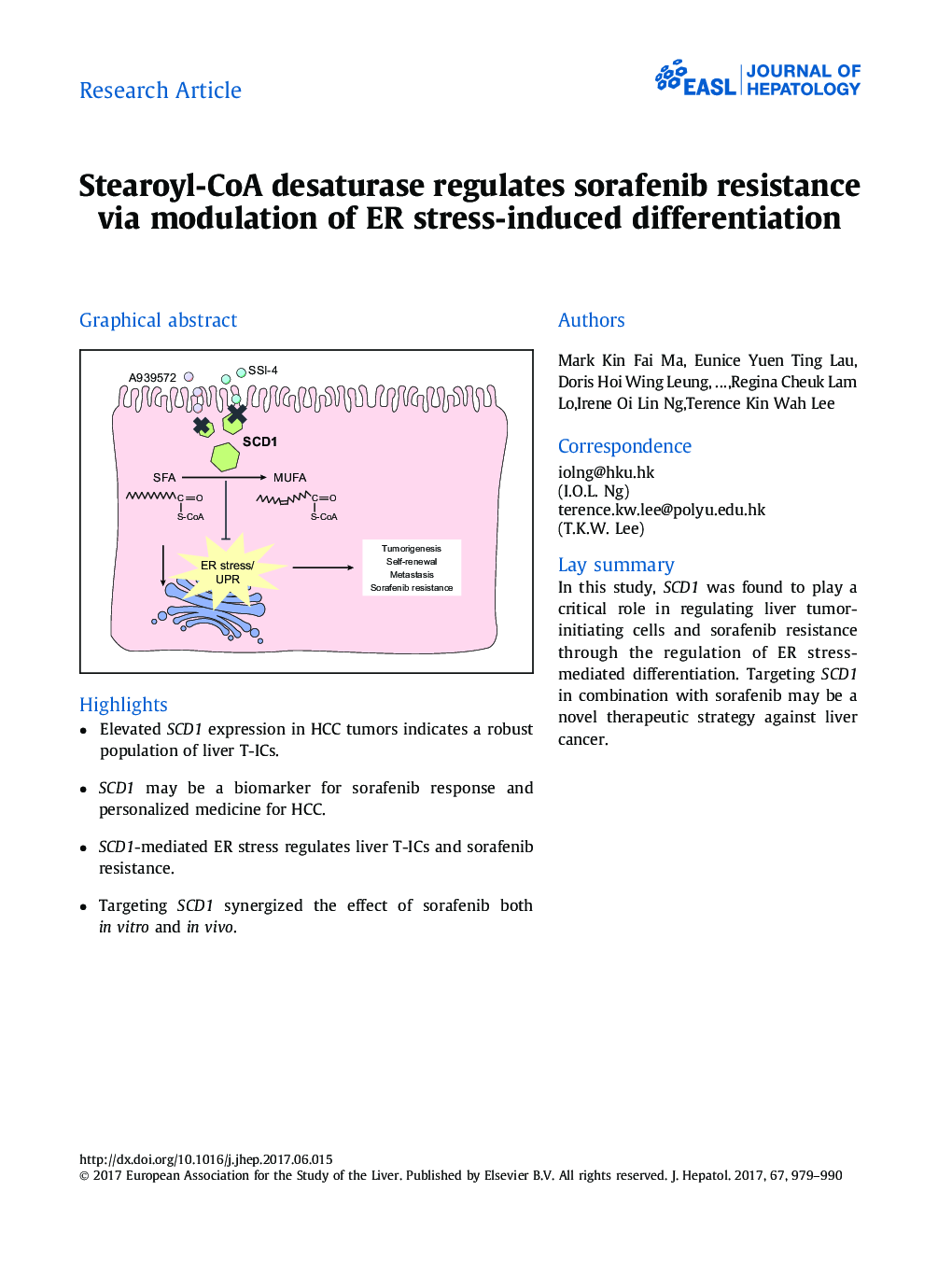
- Elevated SCD1 expression in HCC tumors indicates a robust population of liver T-ICs.
- SCD1 may be a biomarker for sorafenib response and personalized medicine for HCC.
- SCD1-mediated ER stress regulates liver T-ICs and sorafenib resistance.
- Targeting SCD1 synergized the effect of sorafenib both in vitro and in vivo.
Background & AimsWe investigated the functional role and clinical significance of stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 (SCD1) mediated endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress in regulating liver tumor-initiating cells (T-ICs) and sorafenib resistance, with the aim of developing a novel therapeutic strategy against hepatocellular carcinomas (HCCs).MethodsWe evaluated the clinic-pathological relevance of SCD1 and its correlation with sorafenib resistance in large cohorts of HCC clinical samples by qPCR and immunohistochemical analyses. Lentiviral-based overexpression and knockdown approaches were performed to characterize the functional roles of SCD1 in regulating liver T-ICs and sorafenib resistance. Molecular pathways mediating the phenotypic alterations were identified through RNA sequencing analysis and functional rescue experiments. The combinatorial effect of SCD1 inhibition and sorafenib was tested using a patient-derived tumor xenograft (PDTX) model.ResultsSCD1 overexpression was found in HCC, which was associated with shorter disease-free survival (p = 0.008, log rank test). SCD1 was found to regulate the populations of liver T-ICs; while its suppression by a SCD1 inhibitor suppressed liver T-ICs and sorafenib resistance. Interestingly, SCD1 was markedly upregulated in our established sorafenib-resistant PDTX model, and its overexpression predicts the clinical response of HCC patients to sorafenib treatment. Suppression of SCD1 forces liver T-ICs to differentiate via ER stress-induced unfolded protein response, resulting in an enhanced sensitivity to sorafenib. The PDTX#1 model, combined with sorafenib treatment and a novel SCD1 inhibitor (SSI-4), showed a maximal growth suppressive effect.ConclusionsSCD1-mediated ER stress regulates liver T-ICs and sorafenib sensitivity. Targeting SCD1 alone or in combination with sorafenib might be a novel personalized medicine against HCC.Lay summary: In this study, SCD1 was found to play a critical role in regulating liver tumor-initiating cells and sorafenib resistance through the regulation of ER stress-mediated differentiation. Targeting SCD1 in combination with sorafenib may be a novel therapeutic strategy against liver cancer.
124
Journal: Journal of Hepatology - Volume 67, Issue 5, November 2017, Pages 979-990