| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5737322 | 1614591 | 2017 | 10 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
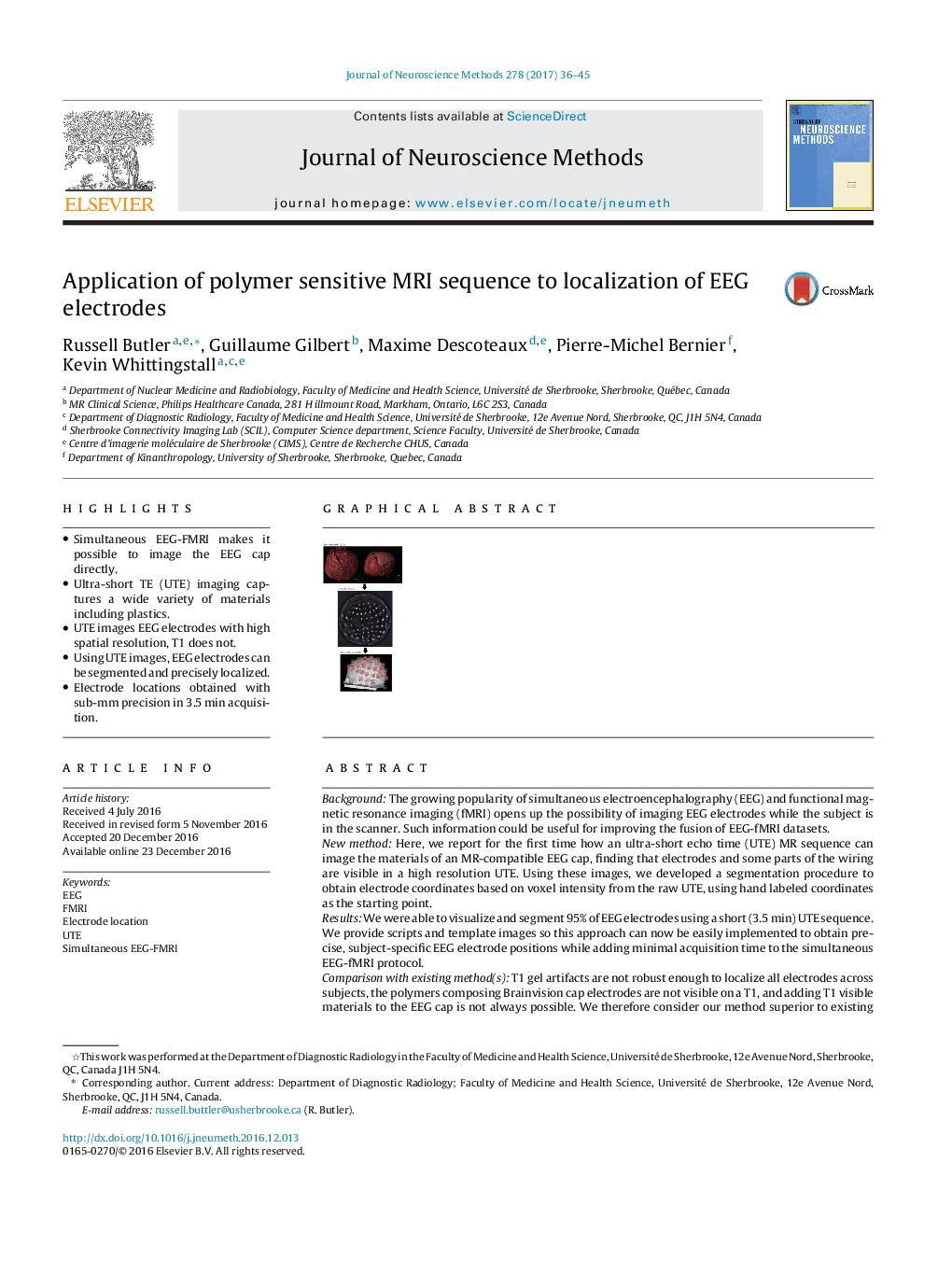
- Simultaneous EEG-FMRI makes it possible to image the EEG cap directly.
- Ultra-short TE (UTE) imaging captures a wide variety of materials including plastics.
- UTE images EEG electrodes with high spatial resolution, T1 does not.
- Using UTE images, EEG electrodes can be segmented and precisely localized.
- Electrode locations obtained with sub-mm precision in 3.5Â min acquisition.
BackgroundThe growing popularity of simultaneous electroencephalography (EEG) and functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) opens up the possibility of imaging EEG electrodes while the subject is in the scanner. Such information could be useful for improving the fusion of EEG-fMRI datasets.New methodHere, we report for the first time how an ultra-short echo time (UTE) MR sequence can image the materials of an MR-compatible EEG cap, finding that electrodes and some parts of the wiring are visible in a high resolution UTE. Using these images, we developed a segmentation procedure to obtain electrode coordinates based on voxel intensity from the raw UTE, using hand labeled coordinates as the starting point.ResultsWe were able to visualize and segment 95% of EEG electrodes using a short (3.5Â min) UTE sequence. We provide scripts and template images so this approach can now be easily implemented to obtain precise, subject-specific EEG electrode positions while adding minimal acquisition time to the simultaneous EEG-fMRI protocol.Comparison with existing method(s)T1 gel artifacts are not robust enough to localize all electrodes across subjects, the polymers composing Brainvision cap electrodes are not visible on a T1, and adding T1 visible materials to the EEG cap is not always possible. We therefore consider our method superior to existing methods for obtaining electrode positions in the scanner, as it is hardware free and should work on a wide range of materials (caps).ConclusionsEEG electrode positions are obtained with high precision and no additional hardware.
82
Journal: Journal of Neuroscience Methods - Volume 278, 15 February 2017, Pages 36-45