| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 606790 | 1454542 | 2015 | 10 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
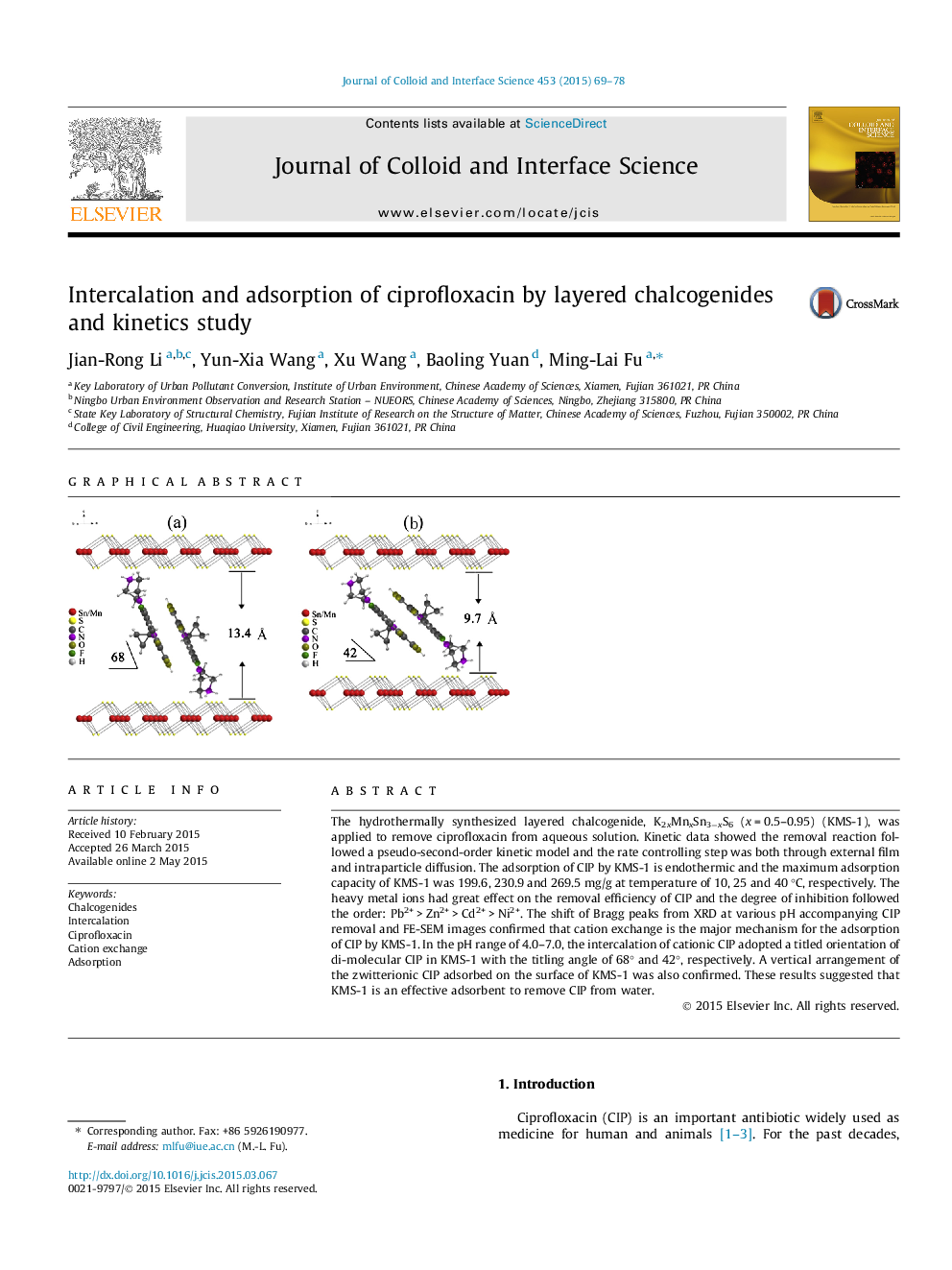
The hydrothermally synthesized layered chalcogenide, K2xMnxSn3−xS6 (x = 0.5–0.95) (KMS-1), was applied to remove ciprofloxacin from aqueous solution. Kinetic data showed the removal reaction followed a pseudo-second-order kinetic model and the rate controlling step was both through external film and intraparticle diffusion. The adsorption of CIP by KMS-1 is endothermic and the maximum adsorption capacity of KMS-1 was 199.6, 230.9 and 269.5 mg/g at temperature of 10, 25 and 40 °C, respectively. The heavy metal ions had great effect on the removal efficiency of CIP and the degree of inhibition followed the order: Pb2+ > Zn2+ > Cd2+ > Ni2+. The shift of Bragg peaks from XRD at various pH accompanying CIP removal and FE-SEM images confirmed that cation exchange is the major mechanism for the adsorption of CIP by KMS-1. In the pH range of 4.0–7.0, the intercalation of cationic CIP adopted a titled orientation of di-molecular CIP in KMS-1 with the titling angle of 68° and 42°, respectively. A vertical arrangement of the zwitterionic CIP adsorbed on the surface of KMS-1 was also confirmed. These results suggested that KMS-1 is an effective adsorbent to remove CIP from water.
Figure optionsDownload high-quality image (170 K)Download as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Journal of Colloid and Interface Science - Volume 453, 1 September 2015, Pages 69–78