| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1228817 | 1495222 | 2015 | 12 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
• Rhodanine azodye (HL) and its metal complexes are synthesized and characterized.
• The thermal activation energies of decomposition of HL and its complexes are calculated.
• The values of ac conductivity are found increases with increasing temperatures.
• The variation of metal affect the values of electrical conductivity of complexes.
5-(2,3-Dimethyl-1-phenylpyrazol-5-one azo)-2-thioxo-4-thiazolidinone (HL) and its metal complexes with copper(II) (1), cobalt(II) (2) and nickel(II) (3) are synthesized and characterized by physico-chemical techniques. The thermal properties of the ligand (HL) and its metal complexes (1–3) are discussed. The thermal activation energies of decomposition (Ea) of HL and its metal complexes with Cu(II), Co(II) and Ni(II) are found to be 48.76, 36.83, 30.59 and 40.45 kJ/mol, respectively. The frequency and temperature dependence of ac conductivity, dielectric constants for HL and its complexes (1–3) are investigated in the temperature range 300–356 K and frequency range 0.1–100 kHz. Both of the ac conductivity and the values of the thermal activation energy for conduction, as well as the dielectric properties of the complexes of HL are found to depend on the nature of the metallic ions. The values of the thermal activation energies of electrical conductivity decrease with increasing the value of test frequency. The small polarons tunneling (SPT) is the dominant conduction mechanism for the ligand (HL), while for complex (2) the overlapping large tunneling model (OLPT) is the dominant conduction mechanism. The correlated barrier hopping (CBH) is the dominant conduction mechanism for both of the complexes (1) and (3).
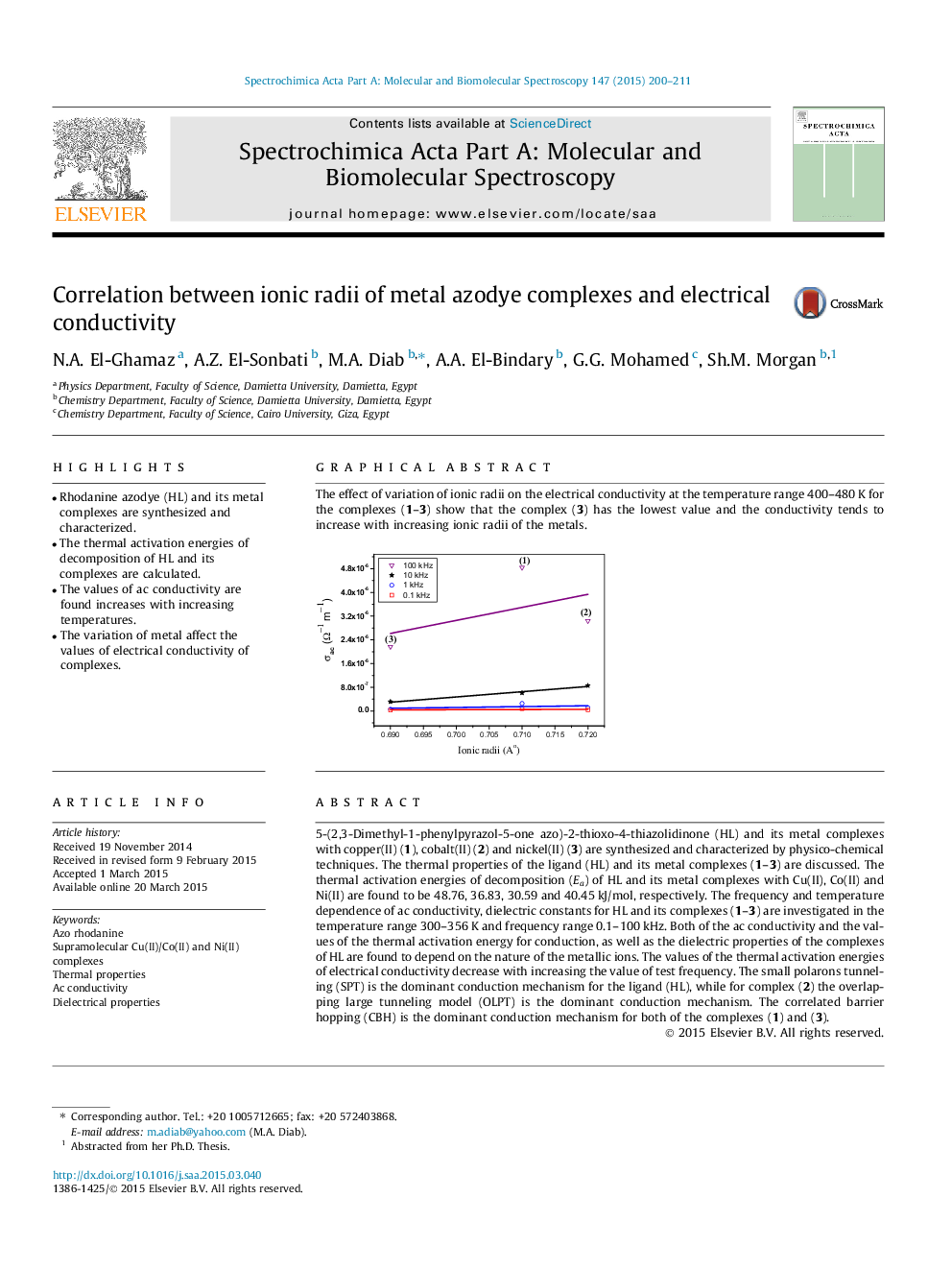
The effect of variation of ionic radii on the electrical conductivity at the temperature range 400–480 K for the complexes (1–3) show that the complex (3) has the lowest value and the conductivity tends to increase with increasing ionic radii of the metals.Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy - Volume 147, 5 August 2015, Pages 200–211