| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1229454 | 968734 | 2015 | 7 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
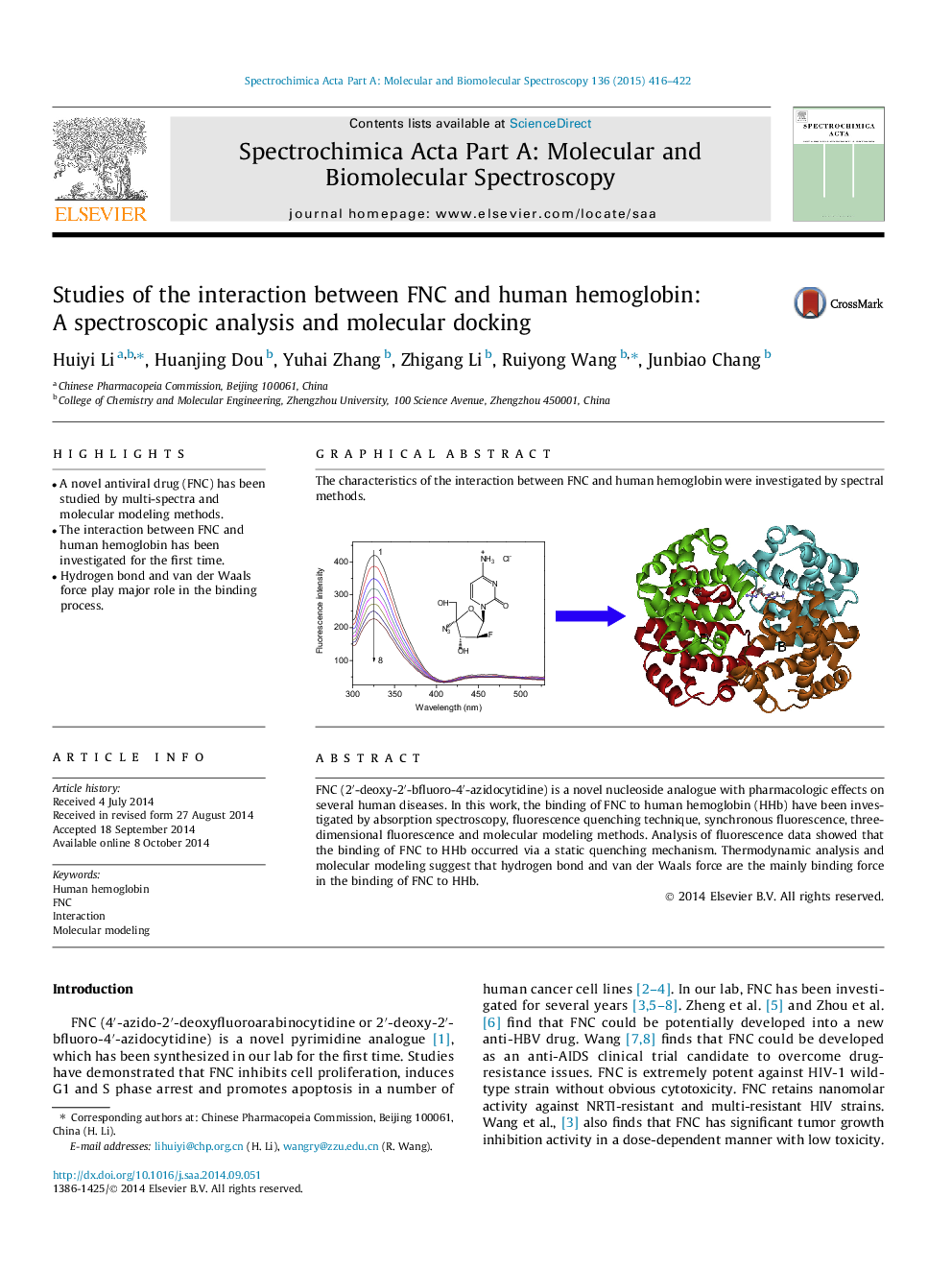
• A novel antiviral drug (FNC) has been studied by multi-spectra and molecular modeling methods.
• The interaction between FNC and human hemoglobin has been investigated for the first time.
• Hydrogen bond and van der Waals force play major role in the binding process.
FNC (2′-deoxy-2′-bfluoro-4′-azidocytidine) is a novel nucleoside analogue with pharmacologic effects on several human diseases. In this work, the binding of FNC to human hemoglobin (HHb) have been investigated by absorption spectroscopy, fluorescence quenching technique, synchronous fluorescence, three-dimensional fluorescence and molecular modeling methods. Analysis of fluorescence data showed that the binding of FNC to HHb occurred via a static quenching mechanism. Thermodynamic analysis and molecular modeling suggest that hydrogen bond and van der Waals force are the mainly binding force in the binding of FNC to HHb.
The characteristics of the interaction between FNC and human hemoglobin were investigated by spectral methods.Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy - Volume 136, Part B, 5 February 2015, Pages 416–422