| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1230367 | 1495238 | 2014 | 7 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
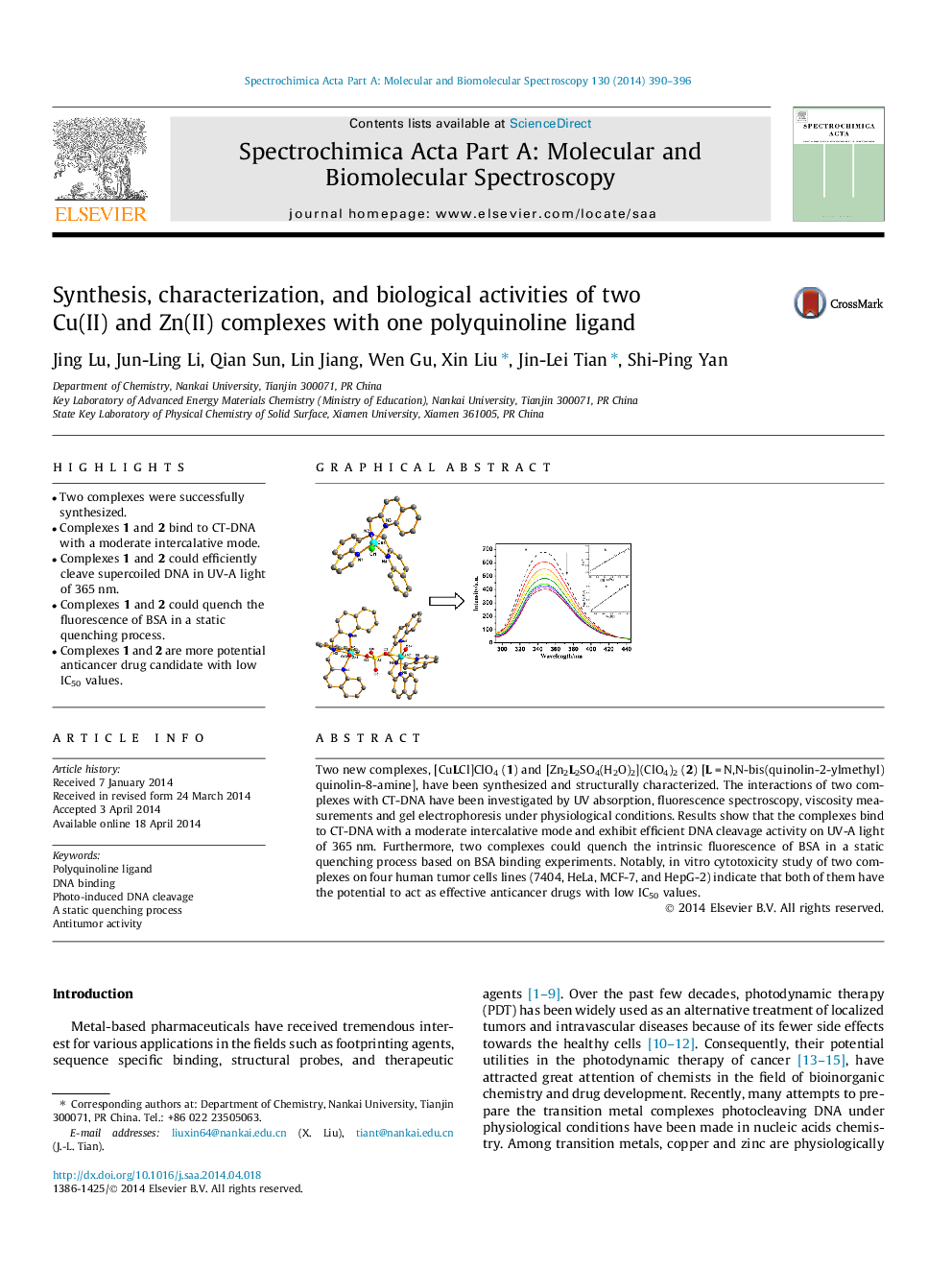
• Two complexes were successfully synthesized.
• Complexes 1 and 2 bind to CT-DNA with a moderate intercalative mode.
• Complexes 1 and 2 could efficiently cleave supercoiled DNA in UV-A light of 365 nm.
• Complexes 1 and 2 could quench the fluorescence of BSA in a static quenching process.
• Complexes 1 and 2 are more potential anticancer drug candidate with low IC50 values.
Two new complexes, [CuLCl]ClO4 (1) and [Zn2L2SO4(H2O)2](ClO4)2 (2) [L = N,N-bis(quinolin-2-ylmethyl)quinolin-8-amine], have been synthesized and structurally characterized. The interactions of two complexes with CT-DNA have been investigated by UV absorption, fluorescence spectroscopy, viscosity measurements and gel electrophoresis under physiological conditions. Results show that the complexes bind to CT-DNA with a moderate intercalative mode and exhibit efficient DNA cleavage activity on UV-A light of 365 nm. Furthermore, two complexes could quench the intrinsic fluorescence of BSA in a static quenching process based on BSA binding experiments. Notably, in vitro cytotoxicity study of two complexes on four human tumor cells lines (7404, HeLa, MCF-7, and HepG-2) indicate that both of them have the potential to act as effective anticancer drugs with low IC50 values.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy - Volume 130, 15 September 2014, Pages 390–396