| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1230571 | 1495240 | 2014 | 5 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
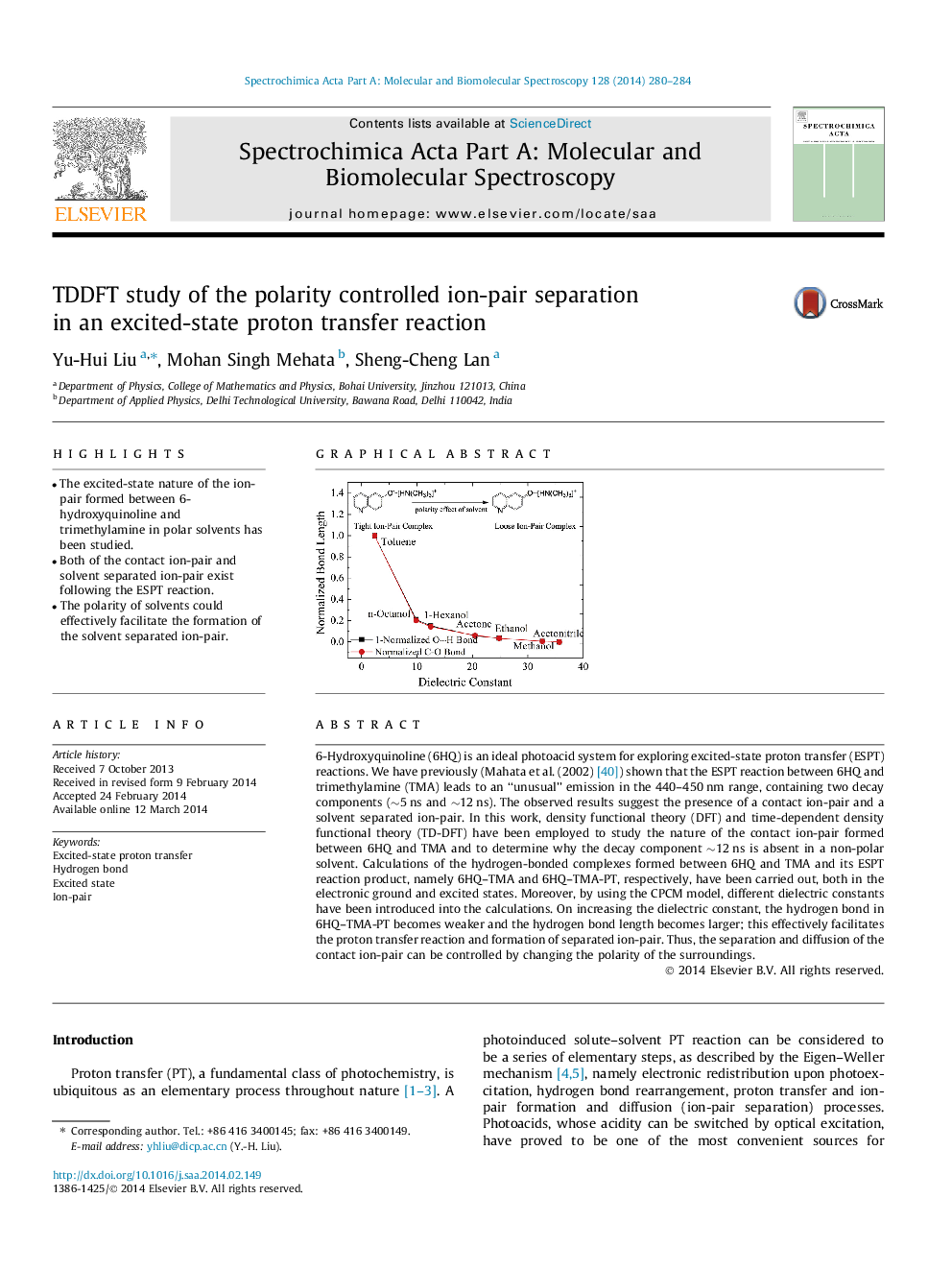
• The excited-state nature of the ion-pair formed between 6-hydroxyquinoline and trimethylamine in polar solvents has been studied.
• Both of the contact ion-pair and solvent separated ion-pair exist following the ESPT reaction.
• The polarity of solvents could effectively facilitate the formation of the solvent separated ion-pair.
6-Hydroxyquinoline (6HQ) is an ideal photoacid system for exploring excited-state proton transfer (ESPT) reactions. We have previously (Mahata et al. (2002) [40]) shown that the ESPT reaction between 6HQ and trimethylamine (TMA) leads to an “unusual” emission in the 440–450 nm range, containing two decay components (∼5 ns and ∼12 ns). The observed results suggest the presence of a contact ion-pair and a solvent separated ion-pair. In this work, density functional theory (DFT) and time-dependent density functional theory (TD-DFT) have been employed to study the nature of the contact ion-pair formed between 6HQ and TMA and to determine why the decay component ∼12 ns is absent in a non-polar solvent. Calculations of the hydrogen-bonded complexes formed between 6HQ and TMA and its ESPT reaction product, namely 6HQ–TMA and 6HQ–TMA-PT, respectively, have been carried out, both in the electronic ground and excited states. Moreover, by using the CPCM model, different dielectric constants have been introduced into the calculations. On increasing the dielectric constant, the hydrogen bond in 6HQ–TMA-PT becomes weaker and the hydrogen bond length becomes larger; this effectively facilitates the proton transfer reaction and formation of separated ion-pair. Thus, the separation and diffusion of the contact ion-pair can be controlled by changing the polarity of the surroundings.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy - Volume 128, 15 July 2014, Pages 280–284