| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1230853 | 1495248 | 2014 | 7 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
• The titanium-doped zinc oxide (Ti-doped ZnO) thin films were deposited onto glass substrate by spray pyrolysis technique.
• The physical properties of these films were characterized by XRD, AFM and PL measurements.
• The crystallographic parameters; microstrain, dislocation density, and lattice constant were estimated.
• The band gap of the films was found to be increased from 3.20 eV to 3.32 eV as the concentration of Ti doping increased.
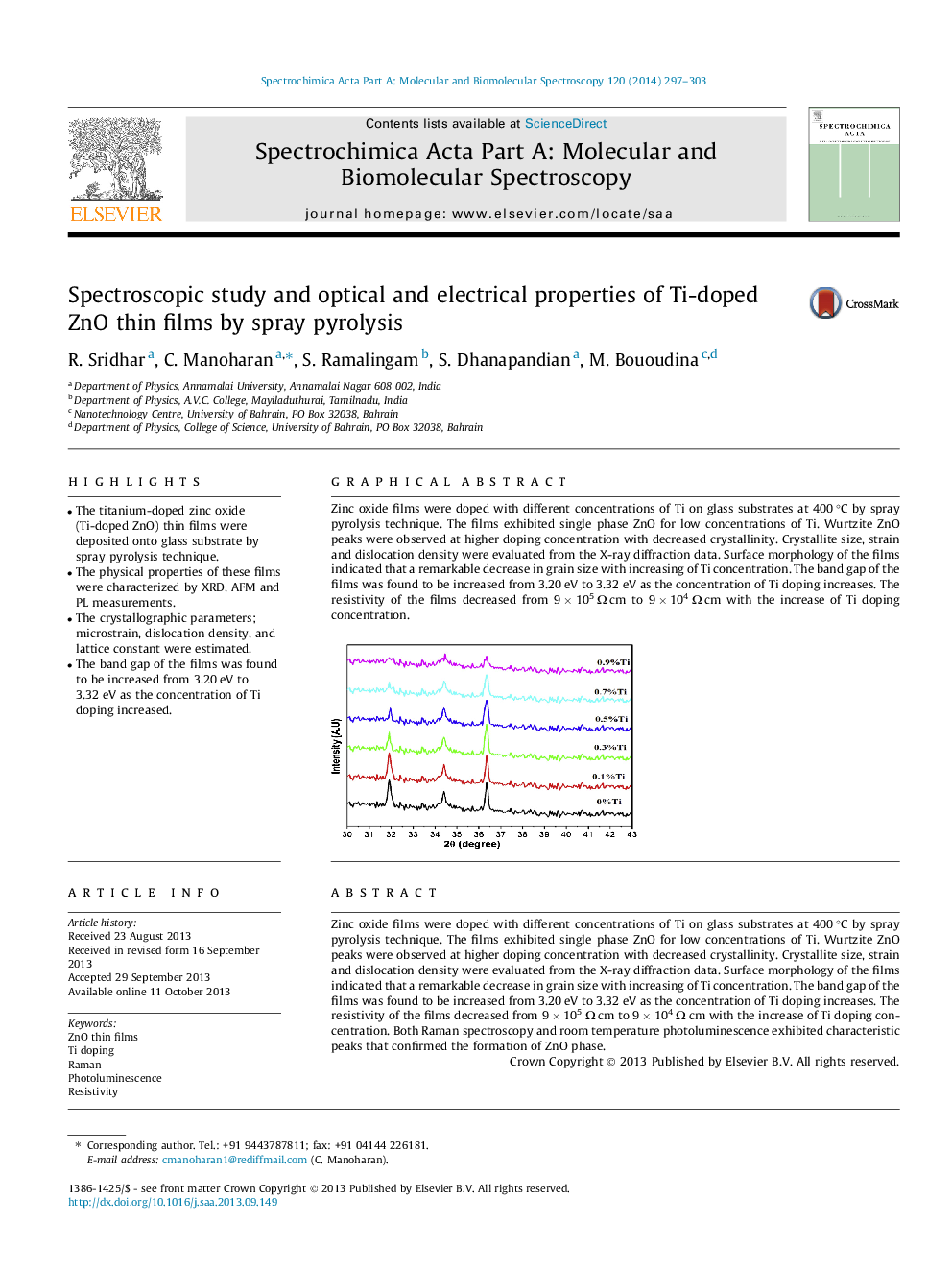
Zinc oxide films were doped with different concentrations of Ti on glass substrates at 400 °C by spray pyrolysis technique. The films exhibited single phase ZnO for low concentrations of Ti. Wurtzite ZnO peaks were observed at higher doping concentration with decreased crystallinity. Crystallite size, strain and dislocation density were evaluated from the X-ray diffraction data. Surface morphology of the films indicated that a remarkable decrease in grain size with increasing of Ti concentration. The band gap of the films was found to be increased from 3.20 eV to 3.32 eV as the concentration of Ti doping increases. The resistivity of the films decreased from 9 × 105 Ω cm to 9 × 104 Ω cm with the increase of Ti doping concentration. Both Raman spectroscopy and room temperature photoluminescence exhibited characteristic peaks that confirmed the formation of ZnO phase.
Zinc oxide films were doped with different concentrations of Ti on glass substrates at 400 °C by spray pyrolysis technique. The films exhibited single phase ZnO for low concentrations of Ti. Wurtzite ZnO peaks were observed at higher doping concentration with decreased crystallinity. Crystallite size, strain and dislocation density were evaluated from the X-ray diffraction data. Surface morphology of the films indicated that a remarkable decrease in grain size with increasing of Ti concentration. The band gap of the films was found to be increased from 3.20 eV to 3.32 eV as the concentration of Ti doping increases. The resistivity of the films decreased from 9 × 105 Ω cm to 9 × 104 Ω cm with the increase of Ti doping concentration.Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy - Volume 120, 24 February 2014, Pages 297–303