| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1231196 | 1495264 | 2013 | 5 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
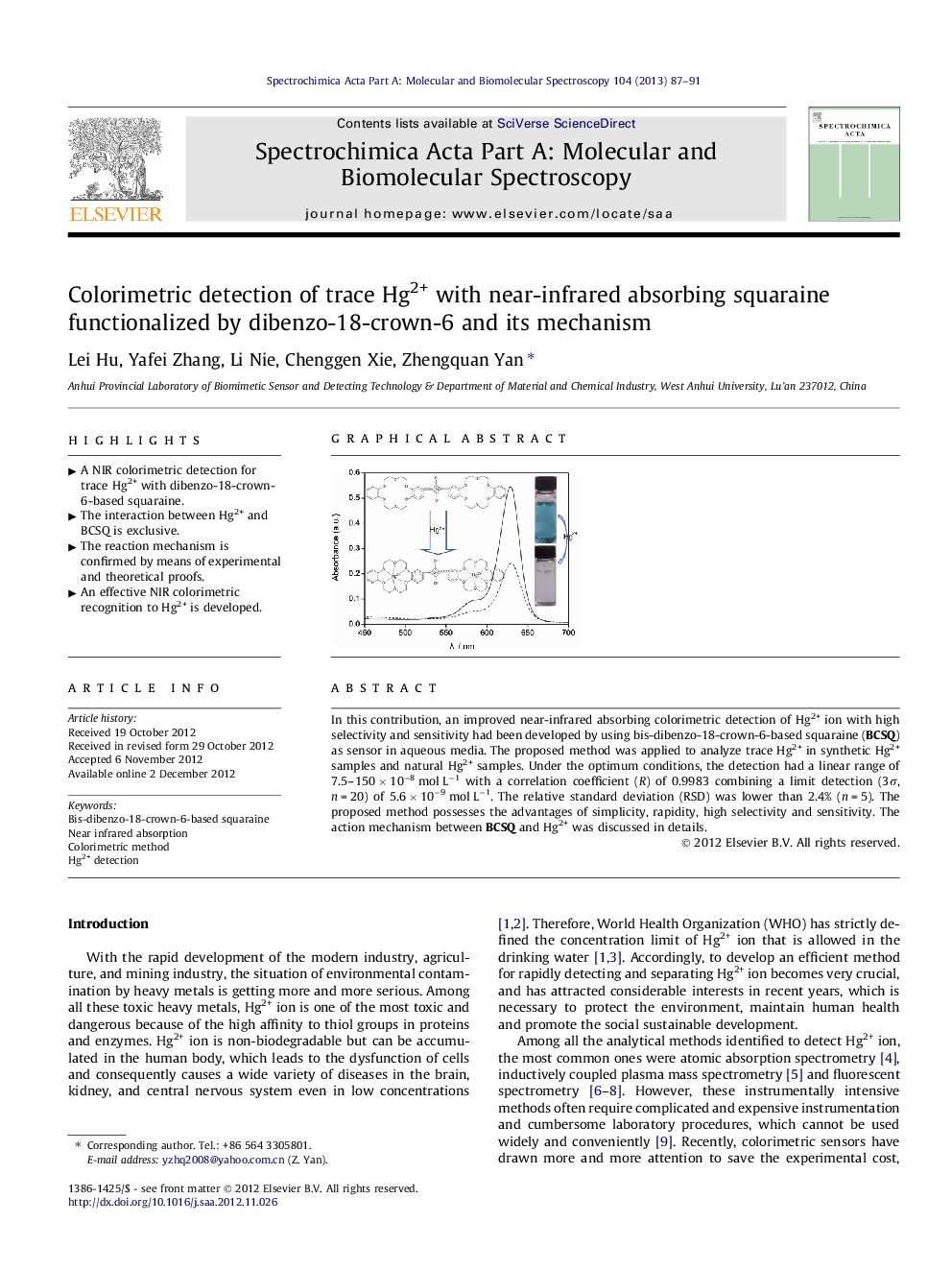
In this contribution, an improved near-infrared absorbing colorimetric detection of Hg2+ ion with high selectivity and sensitivity had been developed by using bis-dibenzo-18-crown-6-based squaraine (BCSQ) as sensor in aqueous media. The proposed method was applied to analyze trace Hg2+ in synthetic Hg2+ samples and natural Hg2+ samples. Under the optimum conditions, the detection had a linear range of 7.5–150 × 10−8 mol L−1 with a correlation coefficient (R) of 0.9983 combining a limit detection (3σ, n = 20) of 5.6 × 10−9 mol L−1. The relative standard deviation (RSD) was lower than 2.4% (n = 5). The proposed method possesses the advantages of simplicity, rapidity, high selectivity and sensitivity. The action mechanism between BCSQ and Hg2+ was discussed in details.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights
► A NIR colorimetric detection for trace Hg2+ with dibenzo-18-crown-6-based squaraine.
► The interaction between Hg2+ and BCSQ is exclusive.
► The reaction mechanism is confirmed by means of experimental and theoretical proofs.
► An effective NIR colorimetric recognition to Hg2+ is developed.
Journal: Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy - Volume 104, March 2013, Pages 87–91