| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1231243 | 1495264 | 2013 | 7 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
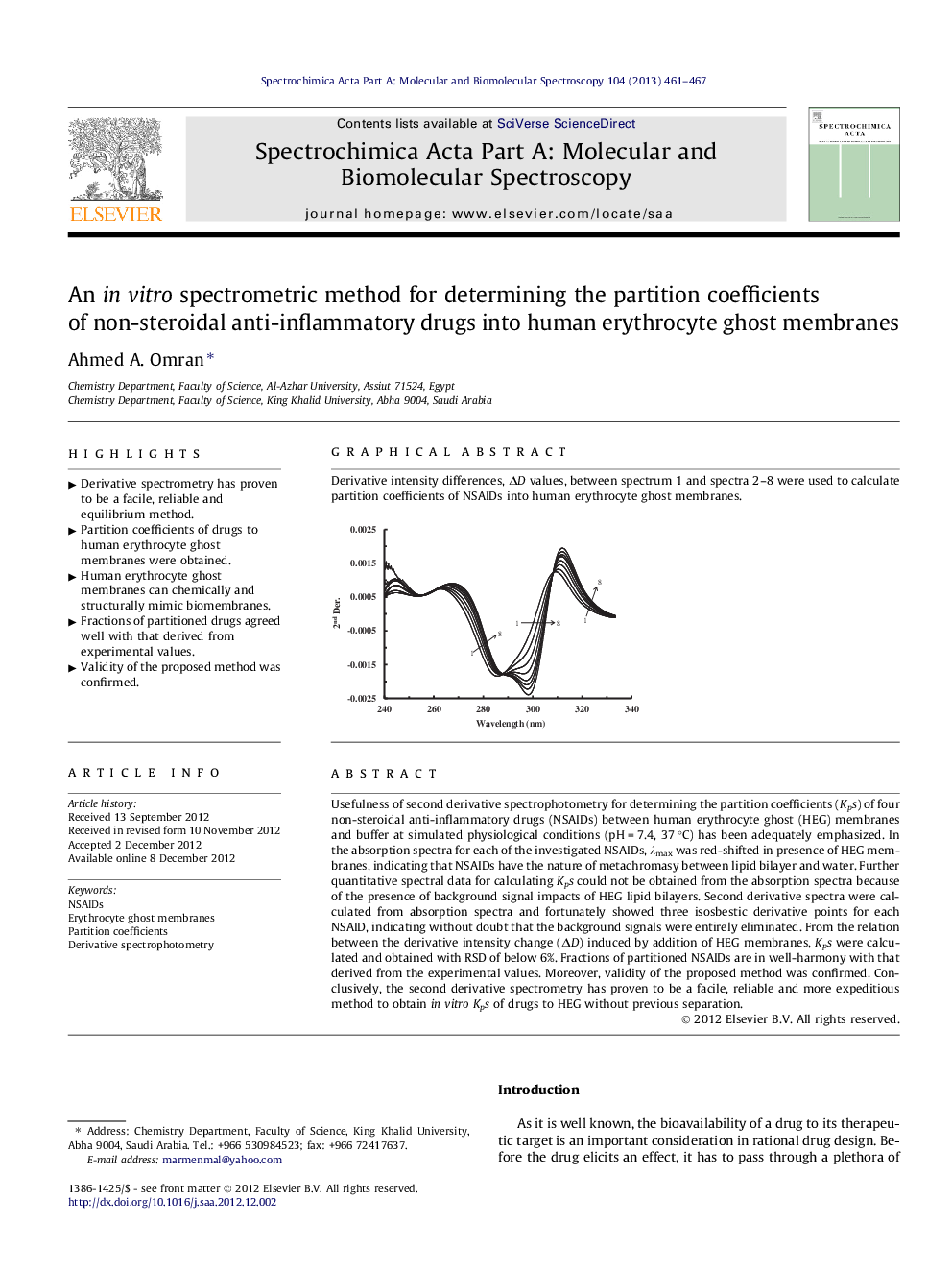
Usefulness of second derivative spectrophotometry for determining the partition coefficients (Kps) of four non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) between human erythrocyte ghost (HEG) membranes and buffer at simulated physiological conditions (pH = 7.4, 37 °C) has been adequately emphasized. In the absorption spectra for each of the investigated NSAIDs, λmax was red-shifted in presence of HEG membranes, indicating that NSAIDs have the nature of metachromasy between lipid bilayer and water. Further quantitative spectral data for calculating Kps could not be obtained from the absorption spectra because of the presence of background signal impacts of HEG lipid bilayers. Second derivative spectra were calculated from absorption spectra and fortunately showed three isosbestic derivative points for each NSAID, indicating without doubt that the background signals were entirely eliminated. From the relation between the derivative intensity change (ΔD) induced by addition of HEG membranes, Kps were calculated and obtained with RSD of below 6%. Fractions of partitioned NSAIDs are in well-harmony with that derived from the experimental values. Moreover, validity of the proposed method was confirmed. Conclusively, the second derivative spectrometry has proven to be a facile, reliable and more expeditious method to obtain in vitro Kps of drugs to HEG without previous separation.
Derivative intensity differences, ΔD values, between spectrum 1 and spectra 2–8 were used to calculate partition coefficients of NSAIDs into human erythrocyte ghost membranes.Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights
► Derivative spectrometry has proven to be a facile, reliable and equilibrium method.
► Partition coefficients of drugs to human erythrocyte ghost membranes were obtained.
► Human erythrocyte ghost membranes can chemically and structurally mimic biomembranes.
► Fractions of partitioned drugs agreed well with that derived from experimental values.
► Validity of the proposed method was confirmed.
Journal: Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy - Volume 104, March 2013, Pages 461–467