| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1232197 | 1495226 | 2015 | 5 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
• Laser excitation energy depended chemical transformation behavior of PATP to DMAB.
• Transformation is due to the synergetic effect between SPR and active oxygen species.
• Temperature dependent transformation behavior.
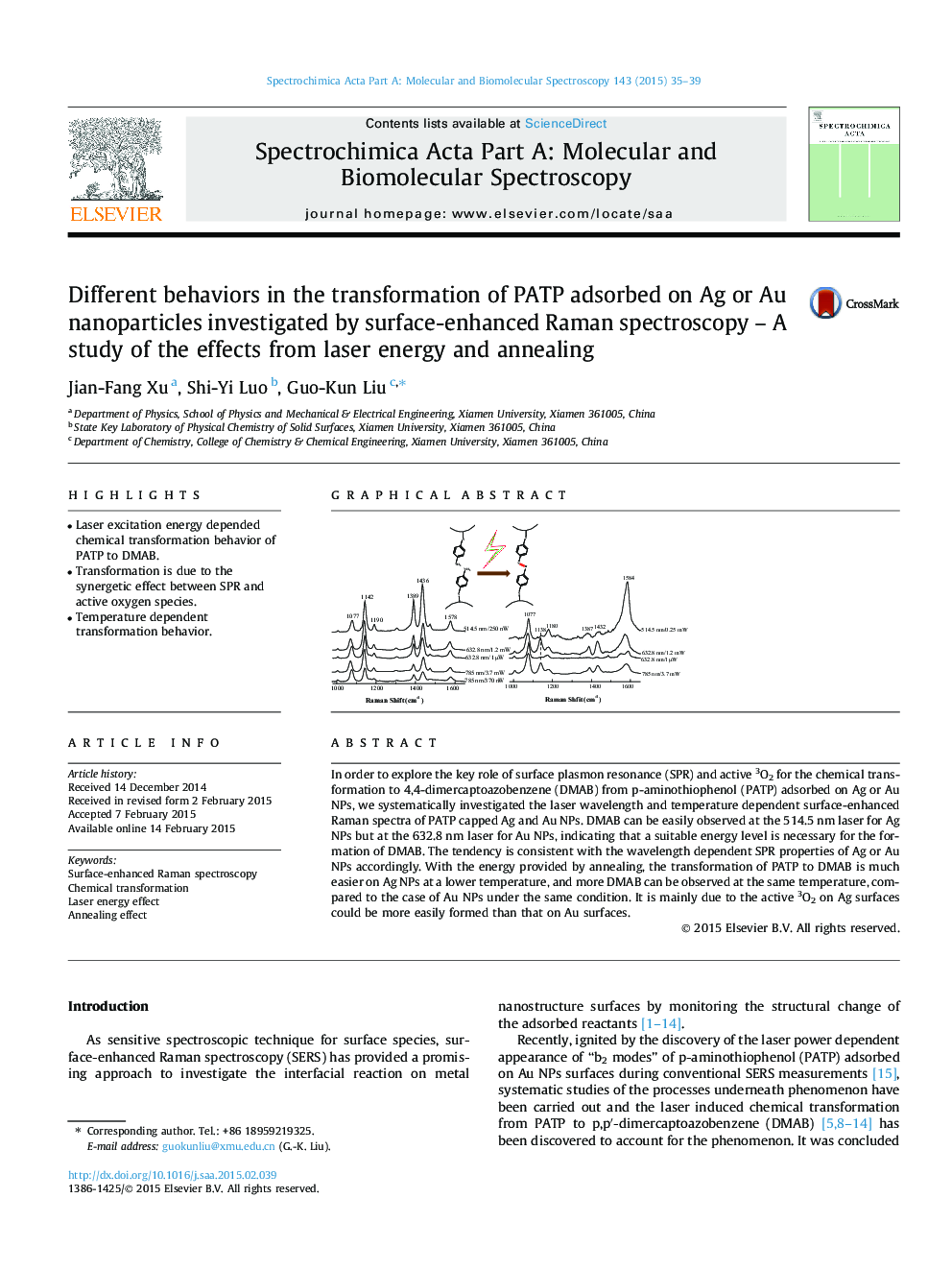
In order to explore the key role of surface plasmon resonance (SPR) and active 3O2 for the chemical transformation to 4,4-dimercaptoazobenzene (DMAB) from p-aminothiophenol (PATP) adsorbed on Ag or Au NPs, we systematically investigated the laser wavelength and temperature dependent surface-enhanced Raman spectra of PATP capped Ag and Au NPs. DMAB can be easily observed at the 514.5 nm laser for Ag NPs but at the 632.8 nm laser for Au NPs, indicating that a suitable energy level is necessary for the formation of DMAB. The tendency is consistent with the wavelength dependent SPR properties of Ag or Au NPs accordingly. With the energy provided by annealing, the transformation of PATP to DMAB is much easier on Ag NPs at a lower temperature, and more DMAB can be observed at the same temperature, compared to the case of Au NPs under the same condition. It is mainly due to the active 3O2 on Ag surfaces could be more easily formed than that on Au surfaces.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy - Volume 143, 15 May 2015, Pages 35–39