| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1233083 | 1495249 | 2014 | 8 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
• B3LYP/cc-pVTZ is efficient to simulate Inelastic Electron Tunneling spectra.
• Provided a scaling factor is used, the RMSE on the frequencies goes down to 18 cm−1.
• Triple-ζ basis sets is a good compromise between accuracy and computational needs.
• Basis set effects on the IET intensities are larger than those of the XC functional.
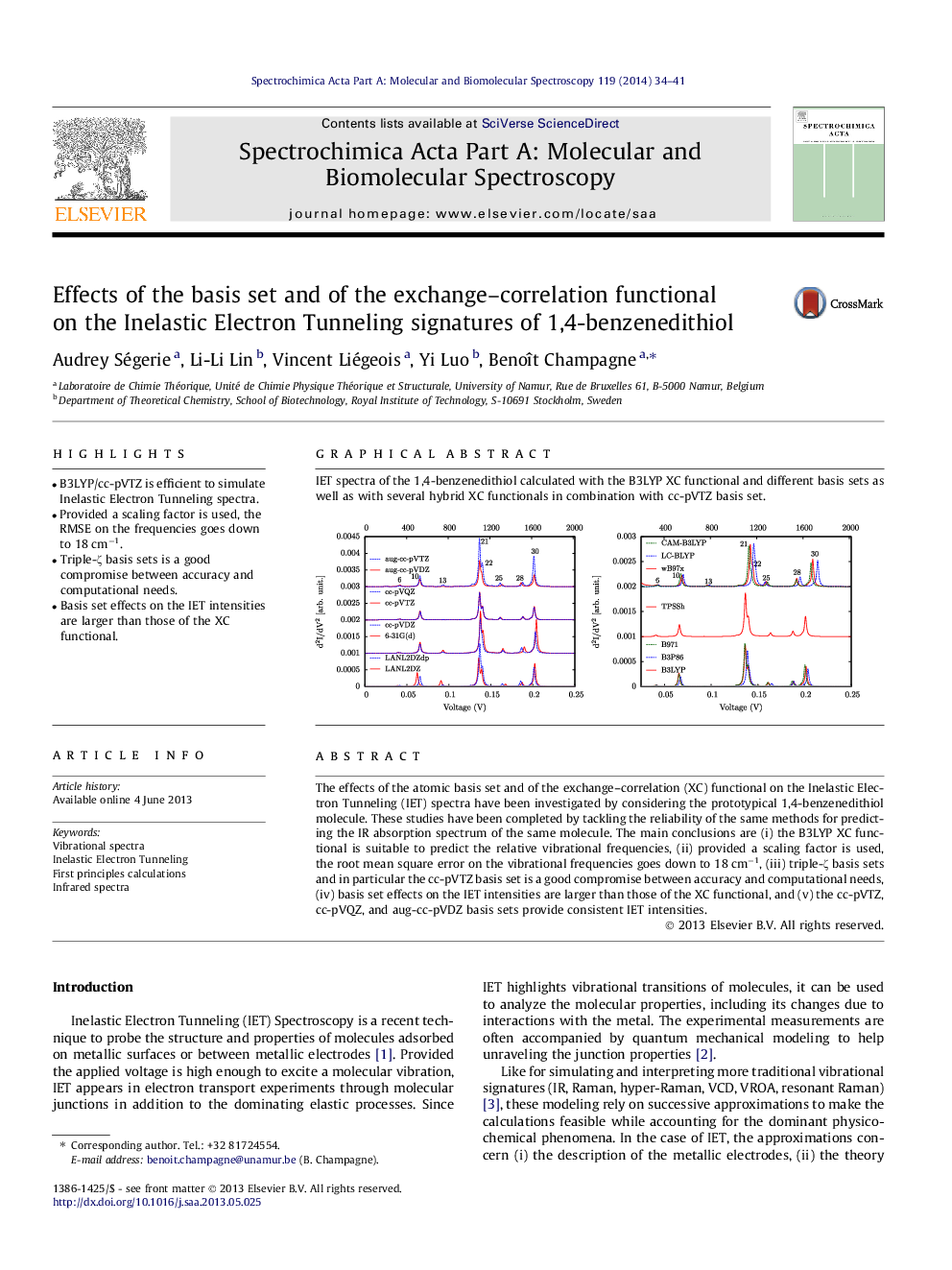
The effects of the atomic basis set and of the exchange–correlation (XC) functional on the Inelastic Electron Tunneling (IET) spectra have been investigated by considering the prototypical 1,4-benzenedithiol molecule. These studies have been completed by tackling the reliability of the same methods for predicting the IR absorption spectrum of the same molecule. The main conclusions are (i) the B3LYP XC functional is suitable to predict the relative vibrational frequencies, (ii) provided a scaling factor is used, the root mean square error on the vibrational frequencies goes down to 18 cm−1, (iii) triple-ζ basis sets and in particular the cc-pVTZ basis set is a good compromise between accuracy and computational needs, (iv) basis set effects on the IET intensities are larger than those of the XC functional, and (v) the cc-pVTZ, cc-pVQZ, and aug-cc-pVDZ basis sets provide consistent IET intensities.
IET spectra of the 1,4-benzenedithiol calculated with the B3LYP XC functional and different basis sets as well as with several hybrid XC functionals in combination with cc-pVTZ basis set.Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy - Volume 119, 5 February 2014, Pages 34–41