| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1234786 | 1495260 | 2013 | 4 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
Boronic acid-based fluorescent sensor is one of the non-enzymatic methods used for the recognition of saccharides. Since bacterial membrane has polysaccharides with diol groups, boronic acids probe could be applied for rapid bacterial recognition. Escherichia coli (XL-1 blue) were recognized by applying (3-(5-(dimethylamino) naphthalene-1-sulfonamide) phenyl) boronic acid (DNSBA) as a sensor and the fluorescence recorded by fluorometer micro-plate reader. Results showed that, fluorescence records of DNSBA increase in a dose dependent manner upon increasing the bacterial cell numbers. Moreover, the increase in the number of bacterial cells induces a shift in the spectra due to the formation of the anionic form of boronic acid complex. Therefore, DNSBA is an efficient sensor for monitoring bacterial cells.
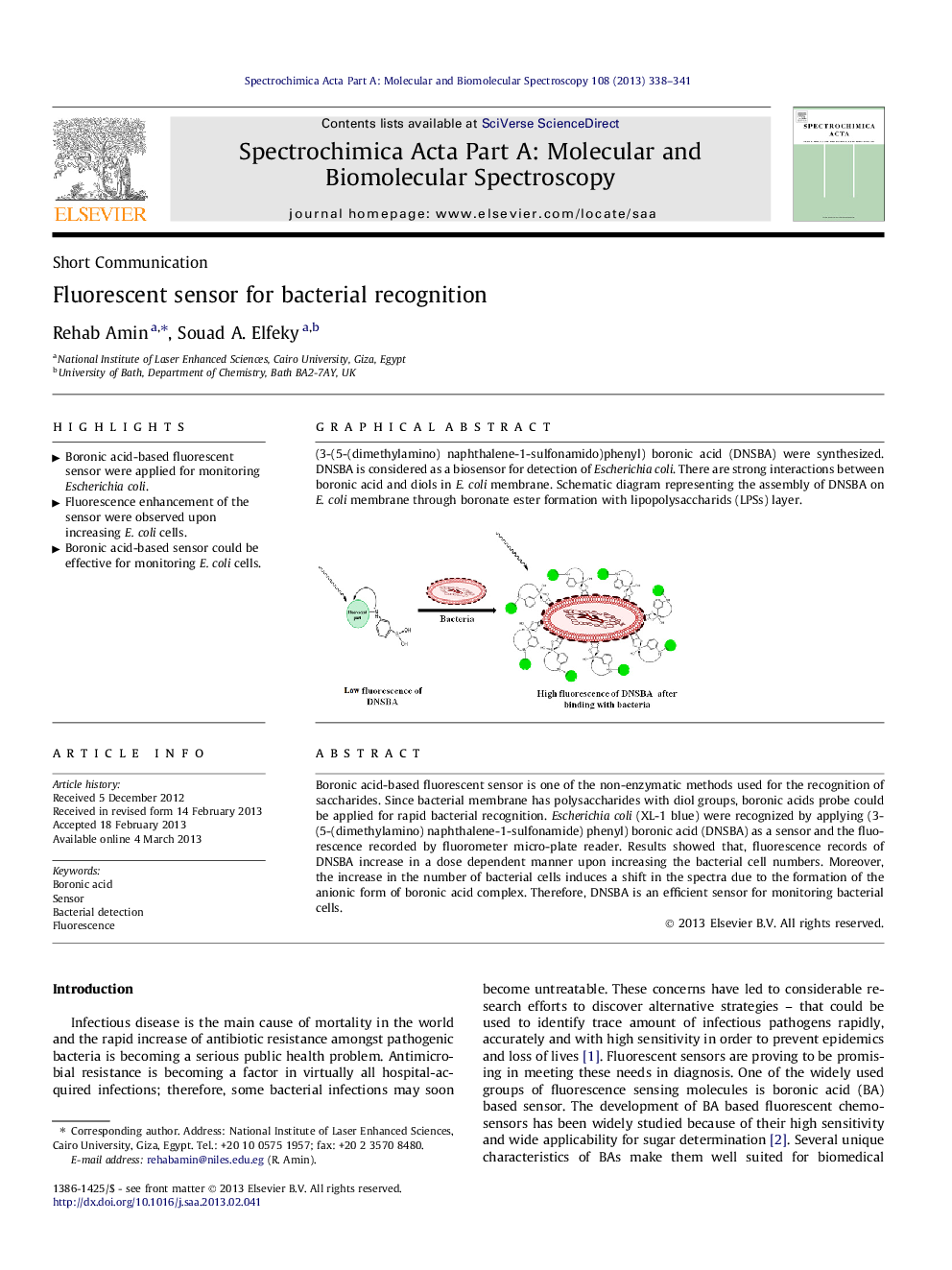
(3-(5-(dimethylamino) naphthalene-1-sulfonamido)phenyl) boronic acid (DNSBA) were synthesized. DNSBA is considered as a biosensor for detection of Escherichia coli. There are strong interactions between boronic acid and diols in E. coli membrane. Schematic diagram representing the assembly of DNSBA on E. coli membrane through boronate ester formation with lipopolysaccharids (LPSs) layer.Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights
► Boronic acid-based fluorescent sensor were applied for monitoring Escherichia coli.
► Fluorescence enhancement of the sensor were observed upon increasing E. coli cells.
► Boronic acid-based sensor could be effective for monitoring E. coli cells.
Journal: Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy - Volume 108, May 2013, Pages 338–341