| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1235382 | 1495269 | 2012 | 6 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
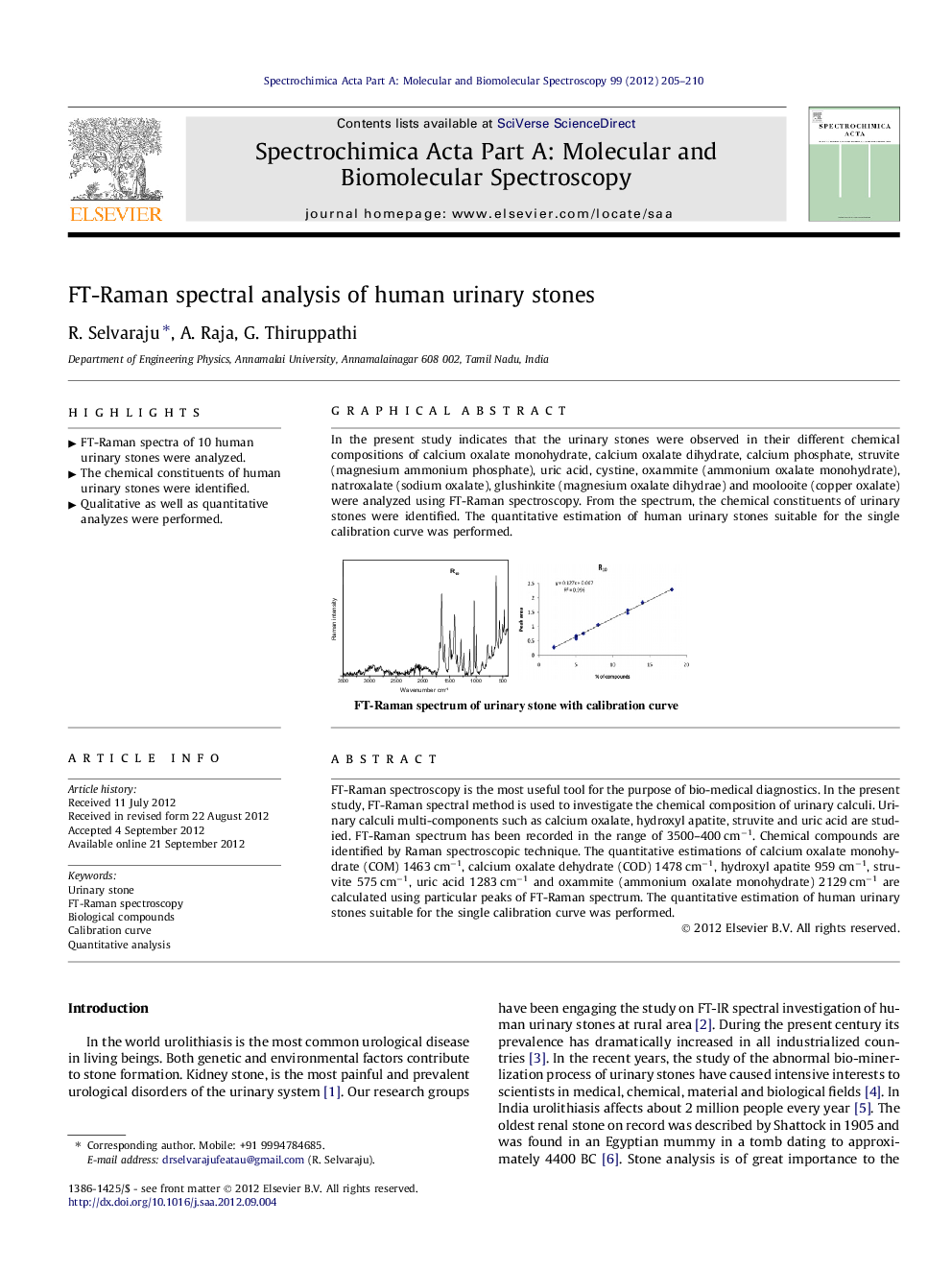
FT-Raman spectroscopy is the most useful tool for the purpose of bio-medical diagnostics. In the present study, FT-Raman spectral method is used to investigate the chemical composition of urinary calculi. Urinary calculi multi-components such as calcium oxalate, hydroxyl apatite, struvite and uric acid are studied. FT-Raman spectrum has been recorded in the range of 3500–400 cm−1. Chemical compounds are identified by Raman spectroscopic technique. The quantitative estimations of calcium oxalate monohydrate (COM) 1463 cm−1, calcium oxalate dehydrate (COD) 1478 cm−1, hydroxyl apatite 959 cm−1, struvite 575 cm−1, uric acid 1283 cm−1 and oxammite (ammonium oxalate monohydrate) 2129 cm−1 are calculated using particular peaks of FT-Raman spectrum. The quantitative estimation of human urinary stones suitable for the single calibration curve was performed.
In the present study indicates that the urinary stones were observed in their different chemical compositions of calcium oxalate monohydrate, calcium oxalate dihydrate, calcium phosphate, struvite (magnesium ammonium phosphate), uric acid, cystine, oxammite (ammonium oxalate monohydrate), natroxalate (sodium oxalate), glushinkite (magnesium oxalate dihydrae) and moolooite (copper oxalate) were analyzed using FT-Raman spectroscopy. From the spectrum, the chemical constituents of urinary stones were identified. The quantitative estimation of human urinary stones suitable for the single calibration curve was performed.Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights
► FT-Raman spectra of 10 human urinary stones were analyzed.
► The chemical constituents of human urinary stones were identified.
► Qualitative as well as quantitative analyzes were performed.
Journal: Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy - Volume 99, 15 December 2012, Pages 205–210