| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2077290 | 1079696 | 2015 | 16 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
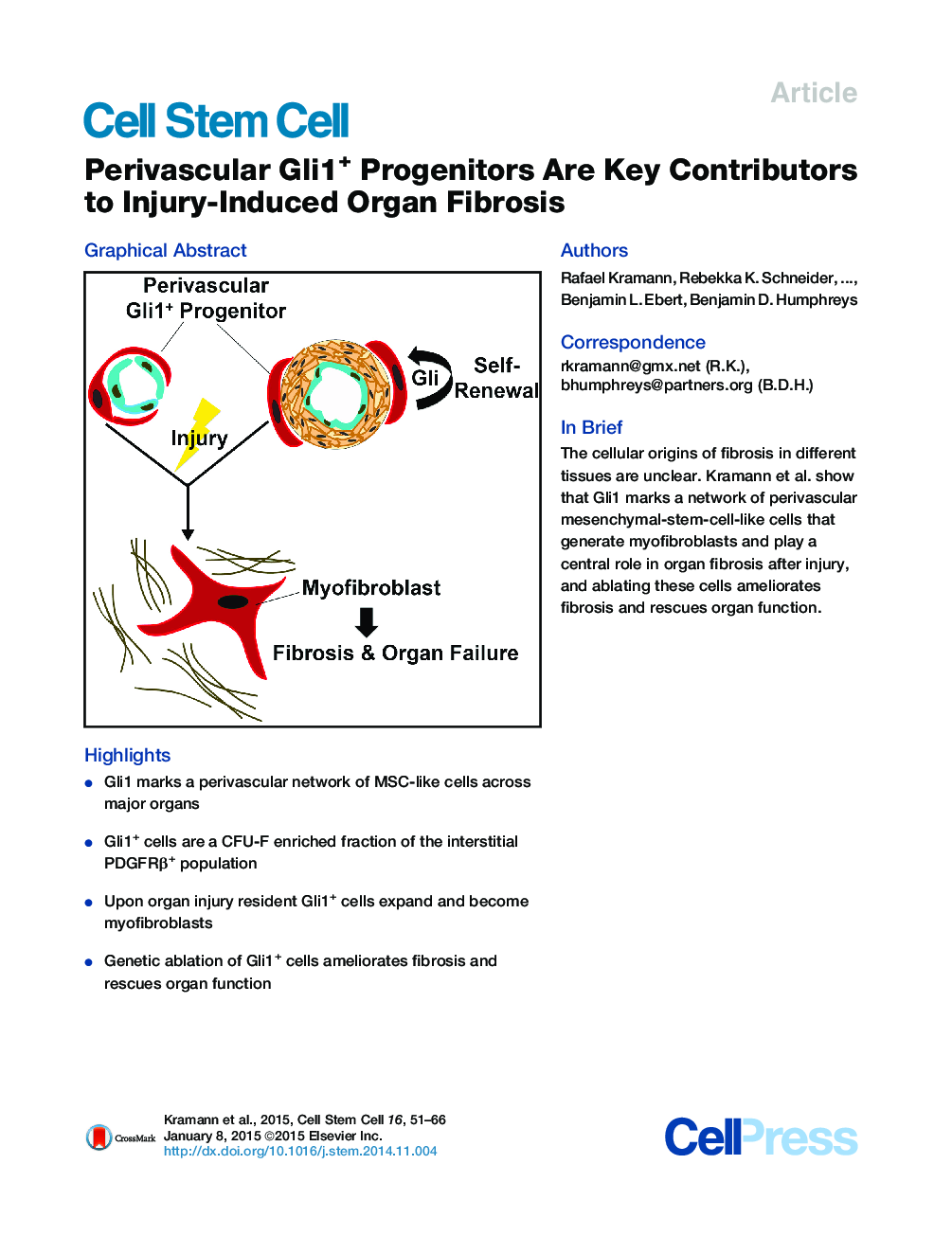
• Gli1 marks a perivascular network of MSC-like cells across major organs
• Gli1+ cells are a CFU-F enriched fraction of the interstitial PDGFRβ+ population
• Upon organ injury resident Gli1+ cells expand and become myofibroblasts
• Genetic ablation of Gli1+ cells ameliorates fibrosis and rescues organ function
SummaryMesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) reside in the perivascular niche of many organs, including kidney, lung, liver, and heart, although their roles in these tissues are poorly understood. Here, we demonstrate that Gli1 marks perivascular MSC-like cells that substantially contribute to organ fibrosis. In vitro, Gli1+ cells express typical MSC markers, exhibit trilineage differentiation capacity, and possess colony-forming activity, despite constituting a small fraction of the platelet-derived growth factor-β (PDGFRβ)+ cell population. Genetic lineage tracing analysis demonstrates that tissue-resident, but not circulating, Gli1+ cells proliferate after kidney, lung, liver, or heart injury to generate myofibroblasts. Genetic ablation of these cells substantially ameliorates kidney and heart fibrosis and preserves ejection fraction in a model of induced heart failure. These findings implicate perivascular Gli1+ MSC-like cells as a major cellular origin of organ fibrosis and demonstrate that these cells may be a relevant therapeutic target to prevent solid organ dysfunction after injury.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload high-quality image (375 K)Download as PowerPoint slide
Journal: - Volume 16, Issue 1, 8 January 2015, Pages 51–66