| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2078431 | 1401223 | 2016 | 15 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
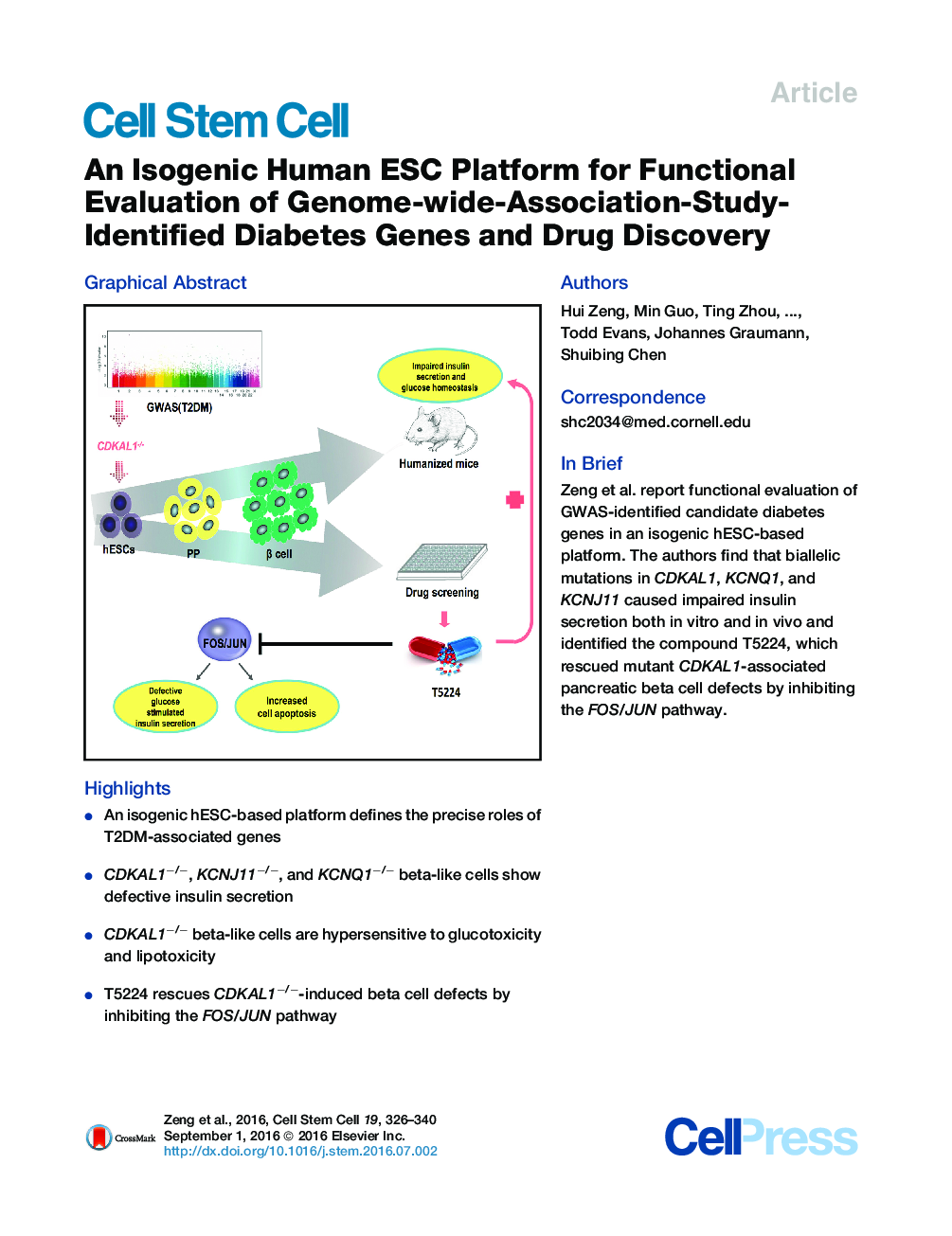
• An isogenic hESC-based platform defines the precise roles of T2DM-associated genes
• CDKAL1−/−, KCNJ11−/−, and KCNQ1−/− beta-like cells show defective insulin secretion
• CDKAL1−/− beta-like cells are hypersensitive to glucotoxicity and lipotoxicity
• T5224 rescues CDKAL1−/−-induced beta cell defects by inhibiting the FOS/JUN pathway
SummaryGenome-wide association studies (GWASs) have increased our knowledge of loci associated with a range of human diseases. However, applying such findings to elucidate pathophysiology and promote drug discovery remains challenging. Here, we created isogenic human ESCs (hESCs) with mutations in GWAS-identified susceptibility genes for type 2 diabetes. In pancreatic beta-like cells differentiated from these lines, we found that mutations in CDKAL1, KCNQ1, and KCNJ11 led to impaired glucose secretion in vitro and in vivo, coinciding with defective glucose homeostasis. CDKAL1 mutant insulin+ cells were also hypersensitive to glucolipotoxicity. A high-content chemical screen identified a candidate drug that rescued CDKAL1-specific defects in vitro and in vivo by inhibiting the FOS/JUN pathway. Our approach of a proof-of-principle platform, which uses isogenic hESCs for functional evaluation of GWAS-identified loci and identification of a drug candidate that rescues gene-specific defects, paves the way for precision therapy of metabolic diseases.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload high-quality image (190 K)Download as PowerPoint slide
Journal: - Volume 19, Issue 3, 1 September 2016, Pages 326–340