| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2078435 | 1401223 | 2016 | 14 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
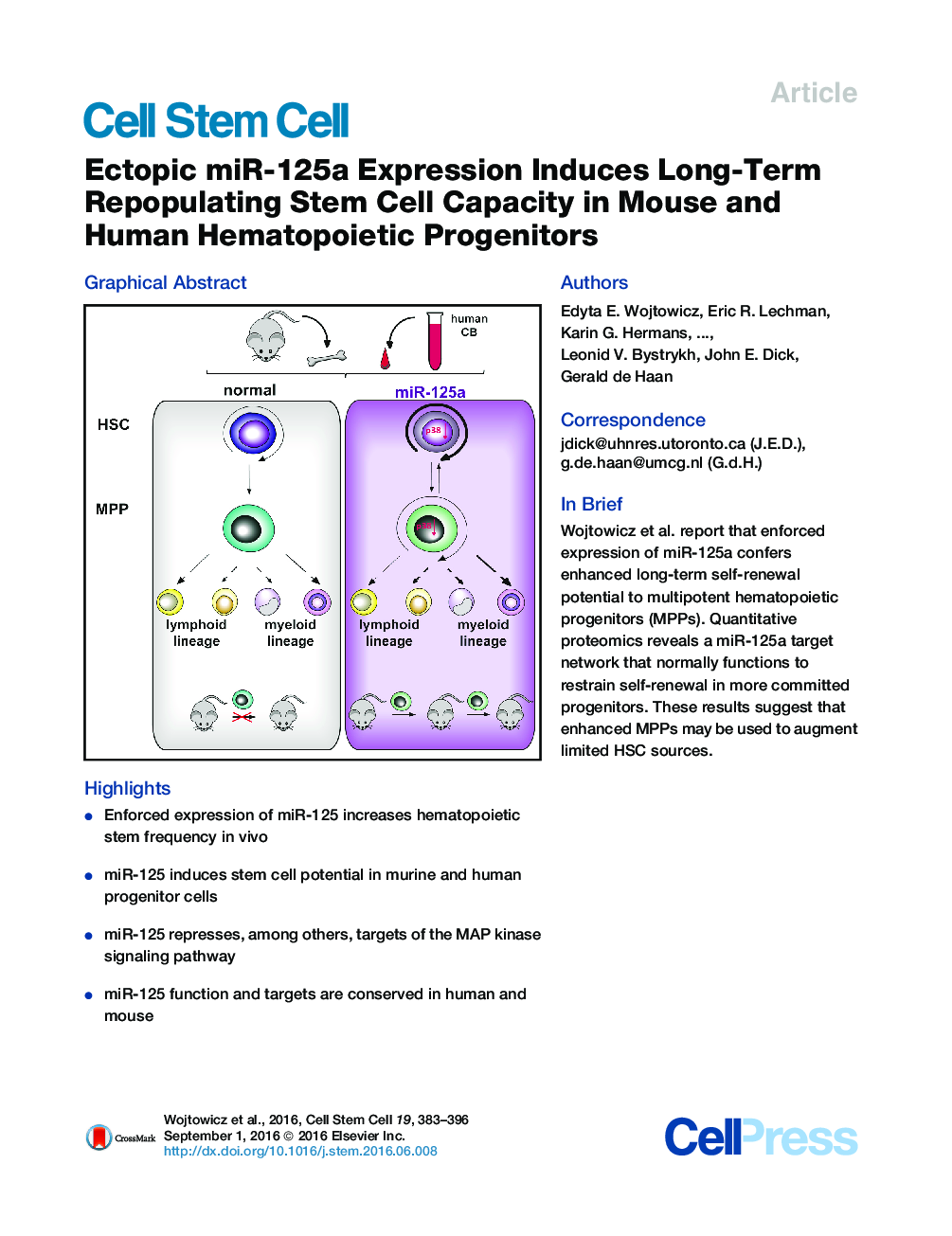
• Enforced expression of miR-125 increases hematopoietic stem frequency in vivo
• miR-125 induces stem cell potential in murine and human progenitor cells
• miR-125 represses, among others, targets of the MAP kinase signaling pathway
• miR-125 function and targets are conserved in human and mouse
SummaryUmbilical cord blood (CB) is a convenient and broadly used source of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) for allogeneic stem cell transplantation. However, limiting numbers of HSCs remain a major constraint for its clinical application. Although one feasible option would be to expand HSCs to improve therapeutic outcome, available protocols and the molecular mechanisms governing the self-renewal of HSCs are unclear. Here, we show that ectopic expression of a single microRNA (miRNA), miR-125a, in purified murine and human multipotent progenitors (MPPs) resulted in increased self-renewal and robust long-term multi-lineage repopulation in transplanted recipient mice. Using quantitative proteomics and western blot analysis, we identified a restricted set of miR-125a targets involved in conferring long-term repopulating capacity to MPPs in humans and mice. Our findings offer the innovative potential to use MPPs with enhanced self-renewal activity to augment limited sources of HSCs to improve clinical protocols.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload high-quality image (197 K)Download as PowerPoint slide
Journal: - Volume 19, Issue 3, 1 September 2016, Pages 383–396