| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 527860 | 869391 | 2012 | 18 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
In this paper, we propose a framework for human action analysis from video footage. A video action sequence in our perspective is a dynamic structure of sparse local spatial–temporal patches termed action elements, so the problems of action analysis in video are carried out here based on the set of local characteristics as well as global shape of a prescribed action. We first detect a set of action elements that are the most compact entities of an action, then we extend the idea of Implicit Shape Model to space time, in order to properly integrate the spatial and temporal properties of these action elements. In particular, we consider two different recipes to construct action elements: one is to use a Sparse Bayesian Feature Classifier to choose action elements from all detected Spatial Temporal Interest Points, and is termed discriminative action elements. The other one detects affine invariant local features from the holistic Motion History Images, and picks up action elements according to their compactness scores, and is called generative action elements. Action elements detected from either way are then used to construct a voting space based on their local feature representations as well as their global configuration constraints. Our approach is evaluated in the two main contexts of current human action analysis challenges, action retrieval and action classification. Comprehensive experimental results show that our proposed framework marginally outperforms all existing state-of-the-arts techniques on a range of different datasets.
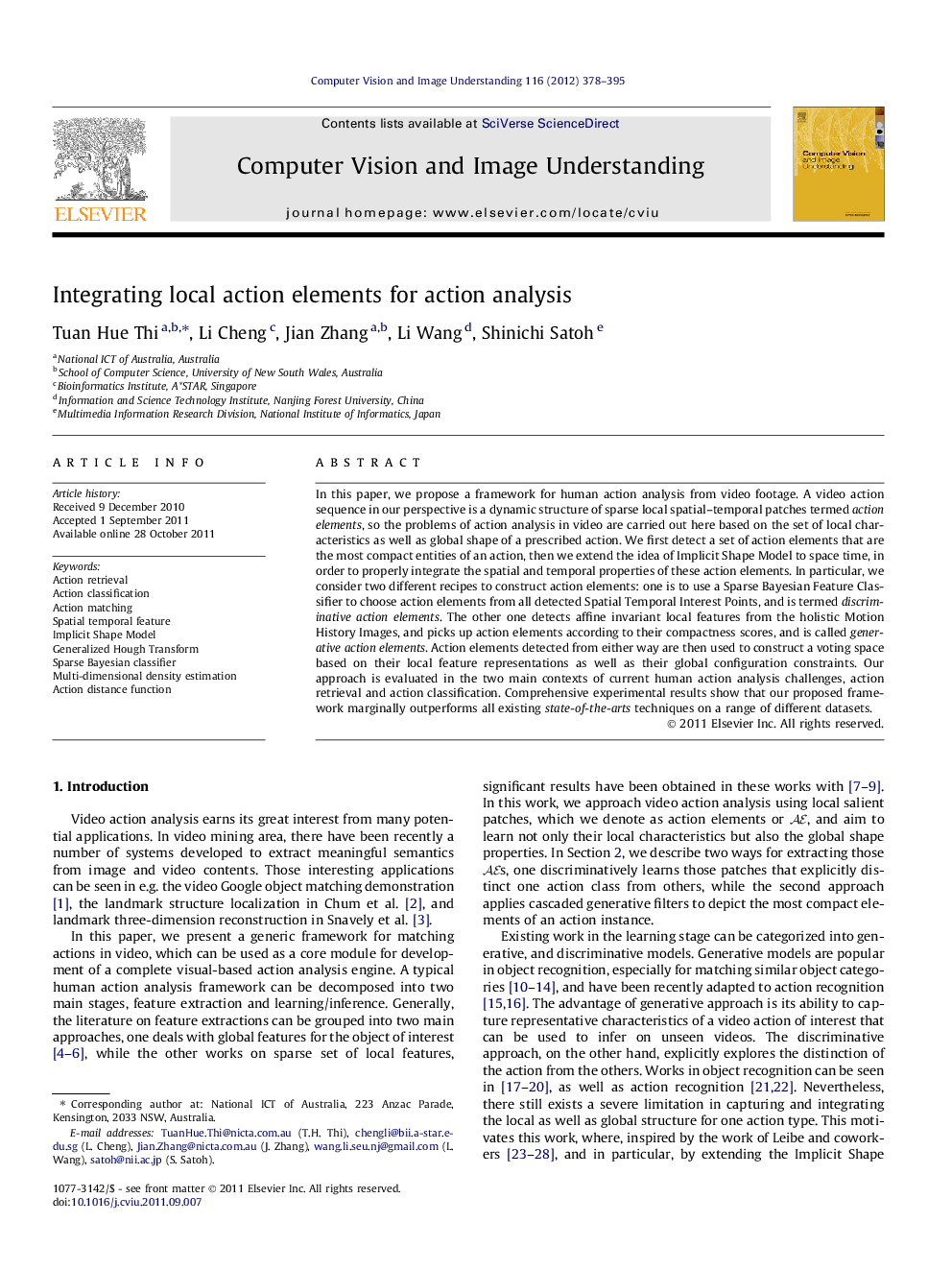
Pipeline of our action analysis framework: Starting with query action on the left, there are two ways to extract action elements, either with discriminative approach using Spatial Temporal Interest Point (STIP) and Sparse Bayesian Feature Classifier (SBFC) or with generative approach using Motion History Image (MHI) and Affine Invariant Feature Transform (AIFT). Action elements are used accordingly to fill a voting space of the Implicit Shape Model. Unknown video sequence on the right is passed through the same process to find action element candidates, which are then fitted into the voting space to produce a matching score.Figure optionsDownload high-quality image (114 K)Download as PowerPoint slideHighlights
► We represent human action in video sequence as sparse sets of action elements.
► Discriminative action elements are generated from Sparse Bayesian Classifier.
► Generative action elements are generated from affine-invariant Motion History Image.
► Action matching score is estimated from action elements’ voting space density.
Journal: Computer Vision and Image Understanding - Volume 116, Issue 3, March 2012, Pages 378–395