| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6268015 | 1614610 | 2016 | 6 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
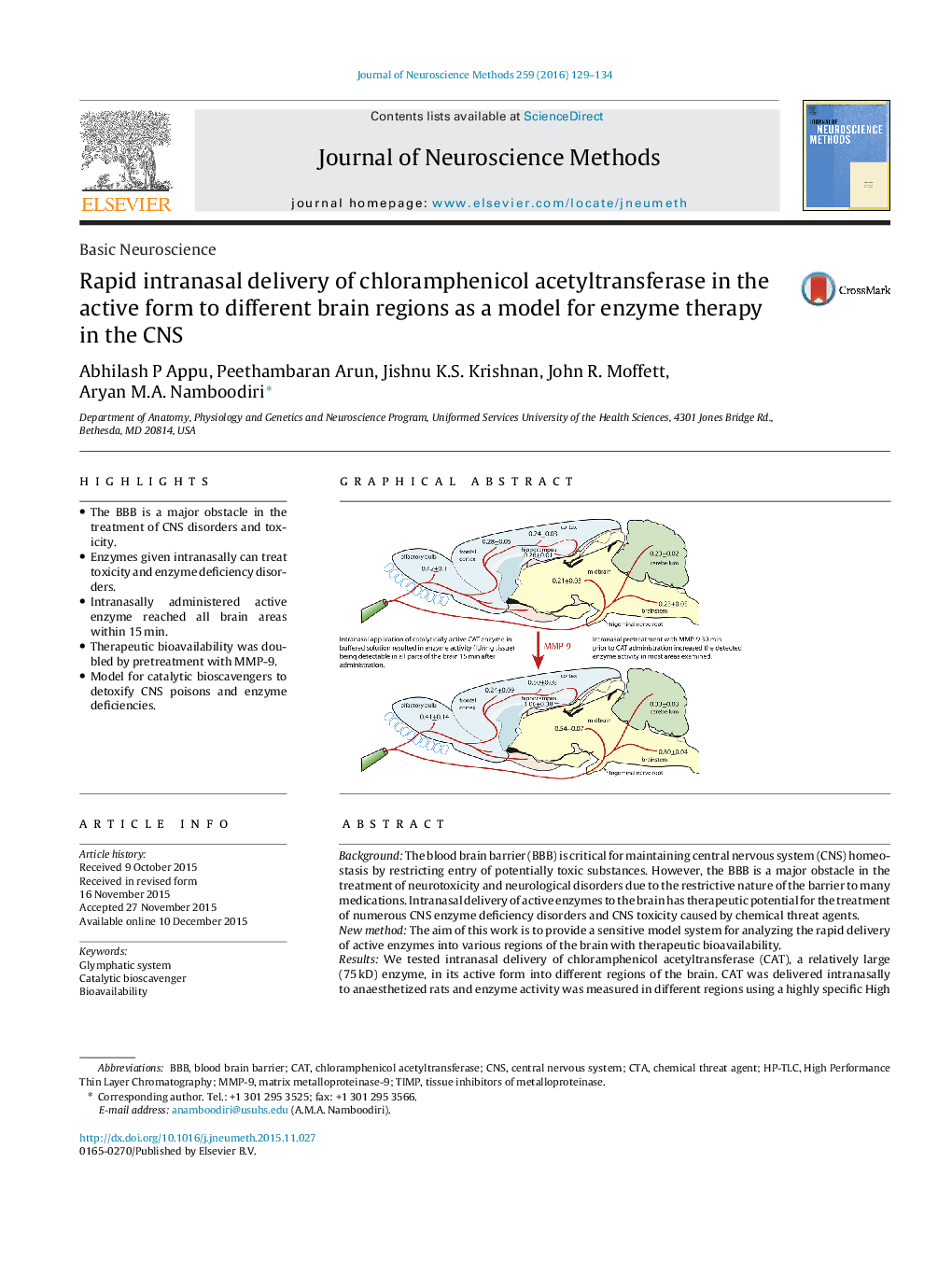
- The BBB is a major obstacle in the treatment of CNS disorders and toxicity.
- Enzymes given intranasally can treat toxicity and enzyme deficiency disorders.
- Intranasally administered active enzyme reached all brain areas within 15Â min.
- Therapeutic bioavailability was doubled by pretreatment with MMP-9.
- Model for catalytic bioscavengers to detoxify CNS poisons and enzyme deficiencies.
BackgroundThe blood brain barrier (BBB) is critical for maintaining central nervous system (CNS) homeostasis by restricting entry of potentially toxic substances. However, the BBB is a major obstacle in the treatment of neurotoxicity and neurological disorders due to the restrictive nature of the barrier to many medications. Intranasal delivery of active enzymes to the brain has therapeutic potential for the treatment of numerous CNS enzyme deficiency disorders and CNS toxicity caused by chemical threat agents.New methodThe aim of this work is to provide a sensitive model system for analyzing the rapid delivery of active enzymes into various regions of the brain with therapeutic bioavailability.ResultsWe tested intranasal delivery of chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT), a relatively large (75Â kD) enzyme, in its active form into different regions of the brain. CAT was delivered intranasally to anaesthetized rats and enzyme activity was measured in different regions using a highly specific High Performance Thin Layer Chromatography (HP-TLC)-radiometry coupled assay. Active enzyme reached all examined areas of the brain within 15Â min (the earliest time point tested). In addition, the yield of enzyme activity in the brain was almost doubled in the brains of rats pre-treated with matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9).Comparison with existing method (s)Intranasal administration of active enzymes in conjunction with MMP-9 to the CNS is both rapid and effective.ConclusionThe present results suggest that intranasal enzyme therapy is a promising method for counteracting CNS chemical threat poisoning, as well as for treating CNS enzyme deficiency disorders.
228
Journal: Journal of Neuroscience Methods - Volume 259, 1 February 2016, Pages 129-134